Mi hija de 8 años es obesa, ¿pueden orientarme sobre su alimentación?
Pregunta: Mi hija de 8 años es obesa, ¿pueden darme alguna orientación respecto a su alimentación? Lucía (Rivas).
Respuesta: Tu hija de 8 años está en una etapa de la vida comprendida entre el periodo preescolar y la adolescencia, que se caracteriza por ser un periodo de crecimiento estable. Las necesidades energéticas son muy diferentes de unos a otros debido a la gran variabilidad en el grado de actividad física. Esta etapa se caracteriza por una consolidación de los hábitos alimentarios y por tanto es fundamental que el niño reciba una adecuada información nutricional tanto en el colegio como en la familia.
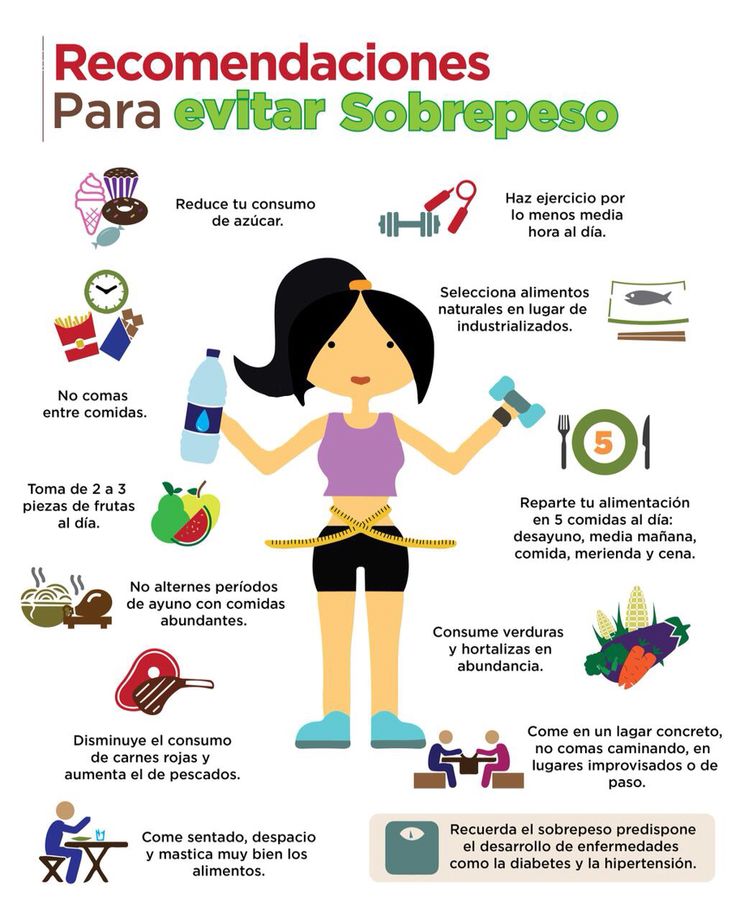
La niña debe realizar al menos 4 tomas: desayuno, comida, merienda y cena. En la siguiente tabla te indicamos las cantidades y la frecuencia con que debe consumir los distintos alimentos que tienen que formar parte de una dieta equilibrada. Tiene que tratar de suprimir el exceso de ingesta de: galletas, caramelos, chucherías, pastelitos, chicles, bollería industrial, hamburguesas, salchichas, embutidos, patatas chips. Sin olvidar la importancia del ejercicio físico a estas edades, a ser posible realizado al aire libre.
Tabla de frecuencia de consumo y cantidad de ración para niños de 7 a 12 años
|
ALIMENTOS |
FRECUENCIA |
|
|
VERDURAS Y HORTALIZAS |
2 raciones diarias |
150-200 g |
|
FRUTAS |
2 raciones diarias |
80-100 g |
|
CARNE |
3-4 raciones semanales |
80-100 g |
|
PESCADO |
3-4 raciones semanales |
120-150 g |
|
HUEVOS |
2-3 raciones semanales |
60-100 g |
|
LÁCTEOS |
2-3 raciones diarias |
150-200 g |
|
ARROZ, PASTAS.  .. .. |
3-4 raciones semanales |
50-80 g |
|
LEGUMBRES |
2-3 raciones semanales |
50-60 g |
|
PATATAS |
3-4 raciones semanales |
100-150 g |
|
PAN |
2-3 raciones semanales |
60-80 g |
|
ACEITE |
diariamente |
30-50 cc |
Tabla de equivalencias nutritivas de algunos alimentos
EN PROTEÍNAS:
100 g de carne equivalen aproximadamente a:
100 g de pescado = 2 huevos = 100 g de vísceras = 4 yogures
= 90 g de jamón cocido = 2 vasos grandes de leche
EN CALCIO:
1 vaso grande de leche equivale aproximadamente a:
2 yogures = 70 g de queso fresco tipo Burgos = 50 g de queso de bola
EN VITAMINA C:
1 naranja = 1 limón = 1 kiwi = 100 g de fresas = 250 g de tomate
CONTENIDOS DEL ARTÍCULO
Como padres, nos interesa que nuestros hijos e hijas crezcan fuertes y sanos. Y entre los 9 y 11 años, se da una etapa importante en su crecimiento, tanto social, como físico y emocional; muchos de los niños y niñas entran en la etapa de la pubertad, además inician su educación secundaria y adquieren mayor independencia de sus padres. En esta etapa de sus vidas una buena alimentación es esencial para su desarrollo. Por ello, es importante saber cuál es la dieta para niños de 9 a 11 años más adecuada. Cabe mencionar que las recomendaciones que brindaremos más adelante pueden variar dependiendo del estado nutricional del niño.
Y entre los 9 y 11 años, se da una etapa importante en su crecimiento, tanto social, como físico y emocional; muchos de los niños y niñas entran en la etapa de la pubertad, además inician su educación secundaria y adquieren mayor independencia de sus padres. En esta etapa de sus vidas una buena alimentación es esencial para su desarrollo. Por ello, es importante saber cuál es la dieta para niños de 9 a 11 años más adecuada. Cabe mencionar que las recomendaciones que brindaremos más adelante pueden variar dependiendo del estado nutricional del niño.
Los niños en este rango de edad requieren consumir en promedio 1750 calorías al día. Esta cantidad de calorías debe estar dividida a lo largo de cinco comidas: desayuno, media mañana, almuerzo, media tarde y cena.
Aunque muchos suelen decir que el desayuno es la comida más importante del día, este no es el que debe contener el mayor porcentaje de calorías. De hecho, las recomendaciones indican que solo debe representar aproximadamente el 20% de las calorías necesarias al día, mientras que el almuerzo, el 40%. La cena, por otro lado, también debe equivaler al 20% de las calorías necesarias para el niño, en el día. Finalmente, las meriendas entre comidas deben representar solo el 10% de las kilocalorías diarias. La cantidad de energía diaria se puede distribuir de otra manera adaptándose a cada niño.
De hecho, las recomendaciones indican que solo debe representar aproximadamente el 20% de las calorías necesarias al día, mientras que el almuerzo, el 40%. La cena, por otro lado, también debe equivaler al 20% de las calorías necesarias para el niño, en el día. Finalmente, las meriendas entre comidas deben representar solo el 10% de las kilocalorías diarias. La cantidad de energía diaria se puede distribuir de otra manera adaptándose a cada niño.
En la siguiente tabla podemos identificar, con mayor detalle la cantidad de calorías a las que equivale cada porcentaje:
Es importante que la dieta para niños de 9 a 11 años esté integrada por alimentos variados, como cereales, verduras, frutas, lácteos, carnes, azúcares y grasas. A continuación, compartiremos la cantidad de alimentos necesarios, según cada grupo.
Los lácteos son necesarios para el fortalecimiento de los huesos y el crecimiento, por ello es necesario consumir de 2 a 3 porciones de lácteos al día, por ejemplo, 1 tajada mediana de queso o 1 taza de leche evaporada preparada, o 1 vaso de yogurt.
La dieta de los niños debe estar conformada por 6 a 7 porciones de cereales al día en promedio, los cuales pueden ser:
Los niños deben consumir al menos dos porciones de verduras al día, de preferencia una en el almuerzo y otra en la cena.
La dieta para niños debe incluir 3 porciones de frutas al día, algunas opciones son:
Las carnes y los huevos son una de las principales fuentes de proteínas, por lo que se deben consumir dos porciones al día en promedio. Una porción equivaldría a 2 huevos, 4 cucharadas llenas de atún en conserva, ½ filete de carne de pescado o pollo, etc.
Aunque los azúcares tienen la función de brindar energía no hay que abusar de ellos. Lo ideal es que se consuman 2 o 3 porciones de azúcares como máximo al día, teniendo en cuenta que una porción equivale a 1 cucharadita de azúcar o de miel o a 2 cucharaditas de mermelada de fruta.
Las grasas cumplen diversas funciones importantes en nuestro organismo, por ejemplo: en la absorción de vitaminas liposolubles, no deberían superar las 3 porciones al día, entendiendo como una porción 2 cucharadas de aceite vegetal o una cucharada de mantequilla, para dar un ejemplo.
Si esta nota te pareció interesante, te invitamos a ver otros consejos de nutrición.
Fuente:
Compartir:
June 26, 2021
July 2, 2021
4 minutes
943
ProWellness
Contents
Disclaimer
Please note that all information posted on the site
Prowellness is provided for informational purposes only and is not a personal program, a direct recommendation for action, or medical advice. Do not use these materials for diagnosis, treatment, or any medical procedure. Consult your physician before using any technique or using any product. This site is not a specialized medical portal and does not replace the professional advice of a specialist. The Site Owner is not liable to any party who has suffered indirect or direct damage as a result of misuse of materials posted on this resource.
Do not use these materials for diagnosis, treatment, or any medical procedure. Consult your physician before using any technique or using any product. This site is not a specialized medical portal and does not replace the professional advice of a specialist. The Site Owner is not liable to any party who has suffered indirect or direct damage as a result of misuse of materials posted on this resource.
Products that cause drowsiness
Today, people devote a lot of time to diets and proper nutrition. It would seem that they know everything about the products. However, there are such everyday dishes from which a person can begin to fall asleep. What are these dishes?
Feeling sleepy after a meal is considered normal. It does not require a visit to a doctor and does not carry any cause for concern. There are several factors that contribute to this phenomenon. What are these factors?
What foods can make you feel sleepy and tired?
 Many people prefer to eat these foods for breakfast. Red meat is useful, able to saturate the body with iron. But most raw meat products are quite fatty. Proteins, along with fats, turn into heavy food, which is difficult for the body to break down and process. A lot of energy is spent on this, so a person feels tired and overwhelmed.
Many people prefer to eat these foods for breakfast. Red meat is useful, able to saturate the body with iron. But most raw meat products are quite fatty. Proteins, along with fats, turn into heavy food, which is difficult for the body to break down and process. A lot of energy is spent on this, so a person feels tired and overwhelmed.  If it is important to focus on serious work, meetings, or preparing reports, snacking on prunes should be avoided.
If it is important to focus on serious work, meetings, or preparing reports, snacking on prunes should be avoided.
Thus, the feeling of drowsiness that occurs after eating, medically explainable, is most often not a dangerous condition. There are foods that can increase fatigue and the desire to take a nap, so on busy workdays, you should refuse them.
Disclaimer
Please note that all information posted on the site
Prowellness is provided for informational purposes only and is not a personal program, a direct recommendation for action, or medical advice. Do not use these materials for diagnosis, treatment, or any medical procedure. Consult your physician before using any technique or using any product. This site is not a specialized medical portal and does not replace the professional advice of a specialist. The Site Owner is not liable to any party who has suffered indirect or direct damage as a result of misuse of materials posted on this resource.
Do not use these materials for diagnosis, treatment, or any medical procedure. Consult your physician before using any technique or using any product. This site is not a specialized medical portal and does not replace the professional advice of a specialist. The Site Owner is not liable to any party who has suffered indirect or direct damage as a result of misuse of materials posted on this resource.
Expert: Marina Rozova, a specialist in the selection of dietary supplements, maintains an Instagram blog “About vitamins”, where she tells in simple terms how to maintain your resource, immunity and beauty from the inside with the help of dietary supplements and healthy lifestyle
Rate the article
(2 votes, average 5 )
Share this article
Parents of small children are particularly afraid of intestinal infections. After all, it is important for a mother that her baby is full and healthy. And the presence of an intestinal infection in the body does not even allow to feed the child properly. Any meal is accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, and in severe forms of the disease, children cannot eat at all.
And the presence of an intestinal infection in the body does not even allow to feed the child properly. Any meal is accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, and in severe forms of the disease, children cannot eat at all.
Experienced grandmothers advise to keep the child on dry rations (ie, to eat crackers, dryers, biscuit cookies), others offer to treat immediately with herbal decoctions. Feeding children with an intestinal infection is a very important and delicate issue, so you should know not only how and what to feed a child, but also other important principles, for example, combating dehydration, drinking regimen, and so on. You can read about all this in the materials of this article.
What is an intestinal infection
Intestinal infections rank second among childhood diseases and are more common in young children (under 3 years of age). In the morning, the child was healthy and cheerful, as after a couple of hours the baby abruptly begins to vomit, the stool is upset and the temperature rises. All these symptoms indicate the presence of an intestinal infection in the body.
All these symptoms indicate the presence of an intestinal infection in the body.
Intestinal infection can be either viral or bacterial. From the names themselves it becomes clear what the difference between their pathogens is. In childhood, it is the rotovirus causative agent of intestinal infection that is more common.
As a type of intestinal infection, one can name:
At the first signs of an intestinal infection in a child, parents should not despair and become depressed. Doctors say that in 90% of cases, medical care is not needed and parents can cope with the disease on their own at home, you just need to follow the rules that will prevent dehydration.
But, in the remaining 10%, the situation is more complicated and at home you can only aggravate the situation. This requires urgent medical intervention and qualified assistance. It is worth remembering that in acute forms of intestinal infection, rapid dehydration of the body occurs and if slowed down with treatment, it can be fatal.
An ambulance must be called if:
How can you get an intestinal infection?
The very moment of infection with an intestinal infection occurs when a bacterium or virus enters the body, namely, it settles in the gastrointestinal tract.
There are several ways to become infected with an intestinal infection:

Treatment of intestinal infection
In the treatment of acute intestinal infection, special attention is paid to replenishing fluid in the body, as well as the use of a number of antibiotics. There is an opinion that antibiotics should be used in moderate and severe forms of the disease. Indeed, against the background of inhibition of the viability of microbes, antibiotics weaken the body’s immunity, which leads to the development of dysbacteriosis, and hence the removal of all useful substances.
Prescribe antibiotics strictly after passing a series of tests, identifying the causes of the disease and monitoring by medical personnel.
Indications for prescribing therapeutic nutrition
One of the important factors in the treatment of children who have had an intestinal infection is proper nutrition or diet therapy. With improper nutrition, prolonged diarrhea, a sharp weight loss and lactose intolerance (milk is not absorbed by the body) can be seen.
With improper nutrition, prolonged diarrhea, a sharp weight loss and lactose intolerance (milk is not absorbed by the body) can be seen.
The main function of diet therapy is the ability to adjust the diet, nutrition of the child and make timely adjustments based on the form of the disease, the state of the body and the rate of recovery. Scientists have proven that even in severe forms of the disease, the gastrointestinal tract retains the function of eating and absorbing nutrients, but if food does not enter the child’s body for a long time (water-tea diets), then the body loses its recovery function, which and leads to dramatic weight loss.
Principles of nutrition in intestinal infections
The main principle of the modern approach to the nutrition of children who have had acute intestinal infections is the rejection of water-tea diets and the correct selection of products that contributed to an increase in the level of body resistance.
The type of food, the amount of servings and the amount of food consumed per day will be determined by a number of factors:
There are several principles that should be applied to all forms of the disease. There must be a break at night, there should not be overfeeding and force-feeding. We should not forget that in feeding you must always adhere to the regimen. In older children, the urge to vomit is associated with overeating. It is necessary to adhere to the generally accepted principle: it is better to eat more often, but in smaller portions.
If the child has a mild form of intestinal infection, without severe intoxication of the body, doctors advise to reduce the amount of food consumed in the first days, the lack of food can be filled with liquid. It can be unsweetened teas, compotes, decoctions of chamomile, purified non-carbonated water. P
P
I’m looking for a better use in pureed form (soup-puree, porridge and scrambled eggs), so it will be easier for the body to perceive it. All cooked food should be boiled or steamed. And already for 5-6 days it will be possible to return to normal life. In mild forms of diarrhea, it is recommended to reduce the volume of food by 15-20% and increase the number of meals by 1-2. By the fourth day after the onset of the disease state, the volume of food becomes the same and the diet is restored. With medium forms, it is necessary to divide meals into 5-6 approaches, the amount of food received per day is reduced by 30%. On the 6-7th day, there is a complete restoration of the volume of portions, and the number of meals.
In severe forms of intestinal infections, the patient is transferred to fractional food intake, and the daily volume is reduced by half – 45-50%. On the fourth day, the volume is gradually increased and only on the 8th day the diet is resumed.
Drinking regimen
First of all, in case of an intestinal infection, doctors try to restore the body’s water balance. The patient is recommended to drink 1 teaspoon of pure water every 5 minutes. Water allows you to remove all toxins from the body. You can also drink decoctions of chamomile, compotes, teas. It is important to take liquid in small portions. Too much fluid taken at one time can cause repeated vomiting and severe dehydration. Instead of water, it is mono to give the child a solution of rehydron, a slightly sweet compote of dried fruits, non-carbonated mineral water.
The patient is recommended to drink 1 teaspoon of pure water every 5 minutes. Water allows you to remove all toxins from the body. You can also drink decoctions of chamomile, compotes, teas. It is important to take liquid in small portions. Too much fluid taken at one time can cause repeated vomiting and severe dehydration. Instead of water, it is mono to give the child a solution of rehydron, a slightly sweet compote of dried fruits, non-carbonated mineral water.
With diarrhea and vomiting, the water-salt balance of the body is disturbed. To restore it, it is recommended to drink Regidron. This drug can be purchased at a pharmacy or prepared at home. For a liter of water, you need to take 2 tbsp. spoons of sugar, 1 tbsp. a spoonful of coarse salt (fine you need to take 0.5 tablespoons) and 0.5 teaspoons of soda. It is not worth drinking such a drink in large doses, it is necessary to alternate. A teenager will need 50 ml 1 time in 1.5-2 hours, a child no more than 1 spoon at the same intervals. If there is a shortage of food, it must be supplemented with liquid.
If there is a shortage of food, it must be supplemented with liquid.
Do’s and don’ts for children with intestinal infection
In case of intestinal infection, remember that all food should be steamed or boiled, in the form of puree, rarely soup, soufflé or scrambled eggs. The less often and lighter the food used, the faster it is absorbed by the body. If, after eating one portion, the patient did not eat and wants more, this is a sure sign that he is on the mend. But do not rush, but rather take care of the body. In this case, try to maintain an interval of at least 30 minutes and then offer the child another meal.
If an intestinal infection is transferred to the diet, you can use:
Do not eat if you have an intestinal infection:
The first few days the child’s diet will be as scarce as possible, but already on the 4th day you can gradually introduce meatballs, steam cutlets, soups with low-fat broth, boiled or steamed fish, eggs, bananas and peeled apples. On the recommendation of a doctor, you can enter milk porridge in a ratio of 1: 1.
Later you can add bakery products: dry biscuits, biscuits, rusks from dark bread varieties, prepared by yourself. By the end of the third week, you can gradually drive rich pastries.
Peculiarities of breastfeeding in case of intestinal infection
If the child is infancy, then you should not refuse breastfeeding, but you can increase the number of feedings, if the baby needs it, switch to feeding on demand.
The only food at this age is mother’s milk. After all, it is believed that children with severe diarrhea tolerate lactose in human milk more easily, so there is no need to refuse it at all. In addition, lactose retains a large amount of useful substances and those that promote growth. All of them affect the speedy recovery of the intestine.
But it should be remembered that for children who are bottle-fed, on the contrary, doctors recommend reducing the dose of the resulting mixture and increasing the number of meals (more often, but in smaller portions). But more detailed recommendations on nutrition can only be obtained from the attending pediatrician. Pediatricians recommend replacing milk porridges with water porridges for children who have already been introduced to complementary foods.