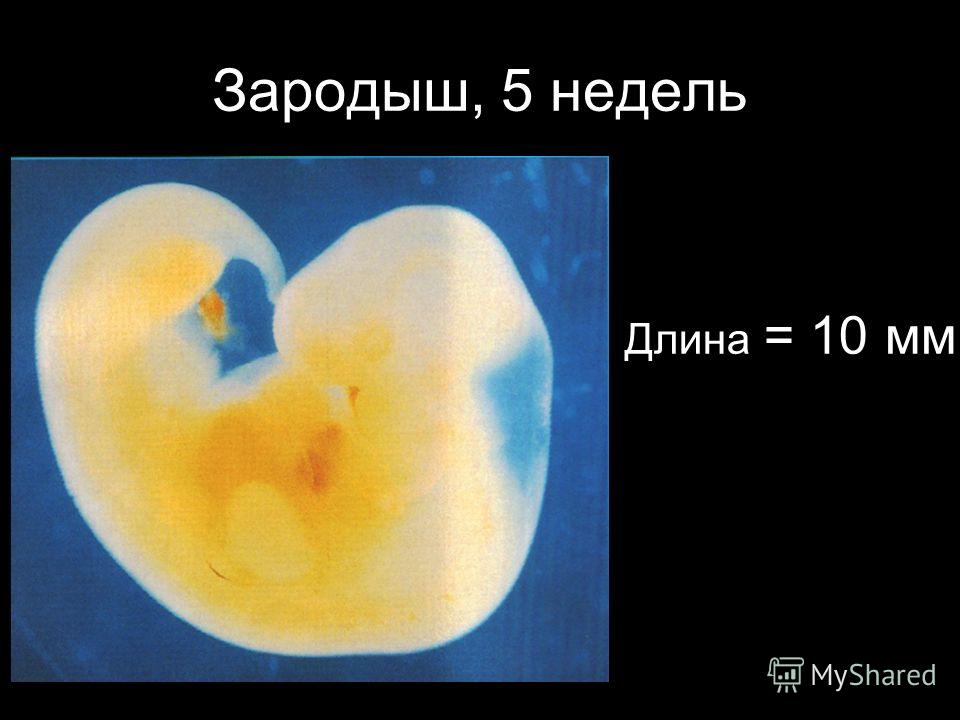
El inicio del primer trimestre del embarazo se produce dos semanas después de la última menstruación que es donde se produce la concepción. El primer trimestre se puede dividir en cuatro etapas: ovulación, concepción, embrionaria y fetal.
La ovulación ocurre dentro de las primeras dos semanas posteriores a la última menstruación, la embrionaria ocurre entre las terceras y quinta semana y es donde ocurre la implantación del blastocisto en el endometrio. Al final de la quinta semana se ha formado el saco gestacional y normalmente mide 5mm de diámetro. En la sexta semana el embrión se hace visible ecográficamente, comienza la organogénesis y la actividad cardiaca al final de la décima semana se termina el periodo embrionario y las próximas dos semanas se llama periodo fetal donde se presenta un continuo crecimiento y desarrollo.
La ecografía transvaginal ayuda a una mejor visualización y se realiza con un transductor de 3 a 7 MHz o más. Durante el estudio también se debe realizar una visualización del útero y sus anexos. Buscar la presencia del saco gestacional y del saco vitelino, proporcionar la edad gestacional midiendo la longitud el embrión si esta no se puede realizar entonces se tomara el diámetro del saco. Se debe reportar la presencia o ausencia de la actividad cardiaca, si hay gestación múltiple se deben observar los amnios y el corión.
Hallazgos normales ecográficos en el primer trimestre.
El primer hallazgo que indica un embarazo es la presencia del saco gestacional el cual se observa como un anillo ecogénico un saco que mide de 2 a 3mm corresponde a una edad gestacional de 4 semanas y 5mm a 5 semanas.
El doble saco decidual es útil para confirma un embarazo intrauterino, el saco vitelino es una estructura anecoica con un reborde ecogénico y es la primera estructura que confirma la presencia de un verdadero saco gestacional presenta un diámetro de 5-6mm a la décima semana y posteriormente disminuye gradualmente.
El embrión es visible entre la quinta y sexta semana con una medición de 5-12mm. La actividad cardiaca es detectada cuando embrión tiene una longitud de 1.6mm se detecta un diámetro de 13-18mm que corresponde a 6-6.5 semanas. La frecuencia cardiaca fetal es de 100-115 latidos por minuto entre las 6ª y 9ª semana, para la 8ª semana aumenta entre 144-159 latidos por minuto.
En el ultrasonido se pueden observar imágenes anormales como útero vacío debido a algún aborto, un endometrio desidual o un embarazo ectópico. Un saco intrauterino vacío se observa cuando el embarazo es muy reciente, en un embarazo anormal o en un pseudosaco gestacional por un embarazo ectópico.
Hay algunas imágenes que son sugestivas de la perdida del embarazo como: sangre intrauterina, un rango cardiaco bajo de 100 latidos por minuto en la sexta semana es indicador de la posible perdida del embarazo, un saco gestacional pequeño, un saco vitelino o amnióticos anormales, factores maternos si hay alguno presente son factores de mal pronóstico para el embarazo.
En un embarazo gemelar el ultrasonido es útil para observar cuantos sacos amnióticos y coriónicos existen.
Conclusión
Es de suma importancia el adecuado empleo del ultrasonido para el adecuado diagnóstico de un adecuado embarazo y también para poder detectar cualquier tipo de anormalidad que se presente y que aun no este presentando síntomas en la paciente para poder ser tratada a tiempo y poder evitar complicaciones durante el primer trimestre. Y esta claro que es el estudio más completo para poder saber la edad gestacional con las adecuadas mediciones del saco gestacional, vitelino, la longitud embrionaria y frecuencia cardiaca.
Inscripciones para curso
Inscripciones para Diplomado
diplomadomedico.com
El programa fue diseñado para llevar de la mano al participante y ofrecerle herramientas que le permitan hacer una evaluación radiológica atinada, lo cual lo llevará a un diagnóstico que por ende arrojará el tratamiento idóneo.
El énfasis se ha dado en la metodología diagnóstica, que es por inducción, así como el manejo del paciente, para crear una conciencia responsable y humana entre los que se dedican o quieren iniciarse en la práctica de la ultrasonografía.
Dado a que existe una aplastante demanda de estudios de ultrasonido ante el insuficiente número de médicos radiólogos certificados, además de que el servicio de rayos x en México ha sufrido de ineficiencia en la aplicación del estudio y elaboración diagnóstica de la patología, la labor de este curso es formar de manera profesional a los médicos para que cubran y aminore en gran medida este problema que habita en el sector de salud.
Payment methods:
You can pay via:
You are here
Embrion 30 mm ZS
Price:
1,94
EUR
za
pcs
Shipping time:
3 dni
product not available in this number of pieces
available amount:
See reviews (0)
The price is for 1 item and does not include shipping costs.
Keep products and packaging out of the reach of children, in a clean and dry place, protect from high temperature.
Use only for fishing purposes.
The product is not suitable for consumption.
Add your opinion
Add review, thus also you will receive reliable information about the product
Opinions added ( 0 )
Enter your e-mail address, if you want to receive the latest information about promotions.
This website uses cookies. By using the website, you consent to their use in accordance with the current browser settings. For more information on the purpose of using cookies and the possibility of changing cookie settings, click here: more
Oprogramowanie sklepu internetowego Sellingo.pl
Photo ultrasound of the fetus during pregnancy 4-5 weeks
The earliest period at which a fetal egg in the uterine cavity can be seen using transvaginal ultrasound is the 30th day of gestation, or 4-5 obstetric weeks of pregnancy. The level of hCG blood in this case should be at least 1000 mU / ml. At this time, neither the embryo nor the yolk sac is visible. When visualizing two fetal eggs, it can be argued that this is a dichorionic multiple pregnancy. When visualizing one fetal egg, it can be argued that this is a monochorionic pregnancy. But at this time, we still cannot say how many embryos are in each fetal egg. In addition, during a single ultrasound, we still cannot tell if this pregnancy is progressing, since the embryo does not yet have a heartbeat. The average inner diameter (SID) of the fetal egg at this time is 2-10 mm. nine0005
The level of hCG blood in this case should be at least 1000 mU / ml. At this time, neither the embryo nor the yolk sac is visible. When visualizing two fetal eggs, it can be argued that this is a dichorionic multiple pregnancy. When visualizing one fetal egg, it can be argued that this is a monochorionic pregnancy. But at this time, we still cannot say how many embryos are in each fetal egg. In addition, during a single ultrasound, we still cannot tell if this pregnancy is progressing, since the embryo does not yet have a heartbeat. The average inner diameter (SID) of the fetal egg at this time is 2-10 mm. nine0005
The conclusion will indicate: Uterine pregnancy of a short term.
Learn more about ultrasound in early pregnancy
Photo ultrasound of the fetus during pregnancy 5-6 weeks
At this time, a white ring appears inside the fetal egg – this is the yolk sac.
Foci of erythropoiesis form in the wall of the yolk sac, which form a capillary network, supplying erythroblasts (nuclear erythrocytes) to the primary circulatory system of the fetus.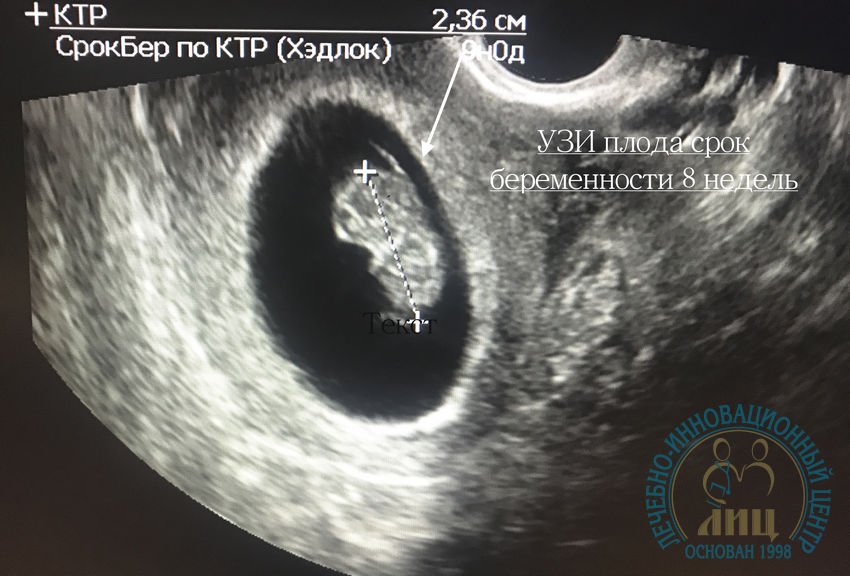 The yolk sac is a source of primary germ cells that migrate from its wall to the anlage of the gonads of the embryo. Until the 6th week after fertilization, the yolk sac, playing the role of the “primary liver”, produces many important proteins for the embryo – alpha-fetoprotein, transferrins, alpha2-microglobulin. By the end of the first trimester of pregnancy, this provisional organ ceases to function and is reduced. nine0005
The yolk sac is a source of primary germ cells that migrate from its wall to the anlage of the gonads of the embryo. Until the 6th week after fertilization, the yolk sac, playing the role of the “primary liver”, produces many important proteins for the embryo – alpha-fetoprotein, transferrins, alpha2-microglobulin. By the end of the first trimester of pregnancy, this provisional organ ceases to function and is reduced. nine0005
The normal size of the yolk sac is 2-6 mm. If two yolk sacs are visualized in the fetal egg, then this is a monochorionic multiple pregnancy. But if one yolk sac is visible inside the fetal egg, and the embryo is not yet clearly visualized, then this may still be monochorionic monoamniotic twins.
At the beginning of the 5th week, the embryo is practically indistinguishable on the wall of the yolk sac, but by the end of the week, the coccyx-parietal size (CTE) of the embryo reaches 3 mm. nine0005
SVD of the ovum 11-16 mm.
Read also: Is ultrasound harmful during pregnancy? Is ultrasound dangerous? How often can an ultrasound be done?
Photo ultrasound of the fetus during pregnancy 6-7 weeks
Inside the fetal egg, we see a “ring with a precious stone” 🙂 – this is the yolk sac and already a well-defined embryo, located nearby. The heart of the embryo begins to beat at the beginning of the 6th obstetric week of pregnancy. It is the presence of a heart pulsation that is a reliable ultrasound sign of a progressing pregnancy. With CTE ≥6 mm and the absence of heart pulsation, a conclusion is made about stopping the development of this embryo. Normal heart rate (HR) of the embryo at the very beginning of the 6th week 70-90 beats per minute, but by the end of the week it becomes more than 100 beats. in min. In the early stages of pregnancy, it is not the heart rate that matters, but the presence or absence of heart contractions as such. Sometimes, with a non-developing pregnancy, you can see the reflection of the pulsation of the mother’s vessels inside the embryo and take them for the baby’s heartbeat. But in this case, the pulsation frequency will be identical to the mother’s heart rate.
The heart of the embryo begins to beat at the beginning of the 6th obstetric week of pregnancy. It is the presence of a heart pulsation that is a reliable ultrasound sign of a progressing pregnancy. With CTE ≥6 mm and the absence of heart pulsation, a conclusion is made about stopping the development of this embryo. Normal heart rate (HR) of the embryo at the very beginning of the 6th week 70-90 beats per minute, but by the end of the week it becomes more than 100 beats. in min. In the early stages of pregnancy, it is not the heart rate that matters, but the presence or absence of heart contractions as such. Sometimes, with a non-developing pregnancy, you can see the reflection of the pulsation of the mother’s vessels inside the embryo and take them for the baby’s heartbeat. But in this case, the pulsation frequency will be identical to the mother’s heart rate.
The presence of one yolk sac, one embryo and one pulsating heart in most cases indicates a singleton pregnancy. But in very rare cases, it may later turn out to be unseparated twins. nine0005
nine0005
SVD of the ovum 13-23 mm. Embryo KTR 4-9 mm.
Read also: “I don’t want an ultrasound, I want a baby!”. Why is ultrasound during pregnancy necessary?
Photo ultrasound of the fetus during pregnancy 7-8 weeks
The distance between the embryo and the yolk sac gradually increases and the yolk duct (ductus vitellinus), which connects the yolk sac and the intestines of the embryo, becomes clearly visible. Just like the yolk sac, the duct becomes empty and resolves at a later date, but if this does not happen for some reason, then a blind protrusion of the ileum wall is formed in a person – Meckel’s diverticulum. nine0005
Until this time, the chorion has an annular shape, surrounds the fetal egg from all sides, and it is still impossible to say which wall of the uterus the embryo has attached to.
In the case of monochorionic twins, the amniotic membranes are not yet visible and in the presence of two yolk sacs it is still impossible to tell whether the pregnancy is mono or diamniotic. If the gestational sac contains two yolk sacs and two fetuses with cardiac activity, the subsequent number of amniotic cavities may be greater than the number of placentas (monochorial diamniotic) or the same (monochorial monoamniotic). In this case, it is possible to accurately determine amnionality after 8 weeks, when the amniotic membranes begin to be clearly visualized. nine0005
If the gestational sac contains two yolk sacs and two fetuses with cardiac activity, the subsequent number of amniotic cavities may be greater than the number of placentas (monochorial diamniotic) or the same (monochorial monoamniotic). In this case, it is possible to accurately determine amnionality after 8 weeks, when the amniotic membranes begin to be clearly visualized. nine0005
Embryo heart rate 130-160 beats per minute.
SVD of the ovum 24-30 mm, CTE of the embryo 9-15 mm.
Photo ultrasound of the fetus during pregnancy 8-9 weeks
During the ultrasound of the embryo, it is already possible to clearly distinguish individual segments – the head, trunk, limbs. The first movement appears. The amniotic membranes become clearly visible and we can already talk about the number of amniotic sacs in multiple pregnancies. The chorion is differentiated into a smooth one, facing the uterine cavity, and a branched one, from which the placenta will subsequently form, so that we can already talk about the predominant location of the chorion along the anterior or posterior wall of the uterus.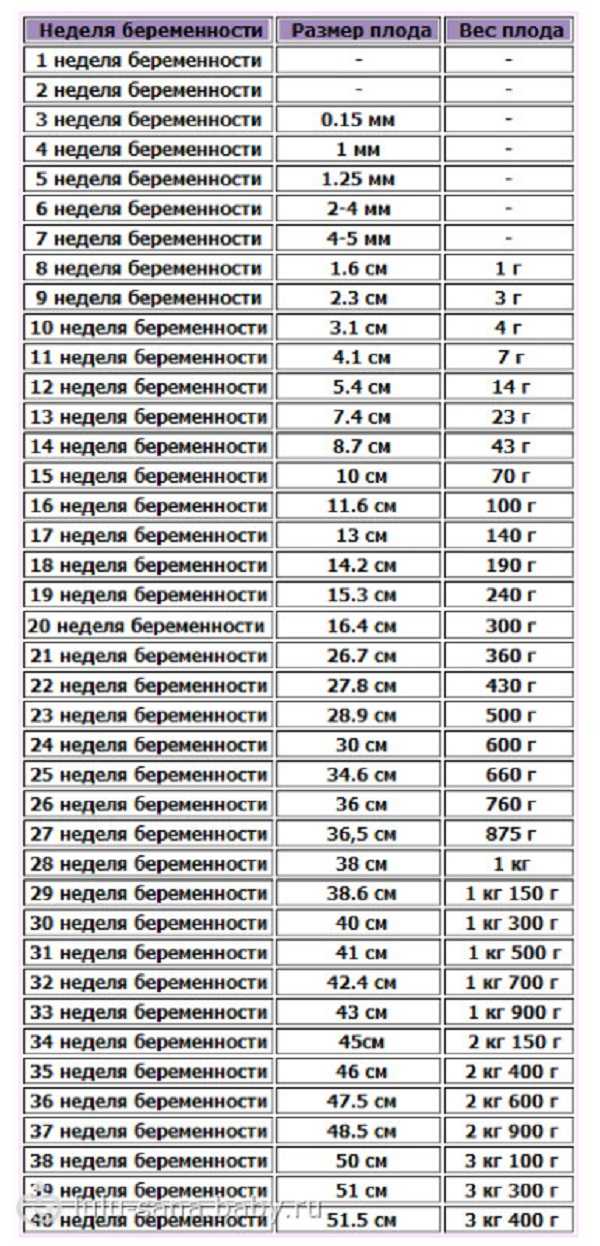 nine0005
nine0005
The heart rate of the embryo increases to 160-180 beats per minute.
SVD of the ovum 31-37 mm. Embryo KTR 16-22 mm.
Photo ultrasound of the fetus during pregnancy 9-10 weeks
The development of the embryo continues. The handles of the legs are already clearly visible, and on a good device, sometimes you can even see the fingers and toes. The heart rate at this time reaches 170-190 beats per minute. The movements of the embryo become active, and there are studies showing that the more active the child, the longer the umbilical cord will be (although there may be an inverse relationship). nine0005
SVD of the ovum 38-44 mm. Embryo KTR 23-30 mm.
In early pregnancy, ultrasonography is performed to identify a viable fetus in the uterine cavity, confirm the gestational age, rule out abnormalities of the fetus, or identify normal variants, such as multiple pregnancy.
The initial sign of pregnancy is thickening of the endometrium, but ultrasound does not allow us to say what specifically caused this thickening. nine0005
nine0005
Using a high-resolution transvaginal transducer, a 1 mm gestational sac is visualized in the uterine cavity 4 weeks and 2 days after the last menstrual period with a regular menstrual cycle.
If menstruation is delayed by 5-7 days or more (gestation period is 5 weeks), a fetal egg with a diameter of 6 mm should be clearly defined in the uterine cavity. It has a clear rounded shape with an indistinct light corolla along the periphery (hyperechoic rim – chorion). At the same time, the level of beta-hCG in the blood is 1000-1500 IU / l (see What is hCG?). At an hCG level of more than 1500 IU / l, the fetal egg in the uterine cavity should be clearly visualized. nine0005
With a lower level of hCG, the fetal egg in the uterine cavity may not be detected by transvaginal echography. In a transabdominal study, the determination of a fetal egg in the uterine cavity is possible at a beta-hCG level of 3000-5000 IU / l.
Fig.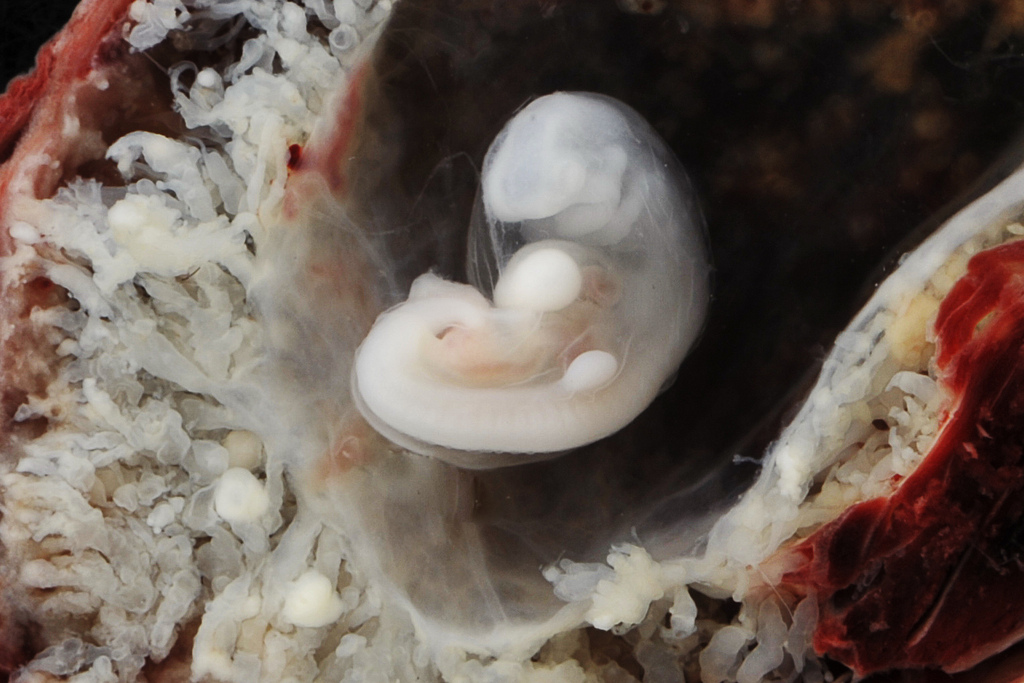 Uterine pregnancy 4-5 weeks. Transabdominal scan. nine0104
Uterine pregnancy 4-5 weeks. Transabdominal scan. nine0104
IMPORTANT: The gestational age cannot be accurately determined by the size of the gestational sac. Many tables on the Internet with the size of the fetal egg – determine the period very approximately (see table below).
From about 5.5 weeks on transvaginal ultrasound, an extraembryonic structure in the fetal egg begins to be visualized – the yolk sac (eng. yolk sac). At the same time, the level of beta-hCG is approximately 7200 IU / l on average (see hCG norms during pregnancy). nine0005
Since the yolk sac is part of the embryonic structures, its detection makes it possible to distinguish a gestational sac from a simple accumulation of fluid in the uterine cavity between the layers of the endometrium, and in most cases, makes it possible to exclude an ectopic pregnancy. The frequency of ectopic pregnancy is 1-2 per 2000-3000 pregnancies. Its risk increases with the use of assisted reproductive technologies (ART). It is necessary to suspect an ectopic pregnancy when the hCG level is more than 1500 IU / L, and the fetal egg in the uterine cavity is not detected. nine0005
It is necessary to suspect an ectopic pregnancy when the hCG level is more than 1500 IU / L, and the fetal egg in the uterine cavity is not detected. nine0005
Fig. 2 Pregnancy 5.5 weeks. The yolk sac is determined. transvaginal scan.
From 6 weeks of gestation (sometimes a little earlier), an embryo, about 3 mm long, can be detected in the fetal egg. From the same period, most ultrasound devices allow you to determine the heartbeat of the embryo. If the heartbeat is not detected or indistinct when the length of the embryo (KTR) is 5 mm, a second ultrasound is indicated after a week. The absence of cardiac activity in this period is not necessarily a sign of fetal suffering or an undeveloped pregnancy. nine0005
Numerical values of heart rate in an embryo during uncomplicated pregnancy gradually increase from 110-130 beats/min at 6-8 weeks of pregnancy to 180 beats/min at 9-10 weeks.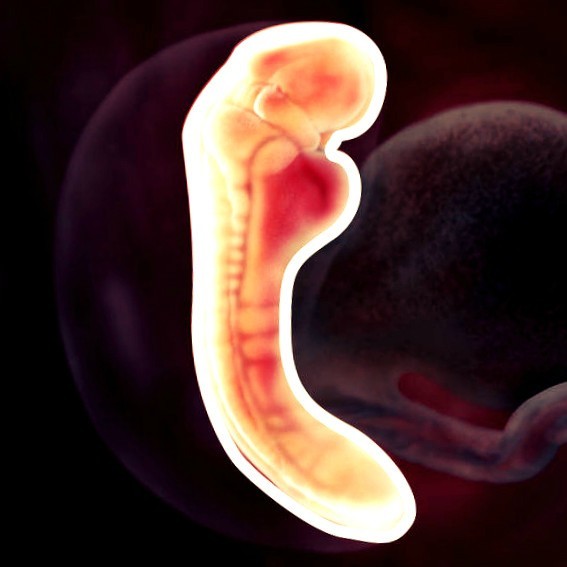
The length of the embryo is measured from the head to the caudal end, and is designated under the term KTP (coccygeal-parietal size), in Eng. literature – CRL (Crown-Rump Length). It should be noted that the coccygeal-parietal size of the embryo is less subject to individual fluctuations than the average internal diameter of the fetal egg, and therefore, its use for determining the gestational age gives better results. The error in this case usually does not exceed ±3 days. With a clear visualization of the embryo, the gestational age is set depending on its length, and not on the size of the average internal diameter of the fetal egg (MID). nine0005
Accurate visualization of the embryo is essential for correct measurement of the coccyx-parietal size of the embryo. In this case, one should strive to measure the maximum length of the embryo from its head end to the coccyx.
In the normal course of pregnancy, the diameter of the fetal egg increases by 1 mm per day.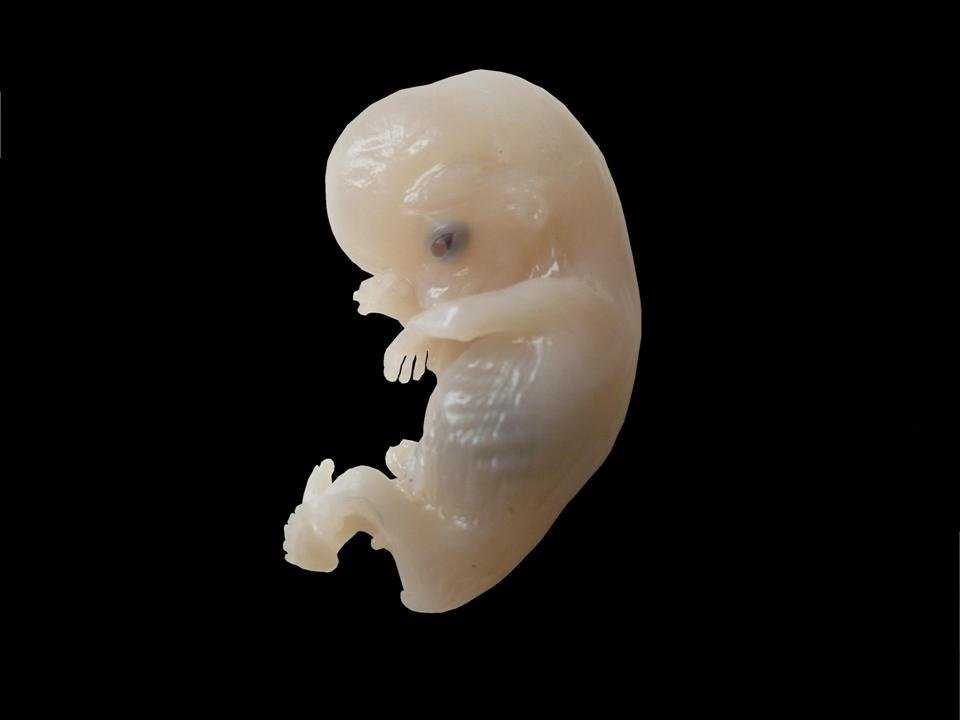 Lower growth rates are a poor prognostic sign. With a gestational age of 6-7 weeks, the diameter of the fetal egg should be about 30 mm. nine0005
Lower growth rates are a poor prognostic sign. With a gestational age of 6-7 weeks, the diameter of the fetal egg should be about 30 mm. nine0005
Medvedev.
th percentile.
It should be emphasized that it is better to determine the gestational age by the length of the CTE before 12 weeks of pregnancy. At a later date, measurement of the biparietal diameter, head and abdomen circumference should be used.
Fig.3 Pregnancy 12 weeks 3 days.
The motor activity of the embryo is determined after 7 weeks of pregnancy. At first, these movements are very weak and isolated, hardly distinguishable during the study. Then, when differentiation into the head and pelvic ends of the embryo becomes possible, the movements resemble flexion and extension of the torso, then separate movements of the limbs appear.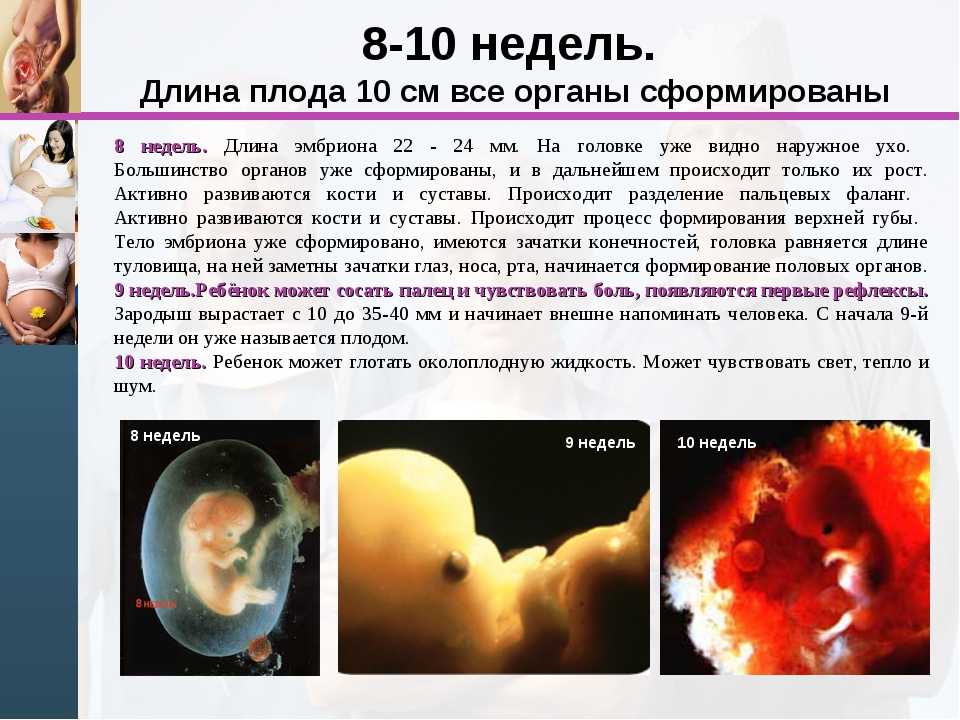 Since the episodes of the motor activity of the embryo are very short and are counted in seconds, and the periods of motor rest can be significant in time, the registration of the cardiac activity of the embryo is undoubtedly a more important criterion for assessing its vital activity. nine0005
Since the episodes of the motor activity of the embryo are very short and are counted in seconds, and the periods of motor rest can be significant in time, the registration of the cardiac activity of the embryo is undoubtedly a more important criterion for assessing its vital activity. nine0005
The diagnosis of anembryony (empty gestational sac) is suspected if no yolk sac is detected in a 20 mm gestational sac. Or if a fetal egg with a diameter of more than 25 mm with a yolk sac does not contain an embryo. And also with a yolk sac size of 10 mm or more. In any case, if anembryony is suspected, all data obtained should be interpreted in favor of pregnancy, and the study should be repeated after 7 days.
A missed pregnancy should not be diagnosed if the gestational sac is less than 20 mm on ultrasound. With an embryo length of 5 mm or more, in most cases, the heartbeat should be clearly defined. If the embryo is less than 5 mm, the ultrasound should be repeated in a week. If, upon re-examination a week later, with KTP = 5-6 mm, cardiac activity is not determined, the pregnancy is not viable.