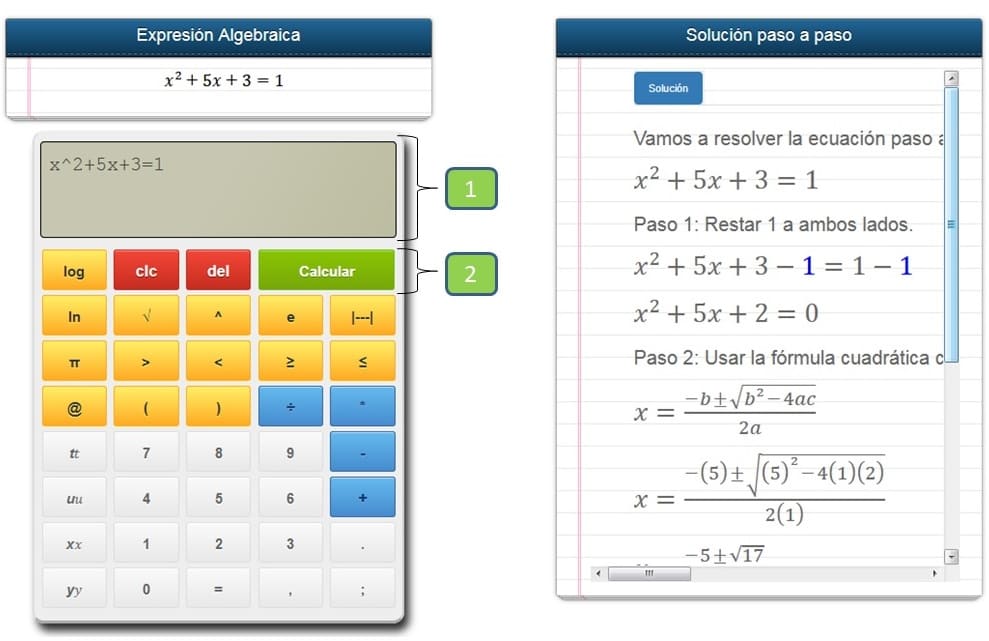
“¿Te preguntas cuándo te llegará el periodo? ¡Always te puede ayudar! Nuestra calculadora menstrual te ayuda a determiner cómo es tu ciclo. Así podrás organizer un viaje a la playa o un evento importante, como una boda, libre de periodos. También puedes caclular tus tiempos “pico” de ovulación si estas intentando quedar embarazada.
¿Lista? Estás a solo 3 preguntas rápidas de obtener tu calendario menstrual personalizado”
Selector de País
surname
o Al registrarme, acepto lo siguiente:
Los términos y la política de privacidad: he leído y acepto los términos y condiciones de P&G y su política de privacidad.
La edad legal mínima: soy mayor de 18 años.
El marketing por correo electrónico: deseo recibir correos electrónicos de Always y de otras marcas y programas de confianza de P&G.
1. ¿CUÁNDO EMPEZÓ TU ÚLTIMO PERIODO?
9
miércoles
noviembre
2. ¿CUÁNTOS DÍAS DURÓ TU PERIODO?
3. ¿CUÁL ES LA DURACIÓN DE TU CICLO?
¡Es ese día del mes otra vez! Tu periodo comenzará, al igual que tu ciclo menstrual. Tu flujo afectará tu día, tu estado de ánimo y tu estilo de vida. Para esos días críticos, ¡no querrás que te tomen por sorpresa! Así que sigue tu ciclo con la calculadora menstrual de Always y para tus días de menstruación, prueba nuestras toallas Always.
Más Información
¿Te sientes incómoda ahí abajo? El flujo vaginal es normal y no se puede controlar. Es parte de tu cuerpo y es tu forma de liberar los residuos de los tejidos no deseados. Además, es la forma de mantener la vagina libre de bacterias y infecciones.
Siéntete preparada para las fugas y flujos vaginales con los productos Always Diários. Son geniales para deshacerse de las molestias y hacer que te sientas fresca y limpia todos los días.
Son geniales para deshacerse de las molestias y hacer que te sientas fresca y limpia todos los días.
Más Información
1/2
Prepárate siempre para tu próximo period menstrual y aprende con antelación cuándo vas a ovular gracaias a la calculadora menstrual de Always. Que no te tomen por sorpresa esos días del mes, ya que nuestra Calculadora Menstrual te asegura saber exactamente cuándo esperar tu próximo ciclo.
Tener un cálculo mensual de tu period y otros síntomas te ayuda a saber cuándo viene tu periodo para que te sientas preparada todos los días de tu ciclo.
Responde a 3 preguntas para empezar:
a. ¿CUÁNDO EMPEZÓ TU ÚLTIMO PERIODO?
b. ¿CUÁNTOS DÍAS DURÓ TU PERIODO?
c.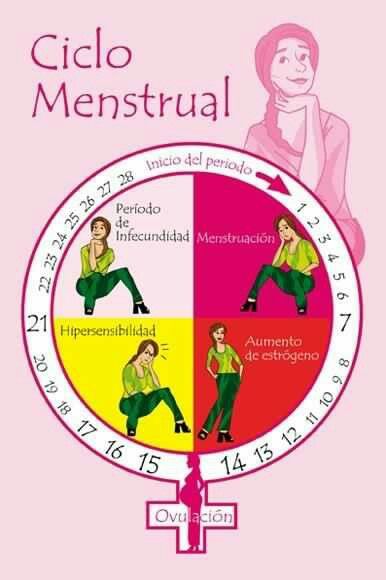 ¿CUÁL ES LA DURACIÓN DE TU CICLO?
¿CUÁL ES LA DURACIÓN DE TU CICLO?
Ahora, hax clic en el botón “Calcular mi ciclo” y ya está. La calculadora menstrual de Always te dirá cuándo es tu próximo periodo.
La Calculadora Menstrual predice tu próxima fecha de menstruación analizando tu historial. Cada persona es diferente y cada ciclo es único, por lo que es importante recordar que ésta es la mejor estimación de tu ciclo menstrual. Es mejor sentirse preparado que sorprendido, ¿verdad?
Por término medio, un ciclo dura 28 días, pero no hay que preocuparse, ya que es completamente normal tener un ciclo ligeramente más largo o más corto. Teniendo en cuenta esto, la Calculadora Menstrual puede no ser 100% precisa cuando su periodo es muy irregular. De todos modos, puede ayudarte a entender mejor cómo funciona tu ciclo y qué puedes esperar en el futuro.
Saber cuándo te espera la próxima menstruación puede te libertar de hacer cualquier tipo de plan. Por ejemplo, queremos que disfrutes tu vacaciones y pensamos que te mereces relajarte en una playa sin preocuparte por tu periodo.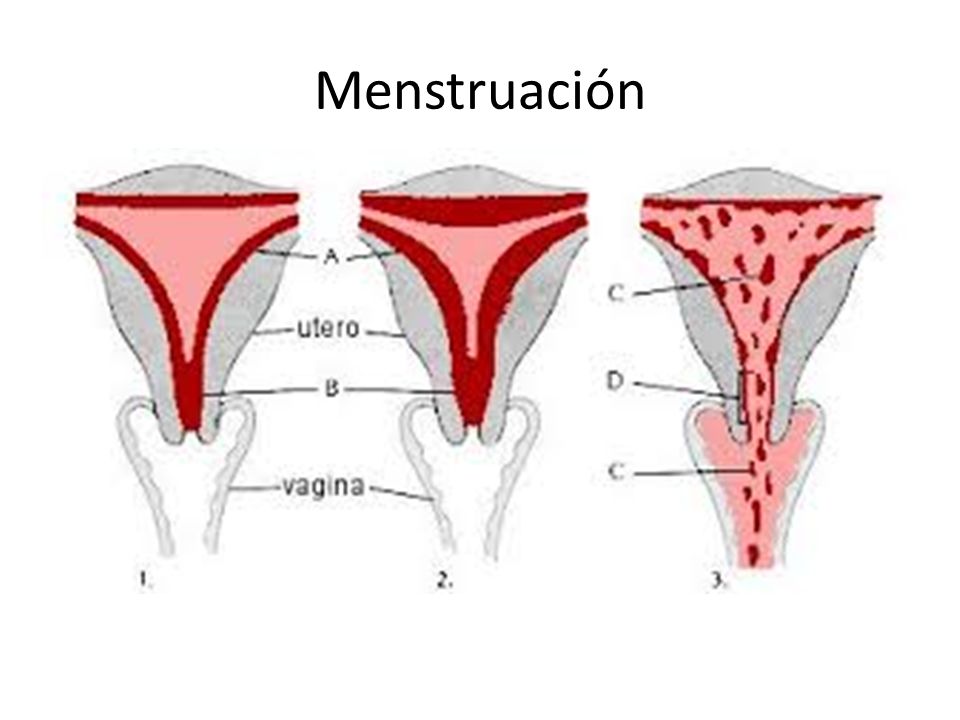
La calculadora Menstrual te da la libertad de saber cuándo debes tener una toalla en tu bolso y nos hace disfrutar de la sensación de confianza en tu vida diaria.
Cada ciclo es único, pero tenemos algunas cosas en común:
PRE PERIODO:
Aqui encontramos el Síndrome Pre Menstrual, también conocido como “SPM”. Es habitual que experimentes algunos síntomas del sindrome premenstrual como dolor de cabeza, hinchazón, irritabilidad y que te sientas más emocional de lo habitual. Por lo general, comienza 3 días antes de la menstruación. Te en cuenta que tu dieta, la cafeína diaria y el estrés pueden aumentar la intensidad de los sintomas del SPM.
PERIODO
Este es el día 1 de tu ciclo y es cuando comienza el sangrado. Quizá te preguntes por qué sangramos. Pues bien, cada mes el cuerpo femenino se prepara para un embarazo y, cuando no se produce la fecundación del óvulo, el endometrio (capa interna de la matriz) se desprende y se convierte en el flujo menstrual, una pérdida espontánea de sangre.
Los periodos menstruales suelen durar entre 4 y 7 días más intensos son el primero y el segundo. Un ciclo medio dura 28 días, pero puede variar entre 21 y 35. Puedes predecir tu ciclo con la Calculadora Menstrual.
Recuerda que debes acudir al medico si tu period dura más de 7 días consecutivos.
OVULACIÓN – FASE FÉRTIL:
Este es el periodo en el que se ovula y son los días de mayor riesgo para que ocurra un embarazo. El periodo fértil dura aproximadamente 6 días. En un ciclo de 28 días, la ovulación suele producirse el día 14. La Calculadora Menstrual te ayuda a averiguar cuáles son estos días.
El primer paso es conocer la duración de tu ciclo menstrual completo. El día 1 es el primer día de la menstruación y el último día es el día anterior a la siguiente menstruación. Si su ciclo dura más de 28 días, la ovulación se producirá alrededor del día 14 (dos semanas antes de la siguiente menstruación).
Aunque sea un poco difícil saber cuáles son exactamente los días fértiles en las mujeres que poseen la menstruación irregular, es posible tener una idea de cuáles pueden ser los días más fértiles del mes, tomando en consideración los últimos 3 ciclos menstruales.
Para esto, es importante que la mujer anote en un calendario el día de cada ciclo en que ocurrió la menstruación, de manera de saber cuántos días en promedio tiene cada ciclo y poder calcular los días más fértiles.
Si su ciclo menstrual es irregular, debe sacar un promedio de los últimos 3 meses de cuántos días fue la duración de su ciclo menstrual, es decir, el primer mes su ciclo duró 28 días, el segundo mes 30 y el tercer mes 26, entonces debe sumar 28 + 30 +26 = 84 / 3 meses = 28 días (siendo este la duración del período que debe colocar en la calculadora).
A continuación, coloque los datos en la calculadora y conozca cuándo será su período fértil:
Primer día de su última menstruación
Erro
help
Cuántos días (en promedio) dura su ciclo menstrual:
212223242526272829303132333435
Erro
help
No obstante, es importante mencionar que este método es una estimación.
El cálculo de los días fértiles en el ciclo irregular puede ser más complicado, ya que la ovulación y la menstruación pueden ocurrir en diferentes períodos y, por lo tanto, es importante que se consulte al ginecólogo para una evaluación más precisa.
A pesar de esto, algunas formas de cálculo populares que pueden ayudar a tener una idea del período fértil, pero no deben considerarse como verdades absolutas:
Para calcular el período fértil o los días fértiles, la mujer debe tener en consideración los últimos 3 ciclos y anotar los días en que ocurrió el primer día de la menstruación, determinar el intervalo entre esos días y calcular el promedio entre ellos.
Por ejemplo, si el intervalo de tiempo entre 3 menstruaciones fue de 33 días, 37 días y 35 días, esto da un promedio de 35 días, que será la duración promedio del ciclo menstrual (para esto basta sumar el número de días de los 3 ciclos y dividir entre 3).
Después de esto, a 35 se resta 14 días, que es igual a 21, lo que significa que a los 21 días ocurre la ovulación. En estos casos, entre una menstruación y otra los días más fértiles serán 3 días antes y 3 días después de la ovulación, es decir, entre el día 18 y día 24 después del primer día de la menstruación.
En este caso, la duración del ciclo debe registrarse en cada mes, de manera que sea posible, al cabo de 1 año, identificar el ciclo más largo y el ciclo más corto. A continuación, se le debe restar 18 al ciclo más largo y 11 al ciclo más corto.
Por ejemplo, el ciclo más largo duró 36 días y el más corto 20 días, por lo tanto, se debe hacer 36 – 18 = 18 y 20 – 11 = 9, lo que es indicativo de que el período fértil debe estar entre el día 9 y 18 del ciclo. Sin embargo, dado que el ciclo es irregular, este período puede ser variable.
Si el método del calendario no funciona y desea quedar embarazada, existen algunas pruebas de ovulación que pueden comprarse en las farmacias, las cuales ayudarán a identificar cuáles son los días más fértiles en los que debe tener el contacto íntimo para aumentar las probabilidades de un embarazo. Vea cómo funciona el test de ovulación.
Vea cómo funciona el test de ovulación.
Otra posibilidad, es tener relaciones sexuales un mínimo de 3 en 3 días durante todo el mes, especialmente en los días en que consiga identificar los signos de periodo fértil, como cambios en la temperatura corporal, la presencia de moco en la vagina y aumento de la libido, por ejemplo. Conozca más sobre estos signos que surgen durante este período.
Vea en el vídeo a continuación más sobre el período fértil:
Para quien tiene un ciclo irregular, la mejor manera de evitar un embarazo no deseado es a través de la ingesta de pastillas anticonceptivas, las cuales ayudarán a regular los días del ciclo menstrual, o a través del uso de preservativo que además de proteger contra un embarazo, protegerá contra las infecciones de transmisión sexual.
El método del coito interrumpido en mujeres con un ciclo menstrual irregular podría aumentar el riesgo de un embarazo, debido a que para usar este método es necesario conocer bien cómo funciona su ciclo menstrual. Vea más sobre este método.
Vea más sobre este método.
PRECISE DIAGNOSTICS
OVER 14 YEARS OF EXPERIENCE
RESULT IN THE SHORTEST TIME
QUALIFIED SPECIALISTS
Calculous cholecystitis is an inflammatory process in the cavity of the gallbladder, which occurs due to stones deposited in it, moreover, formed precisely because of cholesterol, a dye present in bile and calcium impurities.
The service is temporarily not available
Calculous cholecystitis is an inflammatory process in the cavity of the gallbladder, which occurs due to stones deposited in it, moreover, formed precisely because of cholesterol, a dye present in bile and calcium impurities. This type of deposits accumulates in the space of the bile lumen and flow channels, and in case of problems with the outflow of bile, the blood circulation of the gallbladder begins to deteriorate, which contributes to the release of substances that can provoke inflammation.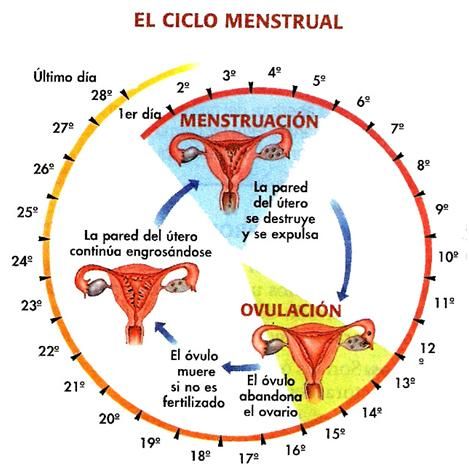
As already mentioned, calculous cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder due to stones. In general, a stone cannot provoke such consequences, but if there are too many of them, then this will be the bright cause of the problem. In this case, it is worth paying attention to the factors that lead to the appearance and development of stones.
These include:
Among the factors that can cause bladder disease such as cholelithiasis and complications, additionally note such concomitant diseases as:
Kisorets
Anzhela Evgenievna
2
Years of Experience
Nurse
Make an appointment
by ordering a call back or via your favorite messenger
Request a call
Calculous cholecystitis is classified into two stages, depending on the course of the disease.
 The consequences, if left untreated, may be the accumulation of pus inside the cavity of the organ, a complication of which is peritonitis.
The consequences, if left untreated, may be the accumulation of pus inside the cavity of the organ, a complication of which is peritonitis. The study of cholelithiasis by ultrasound, provided that the symptoms of cholecystitis appear, allows you to distinguish 4 more stages of the development of the disease.
 In 50% of cases, this form of the disease is not curable.
In 50% of cases, this form of the disease is not curable. The symptoms of chronic cholecystitis differ significantly from the acute form. The acute stage is characterized by:
Chronic calculous cholecystitis is a complication of cholelithiasis that is not in the acute stage and its symptoms are:

In some cases, there may be a sharp pain similar to colic, but not always the inflammatory process is accompanied by such sensations. In general, there are no manifestations in the form of fever, nausea, irritability, or jaundice in chronic cholecystitis.
During an exacerbation, the symptoms may not only increase, but also be supplemented by:
Depending on whether acute calculous cholecystitis or chronic cholecystitis is diagnosed, based on the diagnosis and symptoms, a certain type of treatment for cholelithiasis is selected, which can only be done by a specialist.
Diagnosis of acute or chronic calculous cholecystitis is carried out through examination of the patient, his questioning, as well as clinical studies. This will require such procedures as:
This will require such procedures as:
In special cases, a duodenal intubation can be performed to collect a bile sample.
Cholecystitis is a disease that can be the result of other pathologies formed in the body. Specialists note:
Chronic calculous cholecystitis is treated exclusively at home. If there is an exacerbation process, then urgent hospitalization is needed in the clinic under the supervision of doctors.
If treatment without surgery does not help and the formation of stones occurs again and the manifestation of biliary colic becomes more frequent, then surgery is performed. Operations are of two types.
Calculous cholecystitis: treatment without surgery
What treatment will be carried out, for example, without surgery or, conversely, with surgery depends directly on the form of the disease.
It is strictly forbidden to self-medicate, as this can lead to an acceleration of the formation of stones and their movement through the biliary tract. Therapy includes taking drugs of various effects. Namely:
As soon as the condition stabilizes, a second diagnosis is made to make sure that surgery can be dispensed with. Otherwise, a complete examination of the patient will be required to prepare for surgery. It is worth noting that other concomitant diseases may act as contraindications. What kind of operation will be depends on the general condition of the patient, on the condition of the gallbladder and bile ducts. During the procedure, either a stone in the gallbladder or the organ itself is removed.
After the exacerbation subsides, litholytic therapy is required, during which drugs are used that can dissolve and remove the gallstone, as well as prevent its recurrence. In addition, throughout the treatment of gallstone disease, antispasmodic drugs may be prescribed.
In addition, throughout the treatment of gallstone disease, antispasmodic drugs may be prescribed.
In order to regulate the overall bile composition and speed up the recovery process in case of exacerbation of cholecystitis, it is imperative to eliminate a number of foods from the diet that can become provocateurs of the return of problems. Strictly prohibited consumption:
At first glance, you might think that with calculous cholecystitis you can not eat anything at all, but there are a number of foods that not only can be consumed, but they can also remove the thirst for the above types of food. Allowed consumption:
Allowed consumption:
If you follow the right diet and follow the recommendations of the doctor, you can contribute to the recovery of the body and the overall improvement of the condition.
The treatment of cholecystitis and cholelithiasis, regardless of stage, is carried out exclusively by a gastroenterologist, since it is he who should be contacted for examination, and only then the patient can be redirected to a surgeon, nutritionist or functional diagnostics specialist. It is extremely important that the patient undergoes a completely high-quality examination so that an accurate diagnosis can be made, on which the choice of treatment method and drugs will depend.
You can get more detailed information, sign up for a consultation with a doctor or a procedure by calling: 044 333 4 333 and 0 800 753 357, through the “record on the website” form or a convenient messenger (Fb, Viber, WhatsApp).
Need help?
We will call you
or use your favorite messenger
Author of the article:
References
Our licenses and accreditation certificates
Calculous cholecystitis is an inflammatory process of the gallbladder walls that develops against the background of cholelithiasis. Characteristic manifestations are dull or acute pain under the ribs on the right side, dyspeptic disorders, signs of severe intoxication, jaundice. If symptoms of the disease appear, you should contact a gastroenterologist. Depending on the severity of the pathology, conservative or surgical methods are used in the treatment.
Calculous cholecystitis is a type of cholelithiasis (GSD). In 60–96% of patients, the disease occurs in a chronic form. Most often, the pathology develops after 40 years, in women the problem occurs more often than in men.
Calculous cholecystitis occurs with the progression of cholelithiasis, the causes of development are the same as with the formation of calculi.
The main causes of inflammation of the membranes of the gallbladder:
Abnormal structure of the gallbladder. It is the cause of cholecystitis in 30% of patients. With an irregular shape of the organ or uncharacteristic localization, the secretory fluid stagnates, or its outflow is disturbed.
Irritation of the mucous membrane by stones. At the initial stage, crystals and small stones are in the form of a suspension, they leave the gallbladder along with bile. But gradually the stones increase, injure the walls of the organ, which leads to the development of inflammation, necrosis, and atrophic processes.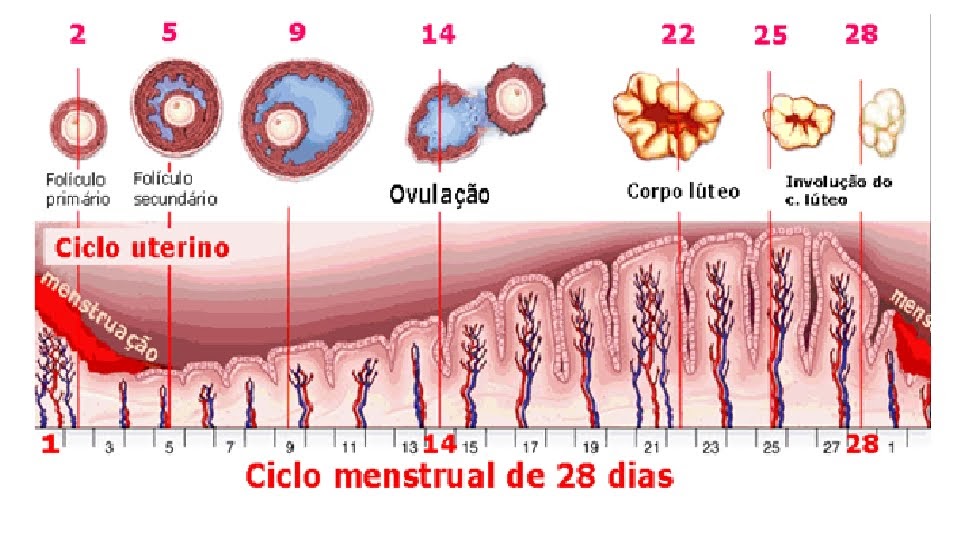 The pathology is aggravated by the formation of large stones with spikes on the surface.
The pathology is aggravated by the formation of large stones with spikes on the surface.
Problems with the outflow of bile. With the rapid growth of calculi, the risk of blockage of the bile ducts by stones, mucosal injury increases, and favorable conditions are created for the active growth of pathogenic microorganisms. The cause of inflammation may be dyskinesia of the gallbladder and bile ducts, compression of the bile ducts by large neoplasms, pancreatic tumors.
Infectious processes in the gallbladder. In most patients with calculous cholecystitis, various pathogenic microbes are present in the bile. Pathogens penetrate into the body with lymph, blood, from the duodenum. Most often, the pathological process causes Escherichia coli, bacterioids. The problem is often observed in people with weakened immunity, pregnant women, diabetics.
Cholecystitis is often detected in children, up to 6–8 years old boys are more often ill, after 12 years old girls. The main reason is nutritional errors, the use of fast food, sweets with dyes in large quantities, chips.
The main reason is nutritional errors, the use of fast food, sweets with dyes in large quantities, chips.
Provoking factors include:
heredity;
overweight;
physical inactivity;
frequent overeating, starvation, rigid diets;
abuse of sweets, spicy, smoked, fatty foods;
pregnancy, multiple births;
diabetes mellitus;
cirrhosis;
Crohn’s disease;
long-term use of hormonal, antibacterial drugs.
Calculous cholecystitis can be acute or chronic. Each type of pathology has its own mechanism of development. But the problem is always associated with the formation of stones.
Stones are made of cholesterol, bile pigments, but most often mixed stones are formed. First, the amount of cholesterol in bile increases, the level of bile acids decreases.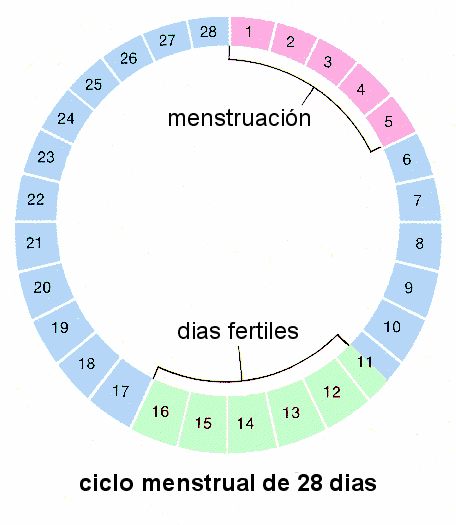 At the second stage, stagnation of bile occurs, the process of crystallization starts. The crystals gradually stick together, forming single or multiple stones ranging in size from 1 mm to 3–4 cm.
At the second stage, stagnation of bile occurs, the process of crystallization starts. The crystals gradually stick together, forming single or multiple stones ranging in size from 1 mm to 3–4 cm.
When a duct is blocked by a stone, the outflow of bile is disturbed, the walls of the organ are constantly in a tense state, the integrity of the mucosa is violated. Additionally, exudation, the production of phospholipase, prostaglandins, is enhanced. Due to squeezing of the vessels, microcirculation is disturbed, the pathological process penetrates into all layers of the walls of the gallbladder. Severe course is accompanied by acute ischemia, necrosis. When infected with pathogenic microorganisms, infectious pathological conditions develop.
Chronic inflammatory process sometimes occurs after the acute phase subsides. But most often, chronic calculous cholecystitis is a consequence of prolonged stagnation of bile, mechanical irritation of the walls of the gallbladder with stones.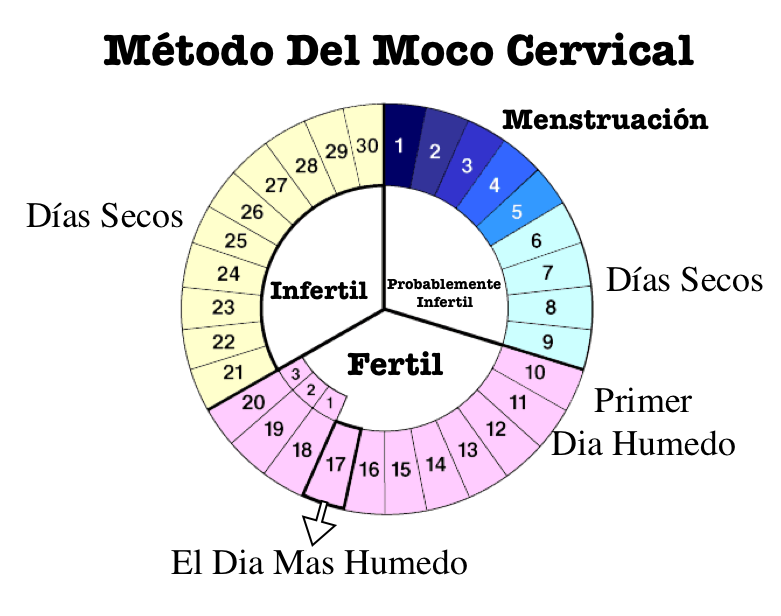 Most often, atrophy of the mucosa is observed, less often – hyperplasia, the formation of polyps. Against the background of prolonged chronic inflammation, scars form, tissue fibrosis develops, and petrification of the organ occurs.
Most often, atrophy of the mucosa is observed, less often – hyperplasia, the formation of polyps. Against the background of prolonged chronic inflammation, scars form, tissue fibrosis develops, and petrification of the organ occurs.
Clinical varieties of the disease are systematized taking into account the dynamics of development and course of the pathological process. Depending on the underlying cause, acute and chronic forms of the disease are distinguished.
Varieties of chronic calculous cholecystitis:
Primary chronic inflammatory process. Dyspeptic disorders slowly increase, the pain is mild. Pathology is often disguised as other disorders in the functioning of the digestive system.
Chronic relapsing process. The disease is characterized by alternating stages of remission and exacerbation, severe pain.
Chronic residual cholecystitis. A consequence of an acute inflammatory process with improper treatment. Accompanied by chronic pain, the development of negative consequences.
Accompanied by chronic pain, the development of negative consequences.
Acute calculous cholecystitis is differentiated according to the severity of the inflammatory process – phlegmonous, catarrhal, gangrenous.
Depending on the number of attacks, a mild course of the disease is distinguished – no more than three colic per year, moderate – attacks occur up to two times a month. In severe cases, more than three relapses occur monthly.
One of the main clinical manifestations of calculous cholecystitis is pain. Biliary colic is an attack of sharp, unbearable pain in the epigastric region with a shift towards the gallbladder. Sometimes discomfort is given to the back, chest. An attack occurs during an acute course of the disease, exacerbation of the chronic form, after stress, with errors in nutrition. Lasts several hours.
Additional features:
increase in body temperature to subfebrile marks;
increased sweating;
skin becomes pale;
worried about severe nausea, frequent vomiting, there are bile impurities in the masses;
with obstructive jaundice, the skin and sclera acquire a yellow tint, severe itching bothers, the stool brightens, the urine darkens.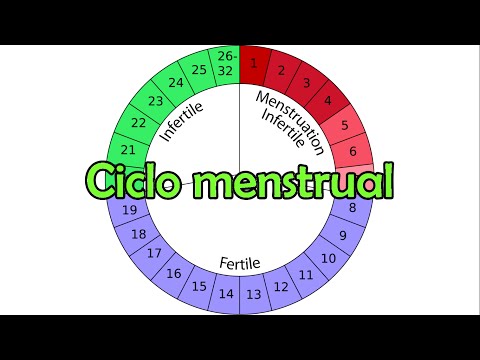
In chronic course, the pain is dull, aching, disturbs periodically, localized under the right ribs. There is nausea and vomiting, a bitter taste in the mouth, constipation alternating with diarrhea, flatulence. Symptoms appear after the consumption of fats in large quantities, in women – before the onset of menstruation. With a long course of the disease, irritability, sleep problems, and increased fatigue appear.
Without proper and timely treatment, dangerous complications develop against the background of calculous cholecystitis:
accumulation of pus in the cavity of the gallbladder – treatment is carried out only by surgical methods;
reactive hepatitis;
acute cholangitis, pancreatitis, secondary biliary cirrhosis;
inflammation of the serous membrane of the gallbladder – the disease is accompanied by constant severe pain;
violation of the integrity of the organ wall leads to the development of bile peritonitis;
sepsis;
the formation of vesico-intestinal fistulas against the background of necrosis, ischemia;
damage to brain tissue due to severe intoxication;
reduction of the cavity of the gallbladder – in 5-7% of patients leads to the formation of a cancerous tumor;
inflammation of hypertrophied anal papillae;
hepatitis, pancreatitis.
If there are signs of calculous cholecystitis, you should visit a gastroenterologist or hepatologist. The doctor collects an anamnesis, fixes the characteristic clinical manifestations during an external examination.
To confirm the diagnosis, assess the severity of the pathological process:
Gallbladder sonography. An ultrasound examination can detect stones larger than 2 mm, reveal a thickening of the walls of the organ, and see the accumulation of fluid around the gallbladder.
X-ray of the abdominal cavity. Carried out to identify complications – the presence of gas in the lumen of the bladder, diffuse calcification of the walls of the organ.
CT scan of the abdomen. Used to clarify the diagnosis, if other methods are uninformative. During the study, the thickness of the walls of the organ, the presence of edema are determined, the presence of signs of inflammation, mucosal rejection is detected.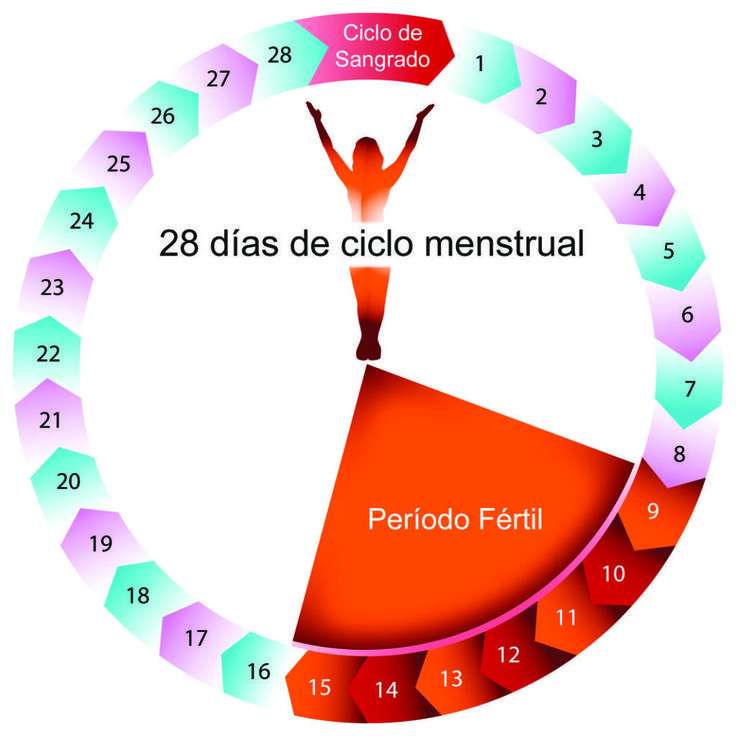
Dynamic scintigraphy of the organs of the hepatobiliary system. Assign to assess the motor-evacuation function. The information content of the method is more than 95%.
Retrograde cholangiopancreatography. X-ray with endoscopy is prescribed to assess the condition of the biliary tract, to identify small stones that were not shown by ultrasound. For medicinal purposes, it is used to remove stones from the bile duct.
Complete blood count. During an exacerbation of the disease, the leukocyte formula shifts to the left, and the ESR rises.
Biochemical blood test. Increased levels of total cholesterol, alkaline phosphatase.
In addition, your doctor may prescribe gastroduodenoscopy to confirm or exclude diseases of the stomach or duodenum.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with chronic and acute cholecystitis, cholesterosis, diseases of the liver, pancreas.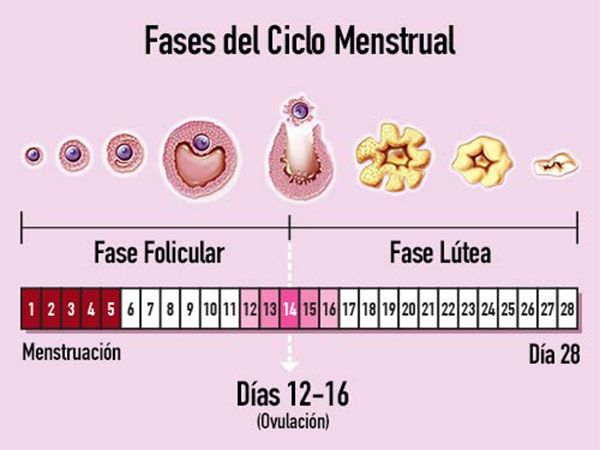 Exclude renal colic on the right side, cardiovascular pathology.
Exclude renal colic on the right side, cardiovascular pathology.
In calculous cholecystitis, conservative therapies are used to treat the chronic form of the disease.
Drug groups:
antispasmodics or anticholinergics;
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
antibiotics to which the opportunistic intestinal microflora is sensitive are usually prescribed a combination of two drugs;
drugs for dissolving stones – used if the stones are cholesterol, the size is not more than 5 mm, the stones are not more than 3 years old, the patient is not obese.
In case of severe intoxication, detoxification therapy is carried out, enzymes and antiemetics are prescribed. After stabilization of the condition, the gallbladder is removed using endoscopic equipment, open or laparoscopic method. Crushing of stones in the cavity of the gallbladder is rarely performed, only if there are strict contraindications to the operation.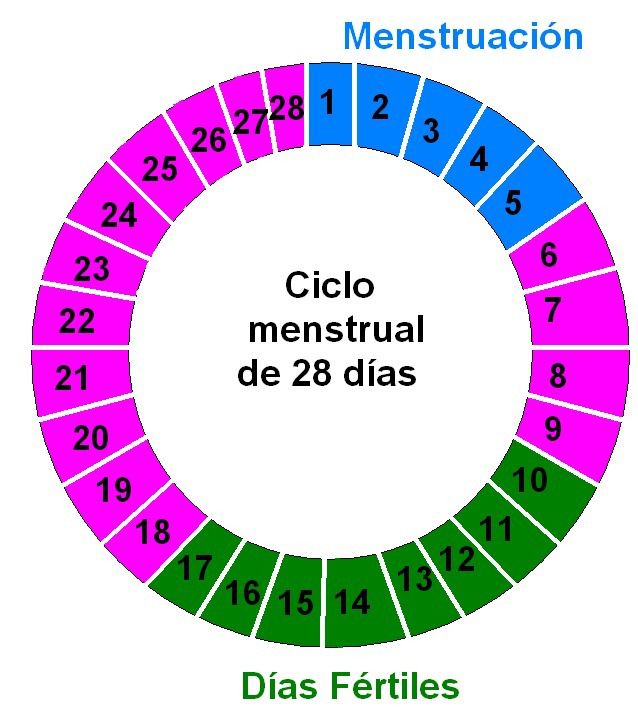
Acute calculous cholecystitis requires urgent surgery. After hospitalization, an examination is carried out, the patient is prepared for laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Intervention must be performed within 72 hours of the onset of an attack. This greatly reduces the risk of death and the development of severe complications.
Elderly patients with severe cholecystitis with complications undergo percutaneous cholecystectomy. Then antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
The gallbladder is not a vital organ. After removal, the quality of life changes slightly. But you have to constantly adhere to a special diet. 2 weeks after the operation, a control biochemical blood test is done. The duration of rehabilitation after laparoscopy is 4-5 weeks, after open surgery – 2.5-3 months.
Diet therapy is an essential component in the treatment of cholecystitis. With an exacerbation of the chronic form of the pathology, fasting is indicated on the first day, you can drink water, weak tea with chamomile, mint, compote, jelly, natural juices, half diluted with water.
Then for 3-4 days you can eat pureed porridge made from rice, oatmeal and semolina, light vegetable soups. Portions should be small, drinking plentiful. It is better to drink jelly from ripe sweet fruits, mineral water without gas, diluted with ordinary purified water.
During an exacerbation, the diet is expanded as well-being improves, this usually occurs on the 7-8th day of diet therapy. To avoid a new attack, it is necessary to exclude from the diet spicy, fatty, spicy foods, smoked meats, canned food and uncleaned first courses. Prohibited foods include legumes, pearl barley and millet groats, mushrooms, chocolate, pastries, and alcohol. These restrictions also apply to nutrition in the chronic form of pathology.
In the chronic form of the disease, it is necessary to consume a sufficient amount of protein – 1.5 g / kg. Reduce the amount of carbohydrates to 4 g / kg, fat – 1 g / kg.
Useful products:
Nutrition in any form of cholecystitis must be fractional – 5-6 times a day strictly by the hour. This will help to avoid stagnation of bile, reduce pain, improve digestion. The calorie content of the daily diet is 2000 kilocalories. It is useful to do a fasting day once a week on fermented milk products or pureed berries, vegetables, fruits.
This will help to avoid stagnation of bile, reduce pain, improve digestion. The calorie content of the daily diet is 2000 kilocalories. It is useful to do a fasting day once a week on fermented milk products or pureed berries, vegetables, fruits.
After removal of the gallbladder, you need to eat 6-7 times a day. In the first months after the operation, you can only eat mashed, steamed or boiled dishes. Expand the diet gradually, introduce animal protein, seasonal vegetables and fruits. You need to exclude fats, complex carbohydrates, alcohol, smoked meats and canned food.
To avoid the development of the disease, it is necessary to prevent the formation of stones.
Basic prevention methods:
correct, balanced, fractional nutrition;
regular moderate exercise;
compliance with the drinking regime;
do not take drugs that promote the formation of stones, unless prescribed by a doctor.