La implantación es un proceso que ocurre después de que el óvulo fecundado desciende a lo largo de la trompa de Falopio y, finalmente, se hunde profundamente en el revestimiento del útero, donde permanecerá evolucionando y desarrollándose hasta el momento del parto.
Una vez que se produce la implantación del embrión, el cuerpo de la futura mamá comienza a liberar una serie hormonas que se encargan de preparar al organismo para el bebé, deteniendo el período menstrual, generando la placenta y todos los productos necesarios para el buen desarrollo de la gestación.
Además, estas hormonas son las principales “culpables” de muchos de los síntomas molestos relacionados con el embarazo, como podría ser el caso del cansancio, las náuseas o los calambres.
Tal y como ha podido demostrar algún que otro estudio científico, en los últimos años se está poniendo el foco en el momento de la implantación como causa de aborto espontáneo.
Y es que una implantación tardía o muy temprana podría ocasionar que tanto el revestimiento del útero como los niveles hormonales no brinden un soporte óptimo para el buen desarrollo del embrión.
Eso sí, aunque en los últimos años la implantación tardía puede llegar a convertirse en un factor más de aborto espontáneo, no se trata de algo que pueda controlarse o prevenirse. Te explicamos por qué.
Cuando la mujer ovula, algo que ocurre a mitad del ciclo menstrual, del ovario se libera un óvulo. Generalmente, este huevo tiene 24 horas para poder ser fecundado por un espermatozoide antes de que deje de ser viable.
Cuando se produce la concepción, el óvulo es fecundado en la trompa de Falopio. Luego, viaje a lo largo de la trompa de Falopio, hasta llegar al útero. Una vez llega al útero, el óvulo se implanta en el endometrio, que consiste en el revestimiento del útero.
El lugar donde el embrión finalmente se adhiere en el interior del endometrio puede acabar rompiendo algunos vasos sanguíneos, que es lo que genera la aparición de un ligero sangrado entre 5 a 10 días después de la concepción. No obstante, esto no ocurre siempre.
No obstante, esto no ocurre siempre.
Implantación tardíaFoto: Istock
El período que comprende desde la concepción hasta la implantación, habitualmente, tiende a durar entre 6 a 10-12 días. De esta manera, lo más común es que la implantación se produzca durante ese período. Sin embargo, si ocurre después de los 10-12 días, se considera implantación tardía.
No produce ningún síntoma, a menos que se produzca el sangrado ligero que en ocasiones puede ocurrir como consecuencia de la implantación.
En este caso, el sangrado es similar al sangrado que ocurre cuando la implantación sí se ha producido durante el período de tiempo normal, por lo que no es posible saber si la implantación se produjo a tiempo, o si se retrasó.
Distintos estudios han encontrado que existiría un riesgo mayor de aborto espontáneo en aquellos embarazos donde la implantación ocurrió más de 8 a 10 días después de la ovulación.
Por ejemplo, un estudio publicado en el año 1999 encontró que la probabilidad de aborto espontáneo aumentaba de manera significativa con cada día de implantación tardía, después, eso sí, del noveno día.
De acuerdo a los estudiosos, la probabilidad de aborto espontáneo al noveno día fue del 13 por ciento, el día 10 fue del 26 por ciento y el día 11 la tasa alcanzó el 52 por ciento. Después de este día, la probabilidad aumentaba hasta el 82 por ciento.
No obstante, como manifiestan muchos especialistas, en realidad es poco probable que, por sí sola, la implantación tardía deba ser entendida como una causa directa de aborto espontáneo. Por ejemplo, cuando un embrión presenta anomalías cromosómicas el riesgo de aborto espontáneo es muchísimo mayor, al igual que podría hacer que el embrión se implante más tarde de lo común.
También existe otra teoría que señala la posible existencia de algún factor, presente en el revestimiento uterino, que podría acabar originando problemas durante la implantación, y con ello, un riesgo mayor de aborto espontáneo en los días o semanas siguientes.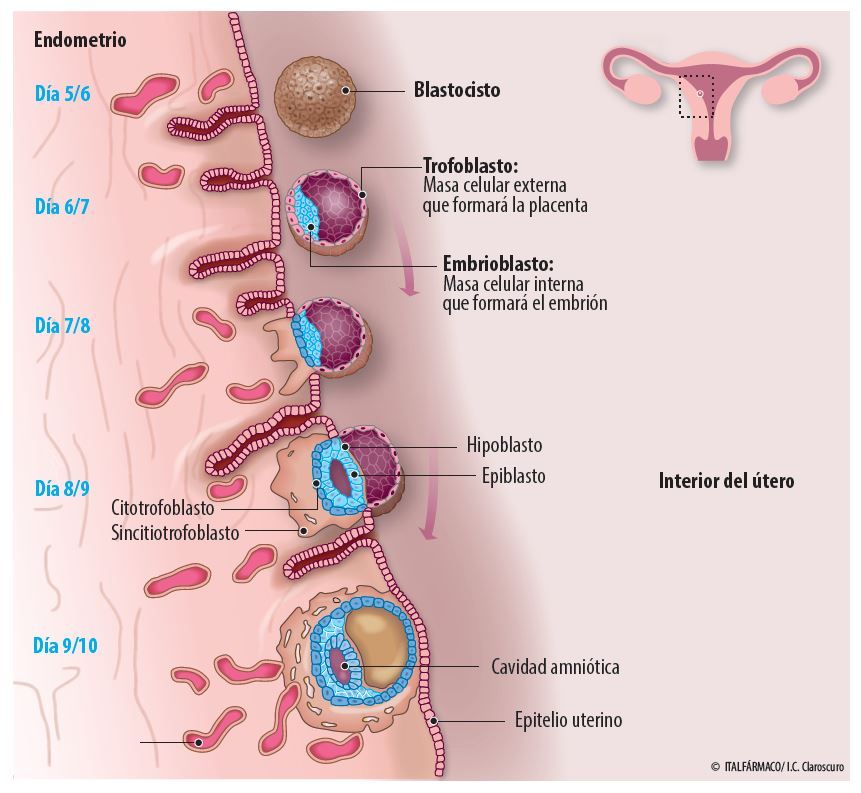
En lo que se refiere a las causas que pueden influir en la implantación tardía, un estudio científico publicado en el año 2011 encontró que el tabaco debía considerarse como un factor de riesgo directo.
El endometrio es el encargado de recibir al embrión durante el periodo de anidación o implantación. Algunas mujeres presentan un periodo de implantación distinto al habitual, lo que se conoce como implantación tardía.
La ventana de implantación o periodo de receptividad es el periodo de tiempo en que el endometrio presenta un ambiente adecuado para que el embrión pueda anidar. Tiene lugar entre los días 19 y 21 del ciclo menstrual, 5-7 días después de la ovulación. En aquellas mujeres que tienen una ventana de implantación tardía el día óptimo para realizar la transferencia se encuentra desplazado.
Cada ciclo menstrual, las hormonas sexuales se encargan de preparar al endometrio para la posible llegada de un embrión. El óvulo fecundado va sufriendo divisiones celulares; a los 3-4 días ya está formado por al menos 16 células y tiene un aspecto similar a una mora. A continuación, circula hacia la cavidad uterina donde se convierte en blastocisto y tiene lugar la implantación.
El óvulo fecundado va sufriendo divisiones celulares; a los 3-4 días ya está formado por al menos 16 células y tiene un aspecto similar a una mora. A continuación, circula hacia la cavidad uterina donde se convierte en blastocisto y tiene lugar la implantación.
Desde el punto de vista embriológico, en día 5 el embrión está formado por dos partes:
La placenta tiene muchas funciones, entre las que se encuentra la de producir hormonas. La primera hormona que se puede detectar es la Gonadotropina coriónica (HCG) y por este motivo, es la que se utiliza para el diagnóstico de embarazo. Se puede detectar mediante una analítica a partir del día 24 del ciclo, es decir, incluso antes de la supuesta llegada de la siguiente regla; y en orina a partir del 9º día de retraso menstrual.
Además de utilizarse para el diagnóstico, también se utiliza para el seguimiento del embarazo y la detección de posibles anomalías.
La implantación es cosa de dos. La salud de los padres tiene un papel clave para conseguir el éxito en la implantación. Llevar un estilo de vida saludable y evitar el tabaco y el alcohol se ha asociado a una mejora en la receptividad.
Del mismo modo, la progesterona es la hormona de la implantación. Normalmente, es suficiente con la que secreta el cuerpo lúteo después de la ovulación, pero en ocasiones, es necesario suplementarla para aumentar la dosis, siguiendo las indicaciones de tu médico.
La transferencia de embriones tiene lugar entre los días 19 y 21 del ciclo, el periodo estándar, pero si una mujer tiene la ventana de implantación tardía, la transferencia no resultará exitosa.
Afortunadamente, en la actualidad disponemos del test ERA (Análisis de receptividad endometrial) que permite identificar la ventana de implantación de cada mujer y llevar a cabo una transferencia embrionaria personalizada (pET).
Está recomendado en aquellas mujeres que han sufrido problemas repetidos en la implantación (ten en cuenta que 3 de cada 10 mujeres tienen una ventana de implantación desplazada).
El test ERA es una prueba sencilla que puede realizar tu ginecólogo sin necesidad de entrar en quirófano ni someterse a anestesia.
Realizar la transferencia de embriones de forma personalizada hace que aumenten las probabilidades de quedarse embarazada, se ha demostrado un aumento del potencial reproductivo en tratamientos con Fecundación in vitro (FIV) y ICSI (Inyección intracitoplasmática de espermatozoides)
Las líneas de investigación actuales están estudiando cuáles son los factores genéticos, inmunitarios e infecciosos que pueden dificultar una adecuada anidación.
Nasser Al Asmar
PhD. Asesor Científico
Nasser Al-Asmar es Licenciado en Farmacia en la rama Sanitaria, Máster
en Biotecnología de la Reproducción Humana Asistida y Doctorado en
Biomedicina y Biotecnología con el tema: “Importancia del estudio
cromosómico de los restos abortivos mediante técnicas de secuenciación
masiva (NGS) y arrays de CGH para un adecuado consejo reproductivo”
todo ello por la Universidad de Valencia (España). Fue Director de
Laboratorio en Igenomix USA (Miami, Florida) desde su apertura en 2012
hasta enero de 2016, cuando se convirtió en Asesor Científico primero
para los Estados Unidos y ahora para España y Latinoamérica.
Nasser Al-Asmar tiene más de 10 años de experiencia en Laboratorio
clínico y de investigación, primero en la Clínica IVI-Valencia (España) en
el Laboratorio de Diagnóstico Genético Preimplantacional, luego en
Igenomix (España) en el Laboratorio de Diagnóstico Genético
Preimplantacional y posteriormente en Igenomix USA (Miami, Florida).
En el ámbito clínico, tiene una amplia experiencia en el estudio de
anomalías cromosómicas en embriones (PGT-A) y espermatozoides
utilizando tecnología aCGH e hibridación “in situ” fluorescente (FISH).
También está desarrollando estos mismos estudios para la nueva técnica
en reproducción asistida, la NGS, así como para el análisis molecular de
los restos abortivos.
One of the stages of the IVF protocol is embryo transfer. Of great importance for its successful implantation is how well the endometrium is prepared for replanting. Hormone therapy helps to maintain it in the right state during the entire IVF protocol.
The onset of pregnancy and its development largely depend on the implantation of the embryo during IVF.
One of the stages of the IVF protocol is embryo transfer. Of great importance for its successful implantation is how well the endometrium is prepared for replanting. Hormone therapy helps to maintain it in the right state during the entire IVF protocol.
Hormone therapy helps to maintain it in the right state during the entire IVF protocol.
Endometrial characteristics change throughout the cycle. The most favorable conditions for the attachment of the embryo occur approximately on the 5-7th day after ovulation; this period lasts literally 2-3 days and is called the implantation “window”. At this point, the endometrium becomes thicker, filled with new blood vessels. Outside, the embryo is covered with a traphoblast. It is these cells that attach to the endometrium and gradually penetrate deeper into it. Full implantation occurs in about 12 days. With successful attachment of the embryo, the endometrium will first supply it with nutrients.
IVF is characterized by late implantation . This is due to the long preparation of the entire procedure (5-8 days pass from fertilization to replanting), in addition, the embryo needs more time to adapt under conditions of artificial insemination. For everything to be successful, a sufficient amount of progesterone in the mother’s body is very important. The conclusion about the onset of pregnancy is made by the increase in the level of hCG in the blood, which begins to be actively produced already a day after successful implantation. There is nothing wrong with the late attachment of the embryo; this does not affect the health of the fetus in any way.
For everything to be successful, a sufficient amount of progesterone in the mother’s body is very important. The conclusion about the onset of pregnancy is made by the increase in the level of hCG in the blood, which begins to be actively produced already a day after successful implantation. There is nothing wrong with the late attachment of the embryo; this does not affect the health of the fetus in any way.
To reduce the risk of miscarriage, a woman after implantation is recommended to:
With late implantation of the embryo, the patient may experience:
If the abdominal pain persists, the bleeding increases, the temperature rises, you should immediately consult a doctor.
It is not worth judging the occurrence/non-occurrence of pregnancy only by the listed signs – sometimes a woman does not observe any changes in her state of health at all, but the implantation is successful, and vice versa. To say for sure whether you are pregnant or not, you can only after an hCG test.
Chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) test is given 2 weeks after the transfer. By this time, the level of its concentration in the blood becomes sufficient to accurately detect pregnancy. Many women rush to the laboratory literally 2-3 days after replanting, but it is not advisable to do this – the results will be unreliable.
In the urine, the level of hCG rises more slowly than in the blood, so even 2 weeks after infusion, a regular test from a pharmacy can show a negative result. For laboratory analysis, blood is taken from a vein, in the morning, on an empty stomach. The pregnancy is finally confirmed by an ultrasound scan, which is performed 3 weeks after the embryo transfer: the pictures already clearly show the fetal egg, the place of its attachment.
The pregnancy is finally confirmed by an ultrasound scan, which is performed 3 weeks after the embryo transfer: the pictures already clearly show the fetal egg, the place of its attachment.
IVF is not always successful. The reason for failed implantation can be:
If pregnancy has not occurred, an additional examination is carried out, the reproductologist examines the clinical picture and draws conclusions about the causes of the incident, draws up a further plan for diagnosis and treatment using IVF.
All information is for guidance only. If you have any health problems, you need to consult a gynecologist.
Infections and reproductive health
How to do IVF without a husband: choosing a donor
Lifestyle and nutrition during IVF
Ovarian reserve
The number of families who turn to in vitro fertilization is constantly growing. IVF is a long and complicated process and is often the last hope for motherhood. During implantation of the embryo, the fetal egg penetrates the uterine cavity and attaches to the endometrium. During successful penetration, pregnancy occurs, otherwise there is no pregnancy. Women are excited and anxious about the period after the implantation of the embryo.
IVF is a long and complicated process and is often the last hope for motherhood. During implantation of the embryo, the fetal egg penetrates the uterine cavity and attaches to the endometrium. During successful penetration, pregnancy occurs, otherwise there is no pregnancy. Women are excited and anxious about the period after the implantation of the embryo.
In this type of fertilization, doctors remove the egg from the female body, place it in special conditions and fertilize it with sperm. The embryo, which turned out in the process of fertilization, is in the incubator for 3-5 days, then it is transferred to the uterus. Successful implantation of an embryo after IVF (pregnancy) is observed in every third case.
In vitro fertilization requires the following conditions:
1. During the first stage, ovulation is stimulated, which is carried out with the help of special medical hormonal preparations.
2. In the second step, the egg and sperm are retrieved. Sperm must be collected on the same day that the egg is retrieved. If this is not possible, then the sperm obtained earlier is frozen with liquid nitrogen.
3. At the next stage, healthy eggs and sperm are selected, after which fertilization takes place.
4. The last stage is the transfer of the fetal egg into the uterine cavity. After successful implantation of the embryo, pregnancy occurs. During the transfer, the woman is located on the gynecological chair, the doctor inserts the embryo into the uterus using a catheter.
Most clinics use new technologies that increase the effectiveness of the procedure. To achieve this result, women are usually planted with 2 embryos. Based on order 67 of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of 2003, it is not recommended to implant more than 4 embryos in order to prevent multiple pregnancies.
Successful implantation of an embryo after transfer depends on the age of the embryo. The possibility of getting pregnant with the replanting of five-day embryos reaches 45%. The transfer of three-day embryos guarantees a result in 38-43% of cases. The replanting of day-old embryos ends in pregnancy only in 16-18% of cases. Sometimes reproductologists plant ten-day embryos. Women should remember that even a successful embryo transfer does not guarantee successful implantation.
Reproductologists give several important recommendations that women should follow 10 days after the procedure. These tips increase embryo implantation after transfer:
Contrary to popular belief, bed rest is not recommended. It is only necessary to reduce physical activity. In order for the implantation of the embryo after the transfer to be successful, it is not recommended to visit public places, since you can become infected with some kind of infectious disease. Compliance with the above recommendations increases the success of implantation.
It is only necessary to reduce physical activity. In order for the implantation of the embryo after the transfer to be successful, it is not recommended to visit public places, since you can become infected with some kind of infectious disease. Compliance with the above recommendations increases the success of implantation.
After an embryo transfer, women begin to listen to their bodies. They are trying to understand if the implantation of the embryo after IVF was successful.
During implantation, women may experience symptoms that are similar to those experienced in early pregnancy. These include:
 The discharge is scanty, due to damage to small vessels during embryonic attachment,
The discharge is scanty, due to damage to small vessels during embryonic attachment, Implantation of an embryo after IVF is similar to the attachment of a fetal egg as a result of natural conception. The only difference is that fertilization during IVF is carried out in artificial conditions, outside the woman’s body. In a normal pregnancy, implantation occurs a week after fertilization. During this time, the fertilized egg moves through the fallopian tubes and attaches to the uterus.
After IVF, the embryo attaches to the endometrium 10 days after the transfer. This is called late implantation. Successful attachment of the embryo must meet the following conditions:
This is called late implantation. Successful attachment of the embryo must meet the following conditions:
Women should remember that the level of hCG in the blood does not rise immediately after the implantation of the embryo. The process is a little stretched in time, it can last three days, until the endometrium begins to change.
The most important sign of pregnancy is an increase in the level of hCG in the blood. The analysis is carried out two weeks after the procedure. The level of the hormone directly depends on the duration of pregnancy.
A level of 25 mU/ml is considered positive, indicating pregnancy. If the hCG level is less than 5 mU / ml, then pregnancy did not occur, the embryo did not attach to the uterus. Normally, the hormone doubles every two days after the transfer. This continues for up to 6 weeks, after which the increase in hCG slows down. After 10 weeks, hormone levels begin to decline.
Slower growth rates of hCG are possible. Determining the level of the hormone must be carried out together with an ultrasound, which allows you to absolutely determine pregnancy.
Before IVF, couples are fully examined. If a woman cannot bear a baby, then you can resort to surrogate motherhood.
In practice, even the good health of the future mother and father does not guarantee the success of implantation. This is due to a number of reasons:
