El acoso escolar es una forma de comportamiento persistente de una persona, en posición de poder, que hiere o reprime a otro individuo, con la intención de infringir daño físico o emocional.
El acoso o bullying (en inglés) puede ocurrir en cualquier lugar. Sin embargo, el hostigamiento en las escuelas es muy crítico. El Centro Nacional de Estadísticas de Educación (National Center for Educaction Statistics en inglés) reportó que, en el año 2017, 20% de los estudiantes entre 12 y 18 años fueron víctimas de acoso escolar durante el año.
Para que un comportamiento sea calificado como acoso escolar debe ser un acto:
El acoso en las escuelas le puede pasar a cualquier niño, pero se ha determinado que hay grupos de alto riesgo. Pero, aun así, el hostigamiento no es justificado y la ley protege a todos por igual.
Considere una posible situación de acoso si nota en su hijo:
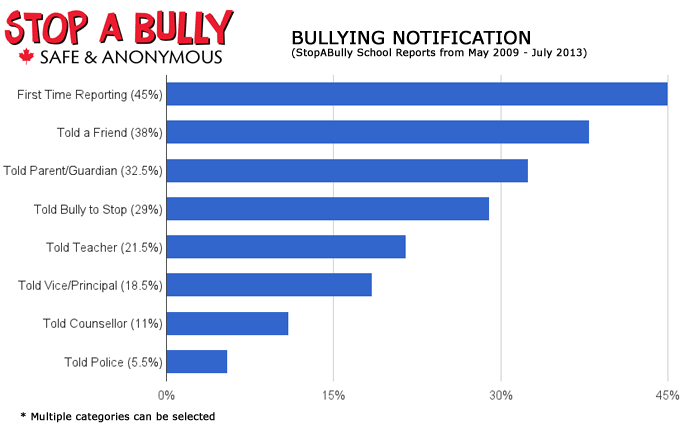
Existen varias formas para hostigar, estas son los más comunes en las escuelas:
 Incluye golpes, heridas, patadas, empujones, escupitajos, etc.
Incluye golpes, heridas, patadas, empujones, escupitajos, etc.En los últimos años el ciberacoso o cyberbullying ha estado en aumento (en inglés) y es la forma más agresiva de hostigamiento entre la población de 12 a 18 años.
El cyberbullying involucra compartir y distribuir información negativa o personal que puede hacer daño a la reputación e integridad del niño acosado.
Además, el acoso cibernético es muy peligroso porque se utiliza como un medio de presión para obtener algo del niño, y en ocasiones deriva en otros tipos de delitos, como tráfico de drogas, abuso sexual o robo, ya que la víctima de las situaciones de acoso es obligada a hacer cosas que no desea a cambio de que su información personal no se haga pública.
Las leyes que rigen los casos de acoso en las escuelas son diferentes en cada estado. Pero, todos los distritos escolares tienen la obligación de proteger a los estudiantes del hostigamiento, y deben manejar estos asuntos siempre que ocurren en los centros educativos.
Los distritos escolares están requeridos por la ley federal a reportar al Departamento de Educación cada incidente de acoso o cyberbullying para incluirlo luego en el banco de información de Civil Rights Data Collection.
Y si un estado no posee leyes específicas con respecto al acoso en las escuelas, de igual forma una persona afectada está protegida, porque de acuerdo con la ley federal de derechos civiles, ninguna persona puede ser maltratada o discriminada por su raza, color, origen nacional, orientación sexual, dificultad física o religión.
Si sospecha que su hijo es acosado en el entorno escolar consulte qué dice la ley en su estado (en inglés) y verifique cuáles son sus derechos. Las escuelas están obligadas a tener una política y un manual sobre cómo actuar en caso de acoso escolar y además deben demostrar eficiencia y esfuerzo para resolver un problema de este tipo. Si no, entonces la escuela podría estar actuando de manera negligente.
Las demandas por acoso o violencia escolar son posibles en algunos casos. Por ejemplo, si su hijo sufre una herida o daño físico causado por otro niño, debido a una situación de acoso, se puede presentar una demanda en contra de los padres de ese niño por daños físicos a su hijo. Pero, presentar una demanda contra la escuela por un caso de acoso es más complicado.
No todos los incidentes de bullying en las escuelas son susceptibles a una demanda y además son difíciles de consolidar. Las escuelas públicas están amparadas por una figura legal llamada inmunidad soberana o “sovereign immunity” (en inglés). Esto significa que cualquier oficina o departamento público del gobierno no puede ser demandado sin permiso, salvo en casos cuando la escuela haya actuado con absoluta indiferencia. Además, hay leyes estatales y federales que regulan esta figura legal.
Esto significa que cualquier oficina o departamento público del gobierno no puede ser demandado sin permiso, salvo en casos cuando la escuela haya actuado con absoluta indiferencia. Además, hay leyes estatales y federales que regulan esta figura legal.
Por lo tanto, si luego de consultar que dice la ley en su estado, usted determina que la escuela actuó con negligencia absoluta en una situación de acoso escolar, o tomó en cuenta el problema y su hijo fue discriminado, es posible que una demanda siga su curso.
Muy conocido es el proceso de Vance v. Spencer County Public School District (en inglés). En cualquier caso, un abogado con amplia experiencia en casos de derechos civiles le puede orientar y respaldar su reclamo.
Este artículo pretende ser útil e informativo, pero los asuntos legales pueden llegar a ser complicados y estresantes. Un abogado calificado en derechos civiles puede atender a sus necesidades legales particulares, explicar la ley y representarlo en la corte. Dé el primer paso ahora y póngase en contacto con un abogado calificado en derechos civiles cerca suyo para hablar sobre su situación jurídica particular.
Un abogado calificado en derechos civiles puede atender a sus necesidades legales particulares, explicar la ley y representarlo en la corte. Dé el primer paso ahora y póngase en contacto con un abogado calificado en derechos civiles cerca suyo para hablar sobre su situación jurídica particular.
Ingrese su lugar para conectarse con un abogado de Derechos civiles calificado hoy.
Para muchos jóvenes que se identifican como lesbianas, gays, bisexuales, transexuales y transgénero (LGBTT), o aquellos percibidos como tal y sus amigos, el acoso escolar es una realidad muy seria. Pero no significa que no lo puedas evitar o parar.
Tienes el derecho de ser quien eres y de sentirte seguro. Te presentamos una guía rápida de los pasos a seguir si tú o alguno de tus amigos sufren debido al bullying o acoso escolar.
Habla con alguien en quien confías: amigos, padre o madre, hermano o hermana. Avisa a otras personas.
Avisa a otras personas.
Desarrolla un plan de seguridad: identifica una nueva ruta para regresar a tu casa después de la escuela. Pídele a alguien que te lleve en carro a tu casa. Y asegúrate de tener un teléfono celular o dinero para hacer llamadas de emergencia.
Apunta lo que te está sucediendo: incluye detalles de qué fue exactamente lo que pasó, quién estuvo involucrado, dónde y cuándo ocurrió el incidente, y si hubo o no testigos.
Habla con el director o principal de la escuela: los orientadores y maestros no siempre tienen la obligación legal de tomar acción en contra del acoso escolar. Pero el principal o director tiene una mayor responsabilidad. Presenta informes y denuncias por escrito, y guarda copias de todos y cada uno de los documentos que entregues y recibas.
Presenta tu queja a un nivel más alto. Si el principal de tu escuela no responde lo suficientemente rápido, presenta tu queja formal al superintendente o al consejo escolar.
Identifica si tu escuela tiene un procedimiento de denuncias. Muchas escuelas públicas reciben fondos federales. Si la tuya es una de estas, la ley federal la obliga a contar con un procedimiento para hacer denuncias (quejas formales).
Avisa a la policía. Las amenazas serias y la agresión física van en contra de la ley. Si ocurren, no dudes en poner una denuncia con la policía.
Haz una denuncia anónima. Si sientes que al identificarte te estás poniendo en riesgo, manda una queja anónima al principal. De esta manera se podría encontrar a los hostigadores particulares en tu escuela, o describir de manera más general el problema de hostigamiento de tu escuela. Por otra lado, pídele a una persona adulta de confianza, como un orientador, que le comunique al director, sin usar tu nombre, que el acoso escolar es un problema real en la escuela. Muchas escuelas tienen procedimientos para dar quejas de forma anónima. Siempre guarda copias de las denuncias que tú mismo hayas presentado o que alguien más haya presentado en tu nombre. No obstante, ten presente que la escuela probablemente tenga la obligación legal de protegerte si los administradores saben que eres víctima de maltrato.
Siempre guarda copias de las denuncias que tú mismo hayas presentado o que alguien más haya presentado en tu nombre. No obstante, ten presente que la escuela probablemente tenga la obligación legal de protegerte si los administradores saben que eres víctima de maltrato.
Denuncia el bullying o acoso escolar aun y cuando no sepas quiénes son los acosadores. Es importante que el director de tu escuela sepa que el acoso escolar existe, aun si no eres capaz de identificar quién lo hizo. Como siempre, debes presentar quejas por escrito y guardar una copia. Cuando la ayuda que te han dado en realidad no sea útil, comunícalo.
No te des por vencido si los intentos de tu escuela de parar el acoso escolar no sirven de nada. Habla con el principal sobre distintas opciones para resolver el problema.
Contacta a Lambda Legal si tu escuela no te da una respuesta útil al 866-542-8336 o utiliza nuestro formulario para mandarnos un correo electrónico disponible en www.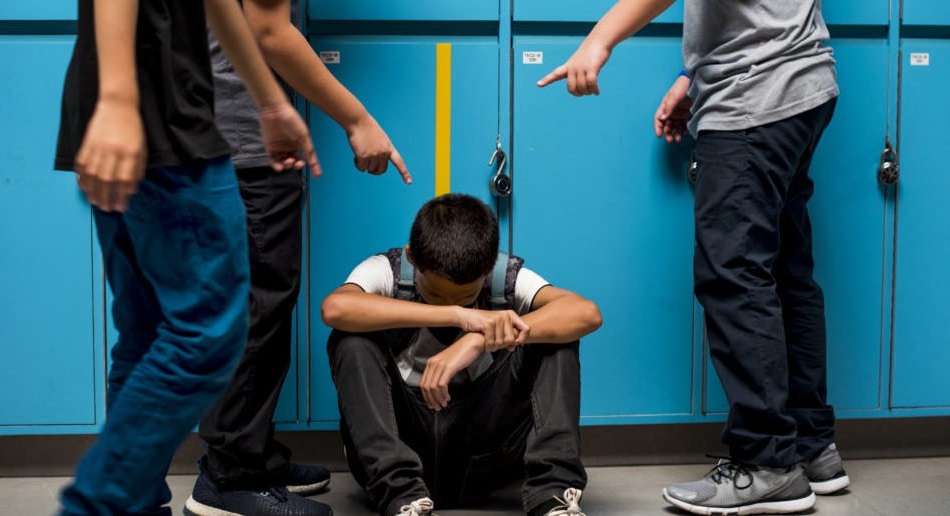 lambdalegal.org/es/linea-de-ayuda. A través de este enlace puedes conocer las distintas formas en las que Lambda Legal ha ayudado a estudiantes que han sufrido de acoso escolar.
lambdalegal.org/es/linea-de-ayuda. A través de este enlace puedes conocer las distintas formas en las que Lambda Legal ha ayudado a estudiantes que han sufrido de acoso escolar.
The Fund staff joined forces with experts, as well as representatives of social networks – Facebook, Instagram and Twitter. They encouraged teenagers around the world to ask questions about online bullying, its consequences and how to counter it.
So, the 10 most common questions about cyberbullying that interest children and the answers to them.
Friends often play good jokes on each other. But sometimes it can be difficult to tell if a person is joking or intentionally trying to hurt you. People sometimes make nasty comments about us, and then brush them off and say: “Come on, I was just joking”, “It’s just a joke”, “You take everything too personally”.
If you feel uncomfortable, hurt, and people are clearly laughing not with you, but at you, then things have gone too far. If you tell them about your feelings and ask them to stop bullying, but they continue in the same spirit, this is already bullying. You should not put up with this – it is better to immediately seek help.
Cyberbullying has many serious consequences. Bullying can negatively affect a person’s emotional state. You may constantly feel depressed, upset, feel ashamed, or lose interest in things that normally give you pleasure.
In some cases, the emotional state begins to affect the physical – you can lose your appetite, sleep poorly, feel tired, experience headaches. In rare cases, cyberbullying can even lead to suicide.
If you feel like you’re being bullied, the first thing you should do is turn to an adult you really trust – your parents or another relative with whom you have a close relationship.
At school you can talk to your favorite teacher, coach or psychologist.
If for some reason you don’t want to talk to anyone you know personally, you can seek professional help – find a helpline for children and teenagers on the Internet. Typically, such phones work around the clock, calls are answered by experienced psychologists who have been dealing with such issues for many years.
If you think you are in danger right now, call the police immediately.
It would also be good to collect “evidence” – save text messages and take photos of posts or comments on social networks that you think are offensive and degrading.
Do not forget about the possibility to complain about the bullying directly to the employees of social networks. Here you can find information on how to ask for help on the Facebook platform. Twitter has a similar service.
Relationships with parents are different for everyone, but it is very important to start such a conversation. It is better to choose a time that is convenient for everyone, when the parents are not busy, are not in a hurry and can listen to you calmly. Try to explain to them that this is a very serious problem for you. Most likely, your parents will want and try to help you.
It is better to choose a time that is convenient for everyone, when the parents are not busy, are not in a hurry and can listen to you calmly. Try to explain to them that this is a very serious problem for you. Most likely, your parents will want and try to help you.
Keep in mind that your parents may know much less about social media than you do. They may need further clarification on this topic.
Any person needs support. To begin with, try to just bring to the conversation and listen to your friend or girlfriend. How does this person feel? Does he want to report what is happening to one of the adults, ask for help? If not, why not?
Offer to go to the adults together. If the person continues to refuse, try to find an adult you can trust and ask for help. Inaction can lead to catastrophic consequences.
Of course, it is impossible to stop using the Internet. And you don’t need to – there is a lot of useful information and resources there. However, you can block certain “friends” in social networks, delete individual applications and programs, or go offline for a while, giving yourself the opportunity to take a break from the Internet.
And you don’t need to – there is a lot of useful information and resources there. However, you can block certain “friends” in social networks, delete individual applications and programs, or go offline for a while, giving yourself the opportunity to take a break from the Internet.
It is also important to work together to create an Internet that will be comfortable for everyone. Therefore, you should always monitor your behavior – be polite and show respect for other users.
To begin with, it is very important to think about what and why you post on social networks and who sees your posts. Social networks have settings that allow you to control the situation: you can limit the circle of people who see this or that publication or your entire account in general, block comments of individual users, turn off the “share” function, protect photos from downloading, and use a host of other tools.
It is important to remember that information posted on the Internet, even if it is removed from the personal page, can be stored on the server for a long time. Never publicly post your home address, phone number, or school number.
Many schools have measures against bullying. If you are being bullied by classmates or someone from your school, report it to the teachers. The guilty must be punished.
Unfortunately, many countries do not yet have laws regarding bullying, and especially cyberbullying, as this is a relatively new phenomenon. When the need arises to bring perpetrators to justice, laws dealing with similar phenomena, such as harassment, are usually invoked.
There are certain rules and standards of behavior in social networks, and those who violate them can be complained about, as already mentioned in paragraph 3. Social network teams will take the necessary measures, up to the complete blocking of users.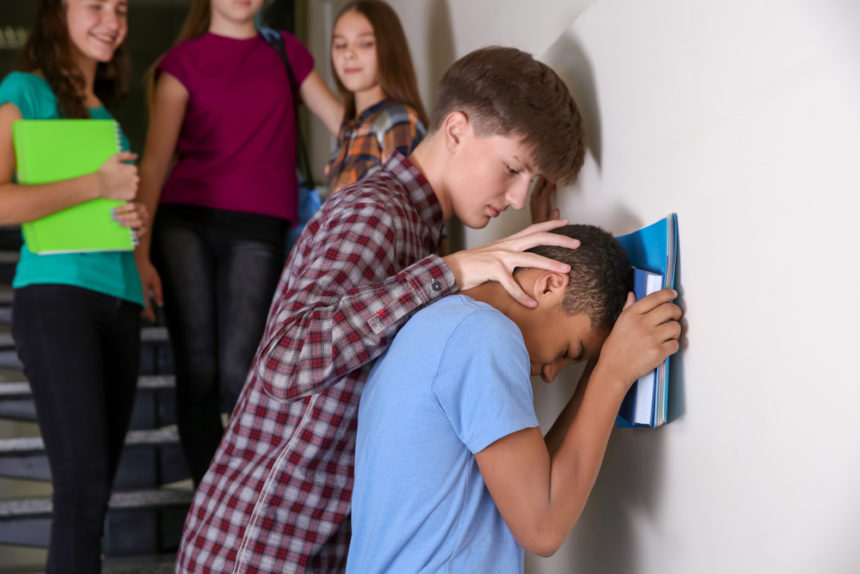
Internet companies are paying more and more attention to this phenomenon and creating appropriate tools, as already mentioned above. However, online platforms must do more to combat bullying, and users must constantly remind them of this by reporting violations and demanding action.
As mentioned above, each social network has certain mechanisms that allow you to report cases of bullying and bullying. Read more about this in paragraph 3.
Komsomolskaya Pravda
WorldwideUkrainian crisis: News
Oleksandr GRISHIN
June 2, 2022 18:43
Switzerland will deprive Ukrainian refugees of privileged status in case of a long absence in the theater of Karabas-Barabas, excuse me, another victory arrived in time for Ukrainian refugees in Europe. And again from the series “friendship is friendship, but you shouldn’t confuse your wool with the state one”.
And again from the series “friendship is friendship, but you shouldn’t confuse your wool with the state one”.
Ukrainian refugees in various European countries begin to slurp their pack of “happiness” with a full spoon. The authorities of Prague announced that from June 15 they will stop accepting Ukrainian refugees. The city no longer has any reserves to provide them with housing, medical care and other types of social support. Even the current amount of available finance is not enough.
The Swiss authorities also began to cheer. They became concerned that many Ukrainian refugees return to their homeland too often and for too long. And the Swiss do not understand why they do it. Moreover, it is not a fact that Ukrainians really go to their abandoned places of residence, and do not register, for example, in Slovakia or Germany in order to receive another allowance there. Since affectionate Ukrainian calves can suck not only two, but countless queens. In general, some kind of muddy topic, they believe in Switzerland, and therefore the Swiss State Secretariat for Migration reported that those refugees from Ukraine who are unable to leave their native land for a long time will be deprived of a special privileged status.
In Poland, Ukrainians, in their opinion, are simply mocked for lawlessness. It would seem that the brotherly people, as the presidents of both countries say, Duda and Zelensky hugged and kissed so much that they had to squeeze out all the bibs. And come on, from July 1, almost all refugees, with the exception of pregnant women, large families and the disabled, will cancel the payment of benefits. Eat, as they say, how and where you want. The deputy head of the Polish Ministry of Internal Affairs has already officially stated that most of the Ukrainian refugees will lose their daily allowances, which, according to the Poles themselves, is quite fair, because Poland is full of Ukrainian migrant workers who ensure their own well-being with their hump. And even their families are sent to live in Nezalezhnaya.
The authorities want to encourage Ukrainians to start looking for a job, start earning and providing for themselves. Polish enterprises, as stated in the analytical center of the employment agency Gremi Personal, have already begun to offer Ukrainian refugees “male jobs”.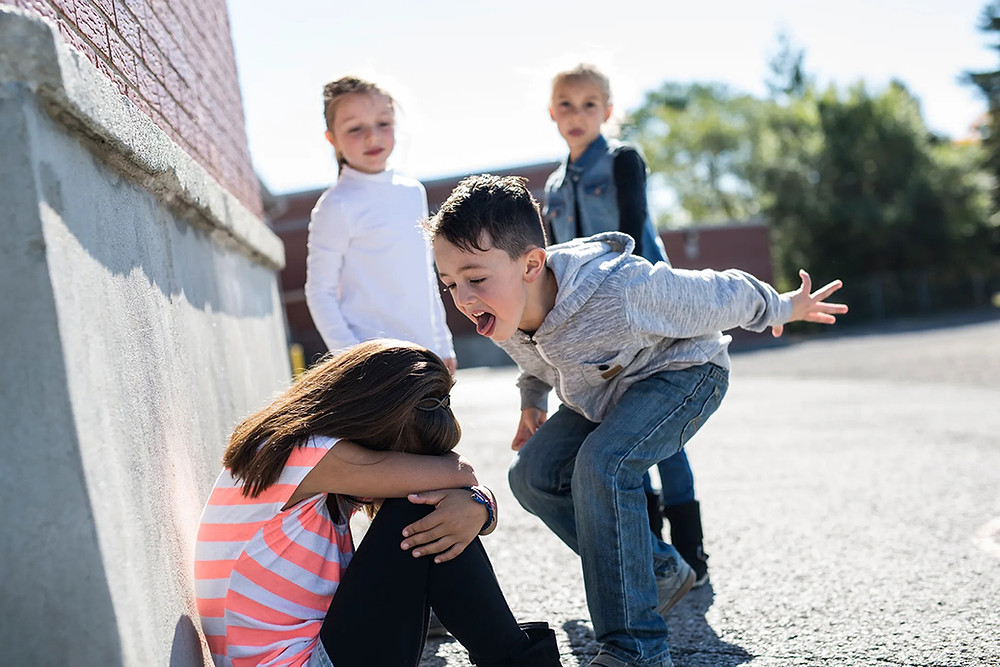
It’s time, in a word, to either start working in the new Motherland, or return to the old one. They didn’t promise to feed them all their lives, the Poles cynically tease Ukrainians, and four months should be quite enough to find their bearings in a new place. The status of “sufferers” among the “parasites” will no longer work.
But, if you read Ukrainian social networks, then even the Poles did not stand next to the meanness of the Bulgarians. The Bulgarian authorities had the audacity to stop the residence of Ukrainian refugees in resort hotels on the sea coast. First, they offered two hundred refugees to take them inland. but the Ukrainians are not fools for you. Who, of their own free will, will change the hotel on the sea for it is not clear that without the sea. Therefore, they formally agreed, but when buses arrived at the hotels to transport them, only five refugees out of more than two hundred came out to them. The Ukrainians began to celebrate the victory over the primitive Bulgarians, but even the Ukrainians could not foresee what would follow. ..
..
One fine (in fact, of course, terrible) morning, buses again drove up to the hotels and gave the unsuspecting refugees a short time to pack. After that, they were taken to a real filtration camp, where they settled to live in sea containers converted into rooms. And now they live in a completely closed area, along the perimeter of which both sides of the fence are decorated with coils of barbed wire.
And all that the Ukrainians could do in such a situation was to write on the walls of the rooms they leave the call “Glory to Ukraine!”
And since paints and felt-tip pens were taken from them, they had to write these slogans with their own feces. Let these Bulgarians choke! And let them know what Ukrainian inflexibility is, with whom they contacted and whom they insulted.
Age category of the site 18+
Online publication (website) registered by Roskomnadzor, certificate El No. FS77-80505 dated March 15, 2021
I.O. EDITOR-IN-CHIEF – NOSOVA OLESIA VYACHESLAVOVNA.