Los países árabes tienen una cultura muy diferente a la nuestra, pero siempre nos ha llamado mucho la atención. Ya sea por un motivo y otro, lo cierto es que nos ha resultado siempre algo exótica. A la hora de escoger un nombre para un futuro bebé, cada familia tiene sus preferencias, pero cada vez hay más personas que miran hacia los países extranjeros buscando la originalidad. Y, en este caso, los nombres de origen árabe son, además de novedosos (aunque cada vez se escuchan más en nuestro país), bonitos y repletos de significado.
Ten en cuenta, además, que la tradición árabe en España es extensa, con un amplio vocabulario de etimología árabe, con lo que no debería resultarnos tan raro siempre que los transcribamos al castellano. Y esa transcripción existe, con una sonoridad muy especial.
No te lo pierdas
No te lo pierdas
Icons / List-viewCreated with Sketch.
Temas en este artículo
Icons / arrow-downCreated with Sketch.
Tomar la decisión de elegir el nombre del bebé es una tarea más complicada de lo que parece. Papá y mamá pueden no estar de acuerdo en los nombres que les gustan, tener muchas opciones, dudar acerca de un nombre en concreto. ..No pasa nada. Lo importante es llegar a encontrar un nombre que realmente guste a los dos miembros de la pareja. Para ello, no es necesario que os limitéis a los nombres en español. Hoy en día, podéis elegir entre una infinidad de propuestas: desde los nombres clásicos de siempre hasta nombres de niños y niñas raros y originales o en otros idiomas, como nombres ingleses, griegos, japoneses, vascos o italianos. ¿Y habéis pensado en la idea de elegir un nombre en árabe de niño? ¡Es una opción muy original! Por si os animáis, nosotros os ofrecemos un listado con 100 nombres árabes de niños con sus significados.
..No pasa nada. Lo importante es llegar a encontrar un nombre que realmente guste a los dos miembros de la pareja. Para ello, no es necesario que os limitéis a los nombres en español. Hoy en día, podéis elegir entre una infinidad de propuestas: desde los nombres clásicos de siempre hasta nombres de niños y niñas raros y originales o en otros idiomas, como nombres ingleses, griegos, japoneses, vascos o italianos. ¿Y habéis pensado en la idea de elegir un nombre en árabe de niño? ¡Es una opción muy original! Por si os animáis, nosotros os ofrecemos un listado con 100 nombres árabes de niños con sus significados.
( Te interesa: Nombres de niños y niñas ‘modernos’ y clásicos )
( Te interesa: Nombres de bebés )
Aban: Antiguo nombre árabe.
Abbas: Hace referencia a un león.
Abdul, Abdel: Literalmente, significa “sirviente”.
Adel: Hombre justo y honrado.
Alim: Hombre que aprende rápido.
Amid: Significa “general”.
Asim: Nombre que significa “protector”, “defensor”.
Ayham: Hombre valiente y con coraje.
Badi: Literalmente, quiere decir “maravilloso”.
Bahij: Hombre alegre y feliz.
Basim, Bassam: Hombre que sonríe a la vida.
Bayhas: Nombre relacionado con un león.
Dabir: Significa “secretario”.
Dirar: Antiguo nombre árabe.
Diya: Nombre con un significado relacionado con la luz y el resplandor.
Fadi: Literalmente, quiere decir “salvador”.
Fadil: Hombre generoso, honorable, considerado superior.
Falah: Hombre de gran éxito en lo que se propone.
Fatin, Fateen: Hombre elegante e inteligente.
Gamal, Gamali: Literalmente, significa “camello”.
Ghaith, Ghayth: Bonito nombre que significa “lluvia”.
Ghali: Hombre valioso, querido y muy amado.
Ghiyath: Hombre protector, que socorre a quien lo necesita.
Habbab: Hombre afable, loable y querido.
Habib: Literalmente, quiere decir “amado”.
Hadad: Hace referencia al dios sírio de la fertilidad.
Halim: Hombre cariñoso, delicado y paciente.
Hamal: Significa “cordero”.
Hashim: Nombre que hace referencia a un hombre destructor del mal.
Hassan: Significa “guapo”, “hermoso”.
Hatim: Literalmente, quiere decir “juez”.
Hudad: Nombre de un rey áraba pre-islámico.
Husain, Husayin, Hussein: Nombre que hace referencia a un descendiente del Profeta y que significa “hermoso”.
Ibrahim: Hace referencia al nombre de un profeta y significa “padre de una multitud”.
Idris: Relacionado con el nombre de un profeta.
Imran: Hace referencia al nombre de un profeta y significa “larga vida”.
Isam: Literalmente, quiere decir “salvaguardar”.
Ishaq: Relacionado con el nombre de un profeta.
Jabalah: Literalmente, quiere decir “montaña”, “colina”.
Jabir: Significa “el que sabe consolar”.
Jafar: Nombre de bonito significado; “bonito arroyo”.
Jalal: Significa “gloria”.
Jasim: Relacionado con un hombre de tamaño grande, enorme.
Jaul: Literalmente, quiere decir “elección”.
Kadar, Kedar: Nombre que está relacionado con un hombre poderoso.
Kahil: Hombre amigable y querido.
Kaliq: Nombre que significa “creativo” y que se refiere a una cualidad de Dios.
Kamal: Hombre atractivo y perfecto.
Kasib, Kaseeb: Literalmente, quiere decir “fértil”.
Kaseem, Kasim: Significa “dividido”.
Kateb, Katib: Hace referencia al arte de escribir.
Kazim: Hombre de buen carácter, paciente y tranquilo.
Khalid, Khaled: Nombre de bonito significado; “eterno”.
Mahir: Hombre honorable y valiente.
Mahjub: Significa “oculto”, “velado”.
Marid: Literalmente, quiere decir “rebelde”.
Mashhur: Nombre que significa “famoso”, “conocido”.
Misbah: Hace referencia a un cordero.
Mishaal: Significa “antorcha”, “luz”.
Miyaz: Hombre distinguido, el preferido.
Mubin: Literalmente, quiere decir “claro” y “evidente”.
Mudar: Nombre relacionado con una tribu árabe y que hace referencia al bisabuelo del Profeta.
Muhammad, Mohammed: Nombre de distintos significados; “alabado”, “digno de alabanza”, “el nombre del Profeta”.
Muslim: Hace referencia a la presentación de uno mismo a Dios.
Mustafa: Significa “el elegido” y hace referencia a uno de los nombres del Profeta.
Nabhan, Nabih: Significa “noble”, “sobresaliente”.
Namir: Hombre de buen corazón, puro y querido.
Nasih: Literalmente, quiere decir “asesor”, “consejero”.
Nasim: Significa “aire fresco”.
Nasir: Hombre protector, que ayuda a los demás.
Qasim: Significa “el que distribuye”.
Qays, Qais: Hombre firme y con las ideas claras.
Rabah: Literalmente, quiere decir “el ganador”.
Rabi: Nombre de bonito significado; “brisa de primavera”.
Radi: Hombre satisfecho, contento y feliz.
Rafi: Significa “exaltar”.
Ramadan: Hace referencia al noveno mes del calendario musulmán, el mes de ayuno.
Rami: Literalmente, quiere decir “tirador”.
Rasmi: Hombre formal, honorable y leal.
Rasul: Significa “mensajero”.
Sadiq: Hombre sincero y veraz, en quien se puede confiar.
Safwan: Hombre de corazón puro y fuerte como una roca.
Sahib: Literalmente, quiere decir “compañero”.
Sahir: Significa “despierto”.
Salah: Hace referencia a la justicia.
Shamim: Se traduce por “fragante”.
Sharaf: Hombre honorable.
Thair: Hombre de corazón puro, casto y modesto.
Tahsin: Literalmente, significa “embellecimiento”.
Usaim, Usaym: Significa “cachorro de león”.
Usama, Usamah: Nombre que hace referencia a un león.
Uthal: Nombre de una montaña.
Yaman: Poético nombre que significa “buenas noticias”.
Yasar, Yasser: Nombre relacionado con la riqueza, la comodidad y la facilidad.
Yasin, Yaseen: Nombre que hace referencia a aas dos letras iniciales de la sura 36 del Corán. Es uno de los nombres del Profeta.
Yasir: Literalmente, quiere decir “adinerado”:
Zafar: Significa “victoria” y se relaciona con un hombre de éxito.
Zafir: Significado muy similar a Zafar; “victorioso”.
Zahid: Nombre que se traduce por “abnegado” y también por “abstemio”.
Zaid, Zayd: Nombre relacionado con el crecimiento y la abundancia.
Zakwan: Literalmente quiere decir “intuitivo”.
Ziad, Ziyad: Significa “de gran abundancia”.
……….
¿Qué te parecen los nombres árabes de niño? ¿Te gusta alguno es especial? ¿Con tu pareja no os ponéis de acuerdo sobre qué nombre elegir para el bebé? Por favor, deja tu comentario al final de este artículo y comparte tu opinión con otras mamás en el Salvamamás.
( Te interesa: Nombres para niños raros y originales )
Views: 973
Archive of the Toledo Mozarabs of the 12th and 13th centuries. was translated from Arabic into Spanish and published in four volumes by Ángel González Palencia in 1926-1930. During the Reconquista, the territory of Toledo repeatedly found itself in the hands of either the Arabs or the Spaniards. The chronological framework of the archive: 1083–1315 This is a collection of 1175 documents that record property transactions between individuals and church organizations. Most of the documents refer to the Cathedral of St. Mary in Toledo. All archive documents (except 25) are written in Arabic, which is evidence of the official status of the Arabic language in Toledo even at the beginning of the 14th century. In Arabic texts, there are words in Alhamiado, i.e. in Spanish in Arabic script. The latter are of particular philological interest. Mozarabic Alhamiado, the language of the Spaniards in Arab-conquered Spain, left no written records, so the early history of the Spanish language is poorly documented. The archive of the Toledo Mozarabs is an important source of lexicon in the Alhamiado of the Moriscos.
was translated from Arabic into Spanish and published in four volumes by Ángel González Palencia in 1926-1930. During the Reconquista, the territory of Toledo repeatedly found itself in the hands of either the Arabs or the Spaniards. The chronological framework of the archive: 1083–1315 This is a collection of 1175 documents that record property transactions between individuals and church organizations. Most of the documents refer to the Cathedral of St. Mary in Toledo. All archive documents (except 25) are written in Arabic, which is evidence of the official status of the Arabic language in Toledo even at the beginning of the 14th century. In Arabic texts, there are words in Alhamiado, i.e. in Spanish in Arabic script. The latter are of particular philological interest. Mozarabic Alhamiado, the language of the Spaniards in Arab-conquered Spain, left no written records, so the early history of the Spanish language is poorly documented. The archive of the Toledo Mozarabs is an important source of lexicon in the Alhamiado of the Moriscos. In his texts there are: Spanish toponyms; Christian onomastics; designations of church positions; names of Christian holidays; designations of some court positions; designations of family ties, etc. Documents are almost always signed in Arabic and romance. In many archive documents, a Romance and Arabic name is indicated for one person. There are frequent cases of name identification, which show that not Romance, but Arabic names were used in everyday life. At the same time, Arabic names contain elements of Spanish morphology, and vice versa, many Romance names are formed according to the Arabic model, including with the characteristic mention of several generations. The transcription of Romance names in documents in Arabic deserves special attention. Some of the Romance names found in Arabic texts (and in the Arabic script) show pronunciations of these names that are closer to Latin than to modern Spanish. Of particular difficulty is to single out Muslims from the signatories, since the majority of Christians had Arabic names.
In his texts there are: Spanish toponyms; Christian onomastics; designations of church positions; names of Christian holidays; designations of some court positions; designations of family ties, etc. Documents are almost always signed in Arabic and romance. In many archive documents, a Romance and Arabic name is indicated for one person. There are frequent cases of name identification, which show that not Romance, but Arabic names were used in everyday life. At the same time, Arabic names contain elements of Spanish morphology, and vice versa, many Romance names are formed according to the Arabic model, including with the characteristic mention of several generations. The transcription of Romance names in documents in Arabic deserves special attention. Some of the Romance names found in Arabic texts (and in the Arabic script) show pronunciations of these names that are closer to Latin than to modern Spanish. Of particular difficulty is to single out Muslims from the signatories, since the majority of Christians had Arabic names.
Keywords: Mosarabs, al-Andalus, Alhamiado, Christian onomastics, Staro-Spanish language
Doi: 10.222250/2072-8662.2019.2.10-16
Download article (pdf)
about autocrats
|
Tikhonova Oksana Viktorovna – Candidate of Philology, Assistant of the Department of Romance Philology St. Petersburg State University; 199034, St. Petersburg, Universitetskaya embankment, 7–9; This email address is being protected from spambots. You must have JavaScript enabled to view. |
|
|
Shakunova Larisa Andreevna – Bachelor of Oriental Sciences, Master student Oriental Faculty of St. Petersburg State University; 199034, St. Petersburg, Universitetskaya embankment, 7–9; This email address is being protected from spambots. |
Speaking of the development of languages, we mean the changes that occur in the language under the influence of social contacts. Human society and its history are inseparable from speech activity. All spheres of human life involve constant communication, both within one linguistic community and outside it. It is interesting that language, on the one hand, is a universal means of communication and does not depend on social history, and on the other hand, being a means of communication, it is subject to specific transformations as a result of certain historical changes.
Today we will talk about the fact that such social upheavals as revolutions, civil wars, extensive conquests of new lands, are reflected in the language. What is it? As a rule, the boundaries of dialect phenomena are shifted, the former normative and stylistic structure of the language is violated, vocabulary and phraseology are updated. Borrowings from other languages make the language colorful and rich, and also carry a piece of history. We are particularly interested in the influence of the Arabic language , life and culture in Spanish.
Borrowings from other languages make the language colorful and rich, and also carry a piece of history. We are particularly interested in the influence of the Arabic language , life and culture in Spanish.
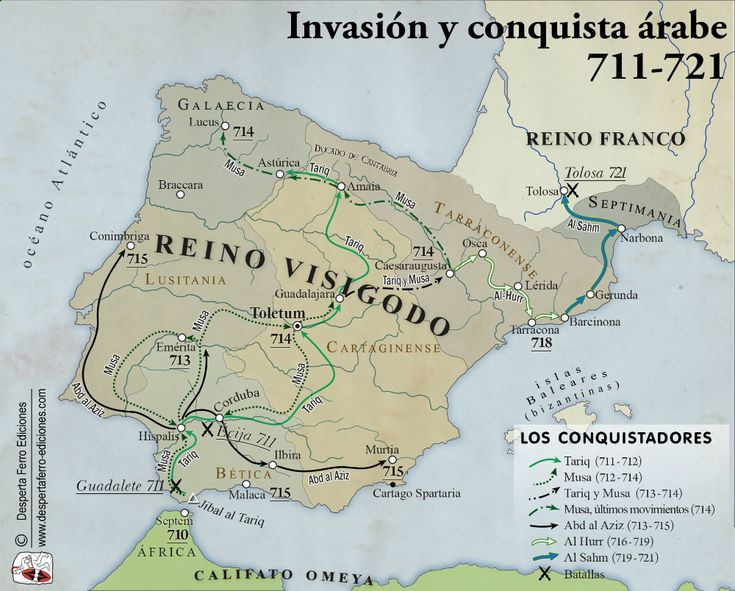
In 711, the second expedition of the Arab-Berber troops (the first successfully landed in the vicinity of Algeciras in the summer of 710, after which they returned to Africa with rich booty), represented by immigrants from the states of the Middle East and North Africa, under the leadership of Tariq ibn -Ziyada, overthrew the king of the Visigoths Roderich (Spanish: Rodrigo) in a battle near the Guadalete River. The Christian Visigoths suffered a complete defeat. It cannot be said that the Spanish population began an extensive struggle with the Arabs, for five who established control over most of Spain. Cities surrendered one after another, where – immediately, where – after the siege. Muslim tolerance and tax breaks offered by the conquerors swayed the Spanish population to the Arab side.
Arab rule over the Iberian Peninsula began, which was destined to last 8 centuries, until 1492, when the Catholic kings Isabella and Ferdinand returned power to themselves. And these eight centuries will be a truly powerful milestone in the history of Spain.
The total number of Arabicisms that came into the Spanish language as a result of Arabic domination exceeds 4000 lexical units, according to the Spanish linguist and historian of the language, Rafael Lapes. It must be said that, of course, not all words of Arabic origin quickly entered the Spanish language immediately after the fall of the Visigoths. This happened progressively, as the assimilation of the Arabs and the adaptation of the Spaniards to their way of life.
Let us first consider Arabic words in a chronological section, then describe the influence of Arabic on Spanish at all levels of the language, and then move on to the thematic distribution of lexical units.
According to the chronological classification, the Arabisms of the Spanish language can be divided into the following groups:
1) words that entered the language during the years of the Arab conquest itself or during the entire period of the conquest and the beginning of the period of the reverse conquest of the Reconquista from 711 to the middle of the 11th century . These Arabisms were common in the territory from Galicia to Catalonia, they can be considered common to the whole country. They are characterized by the following: a) recorded in documents dated before 1050; b) appear in at least three languages: Spanish, Portuguese and Catalan; c) have different phonetic features. Many Arabisms of this period disappeared by the 13th century: avende “flag”, zarama “cloak”, alisare “border”, etc.;
These Arabisms were common in the territory from Galicia to Catalonia, they can be considered common to the whole country. They are characterized by the following: a) recorded in documents dated before 1050; b) appear in at least three languages: Spanish, Portuguese and Catalan; c) have different phonetic features. Many Arabisms of this period disappeared by the 13th century: avende “flag”, zarama “cloak”, alisare “border”, etc.;
2) words that entered the language in the era of the collapse of the caliphate, in the era of the so-called “great” Reconquista (from the middle of the 11th century to the beginning of the 13th century): alaules “pearl”, mancale “table”, alcailo “horse”, yucef i, merini are the names of the coins.
3) words that replenished the language in the era of the final victory of Castile and the formation of the “Castilian standard”, i.e. the beginning of the heyday of Spanish literature, (XIII century): aduana customs, warehouse, azúcar sugar, álgebra algebra, elixir elixir, alcohol alcohol, azimut azimuth 90 algorithm25 , aldea “village”, etc.
Now consider the Arabic linguistic heritage at all levels of the language, starting from phonological . This is a tribute to the rule, although at the level of phonology there are no borrowings as such. There are, however, hypotheses that sound [j] has Arabic roots. Famous Spanish linguists (Rafael Lapeza, Cano Aguilar) testify that the polysyllabic words that appeared in Spanish are the result of Arabic influence and the characteristic stress on the last syllable of this language. In Spanish these words, however, have an accent on another syllable – berenjEna “eggplant”.
Carrying out a morphological analysis, let’s say that Arabisms belong to parts of speech. Most of them are nouns, numerous toponyms are the names of cities, rivers, mountains, etc., very few adjectives, verbs, a few interjections ( ojalá , guay ) and just one preposition – hasta “before”. Some grammatical points are important: the use of the Arabic article al with nouns. Subsequently, the article merged with the noun stem, in addition, the Spanish language retained its articles – la almohada , el alhelí , el albarán …
Subsequently, the article merged with the noun stem, in addition, the Spanish language retained its articles – la almohada , el alhelí , el albarán …
to form adjectives denoting origin ( ceutí , marroquí , yemení ) and other nouns and adjectives ( jabalí , maravedí bal , muladí … … In the 13th century, the word alfonsí appears to designate everything related to King Alfonso X.
Moving on to lexicon , we repeat that here the influence of the Arab conquest was incredible. Arabisms affect almost all spheres of human life; this is the second largest layer of vocabulary after Latin. Let’s try to group them thematically: arrabal aldea, alquería, almunia, alcoba, azotea, zaguán, alfeizar, albañil, alarife, tabique, azulejo, alcantarilla, albañal, alfombra, almohada.
Life, housekeeping: laúd, ajedrez, azar, tarea, alfarero, taza, jarra, ajorcas, alfiler, aljuba, albornoz, babucha, zaragüelles, albóndigas, almíbar, arrope .
There are also many Arabisms among agricultural names, since the Arabs brought a lot of new things in terms of cultivating the land and irrigating the soil: acebuche , jara , retama .
Minerals: como azufre , almagre , albayalde , azogue , almadén .
Names of birds of prey, since falconry was one of the favorite Arab hobbies:
Constant confrontations with Christians contributed to the emergence of a large number of words related to military topics: aceifas, algara, adalid, atalaya, alcazar, zaga, alfange, adarga, aljuba, adarve, tambor, añafil, alférez, acicate, acémilas,jaeces, albarda, barbacana…
Some Arabic words came to Arabic from others languages: from Sanskrit ajedrez alcanfor , from Persian jazmín, azul, naranja, escarlata , from Greek: arroz, alambique, acelga, alquimia . Here we can talk about the preservation and transmission of the knowledge and heritage of other cultures by the Arabs.