El peso de la madre es un factor importante a considerar antes de concebir. Si hay sobrepeso lo más indicado es hacer una dieta para perder peso antes de quedarse embarazada. La mujer debería empezar su embarazo con un peso correcto y estando bien nutrida. Es aconsejable realizar una revisión ginecológica y explicar al médico las intenciones que tenemos.
En cuanto a la dieta lo ideal es llevar una alimentación variada y equilibrada. Lo único a tener en cuenta previamente es el ácido fólico o vitamina B9. Con la alimentación de la sociedad actual es frecuente hacer un déficit de esta vitamina, por esta razón siempre se aconseja tomarla en forma de complemento alimenticio meses antes de quedarse embarazada. Les necesidades diarias de ácido fólico son de 200 µg y durante el embarazo aumentan hasta un total de 400 µg al día. Un déficit de vitamina B9 en las primeras semanas de embarazo puede provocar malformaciones en el feto, como la espina bífida.
En el momento en que una mujer se queda embarazada uno de los cambios importantes es el enlentecimiento de la digestión. El objetivo de esto es que el alimento permanezca durante más tiempo en el intestino y, en consecuencia, la absorción de nutrientes sea mayor.
La ganancia de peso durante los primeros tres meses debe ser de entre 0,5 kg. y 1,5 kg. de peso. Esta ganancia de peso es muy pequeña ya que el feto tan sólo alcanza unos 16 cm de tamaño.
Nutrientes a tener en cuenta durante la primera etapa del embarazo:

A partir del cuarto mes de embarazo empieza aumentar el requerimiento energético y calórico de la futura madre. El peso que se recomienda ganar durante el segundo trimestre del embarazo es de 3,5 a 4 kg, y durante el último trimestre del embarazo es de 5 a 5,5 kg de peso.
El peso que se recomienda ganar durante el segundo trimestre del embarazo es de 3,5 a 4 kg, y durante el último trimestre del embarazo es de 5 a 5,5 kg de peso.
Recomendaciones que hay que tener en cuenta:
 Por esta razón el consumo de hierro es muy importante. Los principales alimentos que lo contienen son las carnes rojas, los mejillones, el huevo, el pescado y las legumbres. Aunque se consuman alimentos ricos en hierro normalmente no es suficiente para combatir la anemia y lo más indicado es tomar suplementos alimenticios. Para combatir la anemia ferropénica también es necesario ingerir cantidad suficiente de vitamina B12 (presente en la carne, el pescado, los huevos y los lácteos) y ácido fólico (presente en los espárragos, las espinacas, los guisantes, la col, los frutos secos, el huevo y la carne). Tomar diariamente alimentos ricos en vitamina C también ayudará a una mejor asimilación del hierro de la dieta.
Por esta razón el consumo de hierro es muy importante. Los principales alimentos que lo contienen son las carnes rojas, los mejillones, el huevo, el pescado y las legumbres. Aunque se consuman alimentos ricos en hierro normalmente no es suficiente para combatir la anemia y lo más indicado es tomar suplementos alimenticios. Para combatir la anemia ferropénica también es necesario ingerir cantidad suficiente de vitamina B12 (presente en la carne, el pescado, los huevos y los lácteos) y ácido fólico (presente en los espárragos, las espinacas, los guisantes, la col, los frutos secos, el huevo y la carne). Tomar diariamente alimentos ricos en vitamina C también ayudará a una mejor asimilación del hierro de la dieta.Mareos: Son frecuentes durante todo el embarazo, sobretodo por las mañanas. Empeoran cuando hay bajadas de tensión o de los niveles de azúcar en sangre. ¿Qué hacer?
Empeoran cuando hay bajadas de tensión o de los niveles de azúcar en sangre. ¿Qué hacer?
Náuseas y vómitos: Para combatir las náuseas y los vómitos se deben seguir las mismas recomendaciones que para los mareos. Si aun así persisten:

Acidez o reflujo: Normalmente estas molestias aparecen los últimos meses de gestación, cuando el tamaño del feto es mayor y empieza a comprimir el estómago. Consejos para mejorar:

Estreñimiento: Es muy frecuente a partir del segundo trimestre del embarazo. No es aconsejable el uso de laxantes en embarazadas pero si se pueden administrar supositorios de glicerina y suplementos de fibra. Recomendaciones dietéticas:
Calambres musculares: Se pueden padecer calambres musculares a partir del segundo mes de embarazo. Una dieta saludable para embarazadas para ayudar a combatirlos debe contener:

Insomnio: Suele ocurrir hacia el final del embarazo. Recomendaciones:
El pescado, además de ser rico en proteínas, nos aporta grasas muy relevantes para el desarrollo del feto como los aceites omega 6 y omega 3. Pero por otra parte, debido a la contaminación de los océanos, estos peces acumulan niveles de mercurio que varían de forma notable según la especie.
Los peces más grandes que tardan más tiempo en crecer y que se alimentan de otros más pequeños, son los que acumulan una mayor concentración de mercurio. Por otra parte, los peces criados en aguas más limpias (pescados de río), los de menor tamaño o aquellos criados en piscifactorías, son los que menos mercurio tienen y son perfectos para consumirlos durante el embarazo.
Por otra parte, los peces criados en aguas más limpias (pescados de río), los de menor tamaño o aquellos criados en piscifactorías, son los que menos mercurio tienen y son perfectos para consumirlos durante el embarazo.
En las mujeres que están en edad reproductiva y, especialmente, aquellas que se encuentran embarazadas o están amamantando, las recomendaciones son el consumo de 2-3 porciones de pescado (o marisco) semanales (del tamaño aproximado de la palma de una mano), de las siguientes especies de pescados: boquerón o anchoa, sardina, corvina, caballa, róbalo, palometa, salmón, calamar, almeja, camarón, raya, pejerrey, eglefino, merluza, arenque, tilapia, lisa o pargo, ostra, lucio, vieira, lacha, lenguado, cangrejo de río, perca, bacalao, cangrejo, platija o lenguado, gado o abadejo, trucha, atún enlatado claro (incluye el bonito), en general el pescado blanco y el estornino del Pacífico.
También se recomienda el consumo de una porción de pescado cada semana de las siguientes especies (de mayor tamaño y con mayor presencia de omega 6): lutjánido o pargo, gallineta o pescado de roca, caballa española, rape, halibut o fletán, dorado/pez delfín, bacalao negro, perca rayada (de mar), blanquillo o lofolátilo, atún o albacora/blanco enlatado y fresco/congelado, chopa, carpa, mero, corvinata real/trucha de mar, corvina blanca/Corvina del Pacífico, bagre búfalo (o bagre boca chica) y perca de mar chilena/Merluza negra.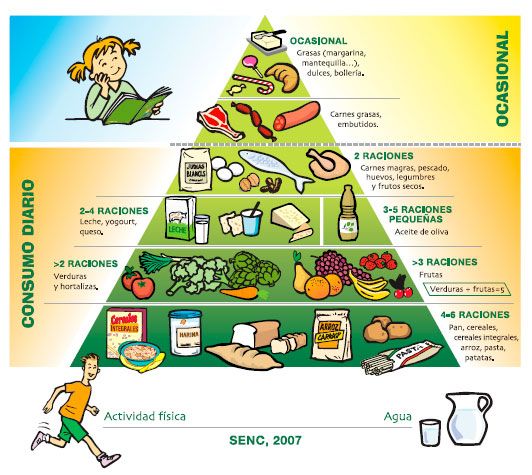
Por último, los pescados más grandes y cuyo consumo debe ser realizado de forma puntual (no incorporado a nuestra dieta semanal), son las especies de macarela rey o caballa, reloj anaranjado, raya o pez emperador, aguja, tiburón blanquillo o lofolátilo (Golfo de México), atún de ojos grandes o patudo, pez espada.
Si sigues estas recomendaciones de consumo de pescado durante el embarazo y lactancia evitarás cualquier riesgo para tu salud y la de tu hijo.
Toma de pliegues
La consulta del dietista – nutricionista es una buena opción para llevar un buen control del embarazo. La realización de una dieta saludable para embarazadas personalizada ayuda a mejorar las molestias del embarazo y a poder hacer un buen control del peso. Una de las herramientas que utilizamos en Alimmenta es la medición del pliegue tricipital y la circunferencia del brazo derecho. Si las medidas se mantienen constantes significará que no se está engordando y que la ganancia de peso que se produce es correcta. Si por el contrario las medidas disminuyen o aumentan significará que la mujer está adelgazando o ganando más peso de lo recomendado. En estos casos es importante corregir la dieta.
Si por el contrario las medidas disminuyen o aumentan significará que la mujer está adelgazando o ganando más peso de lo recomendado. En estos casos es importante corregir la dieta.
El equipo de dietistas – nutricionistas para embarazadas de Alimmenta pueden acompañarte durante esta etapa tan bonita para que te sientas más segura y tranquila.
Durante el embarazo surgen muchas dudas y preguntas, algunas de ellas relacionadas con la comida. Y es que es una etapa de la vida en la que comer bien, sano y saludable ha de ser una máxima.
La buena alimentación en el embarazo, dará el suficiente aporte de energía a la embarazada y ayudará a que el bebé crezca y se desarrolle sin correctamente.
El embarazo es un estupendo momento para adoptar hábitos alimenticios sanos si hasta el momento no se tienen, por ello os proponemos un menú para cada una de las semanas del embarazo.
Estos menús han sido elaborados por Cristina Abascal, nuestra experta nutricionista y tratan de mantener el equilibrio en la ingesta de los diferentes grupos de alimentos.
Cómo verás nuestros menús están basados en la idea de que la embarazada ha de realizar 5 comidas al día: desayuno, media mañana, comida, merienda y cena. En cualquier caso, antes de cocinar cualquiera de las recetas que te proponemos conviene que leas estos consejos:
– Es conveniente que no comas alimentos crudos o poco cocinados, sobre todo si has dado negativo a la prueba de la toxoplasmosis.
– Has de lavar muy bien los utensilios de cocina así como los alimentos que consumes.
– Evita los quesos no pasteurizados y los patés.
– Intenta comer al menos una pieza de fruta al día.
– Mantente siempre hidratada y, aunque no es necesario obligarse a beber agua sin sed, si conviene no beber menos de un litro de agua al día.
Durante el embarazo, la mujer no solo debe seguir una dieta adecuada basada en alimentos naturales, sino que deben evitar por lo menos 5 alimentos.
1. Quesos con moho, como es el caso de queso gorgonzola, roquefort, además del queso brie , el camembert y el chevre, por su baja acidez y su gran humedad, que favorece el cultivo para bacterias malas.
2. Carnes crudas o poco cocidas. La carne en esas condiciones no está indicada por el riesgo de contraer toxoplasmosis, una infección provocada por un parásito que se encuentra en la carne que puede producir ceguera, epilepsia o retraso menta al bebé. La carne o paté de hígado también está contraindicada.
3. Huevos. Durante el embarazo no es recomendable consumir huevos crudos ni ligeramente cocidos porque pueden estar contaminados con salmonela.
4. Pescado azul. El atún rojo, el pez espada o emperador, el cazón, el lucio y la caballa real son pescados con alto teor graso que pueden contener un dosis peligrosa de mercurio, un metal pesado tóxico para las neuronas. Lo más aconsejable es que se consuman pescados pequeños como la sardina y pescados blancos.
Los pescados azules son ricos en ácidos grasos omega-3, pero durante el embarazo se puede conseguir estos ácidos grasos en vegetales como el aceite y las semillas trituradas de lino, de nueves y semillas de chia.
5. Cafeína y alcohol. La cafeína se absorbe y llega a la placenta y al feto, que no dispone de las enzimas necesaria para metabolizarla. Si la embarazada consume mucha cafeína puede poner en riesgo al bebé de que nazca con poco peso.
En lugar del café es recomendable que la embarazada tome infusiones como de manzanilla, menta poleo o hierba buena. El alcohol puede provocar síndrome de alcoholismo fetal, que conlleva deformidades faciales, defectos en el corazón y retraso mental.
Puedes leer más artículos similares a Menús para embarazadas semana a semana, en la categoría de Dietas – menús en Guiainfantil.com.
Content:
What are diets for cardiovascular diseases?
Diet for heart disease. Sample menu
Sample menu
Diet in cardiovascular disease is as important as exercise therapy, psychological stability and preventive measures. Proven by research: lifestyle, regimen, quality and volume of nutrition are important factors in the fight against CVD.
The Mediterranean diet has proven itself well in all cardiac diseases. It is recommended by doctors all over the world, since the products of this diet are rich in vitamins, antioxidant substances and trace elements that are beneficial for the heart and blood vessels. The diet includes a huge variety of vegetables and fruits, as well as olive oil. The risk of acquiring cardiovascular disease is reduced if the menu includes foods with omega-3s, such as nuts and soy. However, one component does not guarantee security. Fats of animal origin are recommended for people with a diagnosis to be replaced with vegetable oil – linseed or olive.
Cardiovascular diet menu may include:
When following a diet for heart disease, it is important to pay attention not only to food, but also to the way food is prepared. You can bake on the grill and in the oven, steam, cook. Fried with CVD is unacceptable.
For arterial hypertension, the DASH diet for diseases of the cardiovascular system is recommended. This nutrition system is designed to maintain normal blood pressure. The consumption of fruits and vegetables, as with the Mediterranean diet, is not limited. Calcium, magnesium, potassium are especially useful, and the sodium content must be minimized. The DASH diet helps you stay healthy and lose weight without starving yourself because it includes protein-rich foods and keeps your sugar levels stable. DASH Diet Nutrition Principles:
DASH Diet Nutrition Principles:
The DASH diet can be followed for life, not only during an exacerbation, ie. make it a lifestyle. The diet for diseases of the heart and blood vessels is suitable for people of any age, and this is its advantage. The main principle of the DASH diet is sodium reduction. Although it is worth reducing the amount of salt consumed not only with high blood pressure, but also with any type of CVD. A low-salt diet reduces the risk of stroke and heart failure. It is worth remembering that canned foods, smoked meats, and sausages contain a lot of salt. The lack of salt is filled with natural supplements such as aromatic herbs.
Although it is worth reducing the amount of salt consumed not only with high blood pressure, but also with any type of CVD. A low-salt diet reduces the risk of stroke and heart failure. It is worth remembering that canned foods, smoked meats, and sausages contain a lot of salt. The lack of salt is filled with natural supplements such as aromatic herbs.
Proper nutrition and diet for cardiovascular diseases is an essential component in the prevention and treatment program. First of all, vegetables and herbs help maintain balance, if there are no contraindications from the gastrointestinal tract.
Diet for cardiovascular diseases: table for arterial hypertension:

Diet for heart disease: menu for coronary heart disease:
In atherosclerosis, it is important to lower bad cholesterol (LDL) without lowering good cholesterol (HDL). A large amount of natural fats is found in milk and meat. Industrially produced artificial trans fats are especially harmful. Fiber-rich foods help lower lipid levels and saturate the body: beans, fruits, oatmeal and barley porridge. Natural carbohydrates in combination with fiber are not harmful, i.e. sweet fruits, and refined carbohydrates like sugar upset the balance of glucose and lipids. It is irrational to completely refuse fats, the main thing is that their consumption does not exceed 30% of the total diet. With a lack of lipids, the HDL level decreases, vitamin E deficiency occurs.
Nutrition for CVD should be fractional in small portions. If cardiovascular disease is complicated by obesity, a low-calorie diet is prescribed. Often, doctors insist on a complete rejection of alcohol or a reduction in doses in terms of alcohol to 20 g for men and 10 g for women. The amount of water should also be limited, especially with edema, to 1.5 liters per day.
Although some diets indicated for cardiovascular disease are suitable for everyone, before changing the diet, it is worth consulting with your doctor to find out if there are any contraindications for switching to a Mediterranean diet or DASH diet. The diet must be selected individually, especially with existing CVD, after strokes, heart attacks, and operations. You can get competent advice from a cardiologist in the Moscow region at the Chekhov Vascular Center. It uses the latest methods of treatment of diseases of the heart and blood vessels. Patients can receive advice on prevention, as well as undergo treatment from highly qualified doctors.
8-800-444-49-59
Appointment for consultation, research
Beregovaya st., 36A, Chekhov, Moscow region, Russia, 142301
This email address is being protected from spambots. You must have JavaScript enabled to view.
Mon-Sun – Around the clock
Co-author, editor and medical expert – Volosov Dmitry Dmitrievich.
Views: 277 657
The date of the last update: 21.10.2022 G.
Average reading time: 12 minutes
Content:
Constipation is a pathological condition of the intestines, in which its emptying is difficult. Since most often it occurs as a result of malnutrition (lack of diet, dry food, etc. ), the most important thing in its elimination and prevention is the preparation of a special diet for constipation, as well as compliance with the rules of eating. Therefore, adults with constipation are prescribed diet number 3.
), the most important thing in its elimination and prevention is the preparation of a special diet for constipation, as well as compliance with the rules of eating. Therefore, adults with constipation are prescribed diet number 3.
It is especially important to keep a child’s diet. Accumulation and retention of feces in the intestine for a long time gradually lead to a significant stretching of the intestinal wall. As a result, its receptors lose sensitivity, and this can later lead to a number of serious disorders and diseases of the digestive tract (for example, encopresis). Therefore, the timely restoration of the functional activity of the small and large intestine is of great importance for the health of children in the future. And diet 3 for constipation for a child is best suited.
Back to content
To get rid of problems with the intestines, you should follow a proper diet for constipation.
Eat as much fiber as possible . Dietary fiber acts on the mechanical receptors of the intestinal wall and leads to increased peristalsis, which as a result contributes to the promotion of stool.
Dietary fiber acts on the mechanical receptors of the intestinal wall and leads to increased peristalsis, which as a result contributes to the promotion of stool.
Drink plenty of pure water . Compliance with the water regime for constipation is a prerequisite for a laxative diet. The volume of liquid per day should be at least 2 liters. This refers to pure water. Broths, juices, teas and other liquids on the menu do not apply to this item. It is plain water that helps to thin the stool, which as a result leads to easier defecation.
Eat frequently. To avoid constipation, you need to eat at least 5-6 times a day. Then the products will be better digested, and the nutrients will be fully absorbed.
Switch to natural products . Be sure to exclude from the diet fast food, food containing preservatives and dyes, semi-finished products. They not only provoke the occurrence of constipation, but also poison the body, lead to dysbacteriosis. Therefore, you need to cook from ordinary natural products.
Back to Contents
Constipation can occur in a variety of bowel conditions, both with exacerbations and periods of calm. For chronic defecation disorders associated with stool retention, in the presence of concomitant diseases, as well as for constipation caused by an improper diet, diet number 3 (or table number 3) is prescribed. If there are any diseases of the digestive tract, then it is indicated only during the absence of exacerbations. Table number 3 for children is also suitable.
|
What is the purpose of diet 3 for constipation |
|||||||
|
Restoration of the functional activity of the intestines |
Normalization of metabolic processes in the body |
Improving the motor function of the small and large intestine |
Strengthening the secretory function of the glands of the intestinal wall |
Ensuring regular bowel movements |
Elimination of processes of putrefaction in the intestinal lumen |
Elimination of intoxication of the body |
Normalization of water exchange |
Thus, diet 3 for constipation is absolutely complete in its composition. Its main difference from the usual diet is that when compiling the menu, preference is given to products that have a laxative effect. They increase peristalsis and accelerate the release of feces. And foods that cause decay processes (fried or saturated with essential oils) are completely excluded from the diet.
Its main difference from the usual diet is that when compiling the menu, preference is given to products that have a laxative effect. They increase peristalsis and accelerate the release of feces. And foods that cause decay processes (fried or saturated with essential oils) are completely excluded from the diet.
Back to Contents
Diet 3 for constipation is based on carbohydrates. The ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the diet is in the proportion of 1: 1: 4. The amount of protein should be about 100 g per day, while only half of the nutrient of animal origin, the rest is vegetable protein. Of 100 g of fat, on the contrary, most of it is the animal component – 70%, and only 30% are vegetable fats. Accordingly, the amount of carbohydrates in the diet is 400 g. The daily salt content in the diet is 15 g, and the minimum volume of liquid is 1.5 liters. In general, the energy value of table number 3 is about 3,000 kcal.
Back to Contents
Diet No. 3 for constipation allows children and adults to eat most foods. However, each group has its own exceptions.
Bread and flour products . A prerequisite is that pastries and bread must be dried, baked a day or two ago. The preferred bread is gray, grain (rye, Borodino). Dietary flour should be no higher than the second grade. Not allowed: products made from high-grade flour, muffins and puff pastry.
Soups. Broth can be any, the main thing is that it is not greasy and rich. The advantage is given to soups and broths from vegetables, fruits, cereals.
Meat products and poultry. Diet menu “Table number 3” includes any lean meat. As a rule, it is cooked in a large piece or chopped. Milk sausages are allowed. It is impossible: smoked and canned meat, as well as fatty poultry (duck or goose).
Fish and seafood. Just like meat, the main condition is the absence of fat content. Cooked in pieces too. It is impossible: smoked and canned seafood and fish, as well as its fatty varieties.
Cooked in pieces too. It is impossible: smoked and canned seafood and fish, as well as its fatty varieties.
Milk and dairy products. All dairy products are allowed in the diet, as well as cheese (mild), cottage cheese, cream. Milk itself is preferably used in cooking.
Egg products. Only fried and hard-boiled eggs are not allowed, other egg dishes are allowed. The amount of product per day – 2 pieces (child – 1).
Cereals and pasta. Preference is given to dietary cereals: buckwheat, barley, pearl barley. They should be boiled in water, and then milk can be added. Dishes: cereals, casseroles. It is impossible: rice, semolina, pasta, legume dishes.
Vegetable crops. Vegetables are boiled and baked. Eat raw and as a side dish, as well as in the form of casseroles. Potatoes are consumed in limited quantities, and products with essential oils (radish, garlic, onion, radish) are completely removed from the diet.
Snacks. In Diet Menu 3 for constipation, you can eat any low-fat and non-spicy snacks. The use of smoked products is also excluded.
In Diet Menu 3 for constipation, you can eat any low-fat and non-spicy snacks. The use of smoked products is also excluded.
Sweet food. Almost everything is allowed: berries, fruits and sweets (honey, jam) in a reasonable amount on any day of the week. You can not eat chocolate, astringent fruits (quince).
Sauces, spices . Sauces with this diet can be any, only low-fat and mild. Seasonings exclude pepper, mustard and horseradish.
Drinks. Freshly squeezed juices with pulp from fruits and vegetables. You can also drink a coffee or tea substitute, rosehip broth. But cocoa and natural coffee, as well as strong tea, should be removed from the diet (especially in children).
Fats. Diet “Table number 3” allows you to eat vegetable oils that can be added directly to meals. From animal fats you can butter several times a week. The rest is prohibited.
Vegetables, as well as fruits in the menu of dietary table number 3, are present both raw and boiled. Products, as far as possible, are not crushed, but cooked in large pieces or whole. The diet does not exclude the use of sweet or cold foods. For constipation, a cold drink is recommended in the morning, for example, water with honey, and in the evening (before going to bed) you need to drink kefir or compote, it is allowed to eat some prunes or fruits. Therefore, the diet “Table number 3” for a child or an adult is not difficult, since you do not need to give up anything.
Products, as far as possible, are not crushed, but cooked in large pieces or whole. The diet does not exclude the use of sweet or cold foods. For constipation, a cold drink is recommended in the morning, for example, water with honey, and in the evening (before going to bed) you need to drink kefir or compote, it is allowed to eat some prunes or fruits. Therefore, the diet “Table number 3” for a child or an adult is not difficult, since you do not need to give up anything.
Back to Contents
Below is a sample weekly constipation diet menu. All dishes can be adjusted when eating according to table number 3.
Monday
In the morning: freshly squeezed vegetable juice.
1st breakfast: steam omelette, fruit salad, weak tea.
2nd breakfast: yogurt.
Lunch: cold beetroot, boiled meat with vegetable garnish, rosehip broth.
Afternoon snack: dry oatmeal cookies, fruit and berry compote.
Dinner: potato-pumpkin casserole with cheese, weak tea.
At night: prunes.
Tuesday
In the morning: cold water with honey.
1st breakfast: vegetable casserole, dry oatmeal cookies, coffee substitute.
2nd breakfast: an apple.
Lunch: vegetable soup, steamed fish, steamed vegetables, weak tea.
Snack: fruit salad, rosehip infusion.
Dinner: zucchini baked with tomatoes, berry-fruit juice.
At night: yogurt.
Wednesday
In the morning: cold dried fruit compote.
1st breakfast: cabbage salad, buckwheat porridge with milk, weak tea.
2nd breakfast: low-fat yoghurt with fruit.
Lunch: botvinia, boiled chicken with buckwheat, dried fruit compote.
Snack: rye biscuits, fruit juice.
Dinner: roll of grape leaves and vegetables, berry compote.
At night: an apple.
Thursday
Morning: cold rosehip tea.
1st breakfast: fresh tomato salad, protein omelet, biscuits, weak tea.
2nd breakfast: fruit salad.
Lunch: chicken broth soup with millet, baked meat with boiled vegetables, compote.
Snack: low-fat yoghurt with fruit.
Dinner: broccoli and pumpkin casserole, weak tea.
At night: kefir.
Friday
In the morning: cold berry compote.
1st breakfast: pumpkin-zucchini casserole, toasted rye bread sandwiches with cheese, coffee substitute.
2nd breakfast: dry biscuits, fruit juice.
Lunch: cucumber soup on kefir, baked fish, stewed vegetables, berry-fruit juice.
Snack: apple, compote.
Dinner: stewed vegetables, fruit juice.
At night: prunes.
Saturday
In the morning: fresh fruit juice.
1st breakfast: coleslaw with apple, wheat porridge with milk, compote.
2nd breakfast: an apple.
Lunch: soup with cauliflower in meat broth, baked fish with vegetables, weak tea.
Snack: cabbage and carrot salad, vegetable juice.
Dinner: buckwheat krupenik, fruit and berry compote.
At night: kefir.
Sunday
Morning: cold rosehip tea.
1st breakfast: beetroot salad, buckwheat porridge with milk, fruit compote.
2nd breakfast: fruit salad.
Lunch: cereal soup in meat broth, stewed beetroot, meat baked in chunks, compote.
Afternoon snack: dry shortbread biscuits, fruit juice.
Dinner: cabbage rolls, weak tea.
At night: fruit.
Back to Contents
For example, below are simple recipes for table number 3, which have a laxative effect and are suitable for inclusion in the menu for constipation.
Millet soup with meat broth
Boil a lean piece of meat. Peel and dice the potatoes and carrots and place them in the broth. Coarsely chop the meat and also add to the broth. Rinse the wheat and put it into a bowl. Boil 15 minutes. At the end, add salt and herbs to taste.
Fruit salad
Deseed apple, pear, cut them into cubes. Chop the banana and orange as well. Combine fruits, pour over yogurt.
Chop the banana and orange as well. Combine fruits, pour over yogurt.
Eggplant baked with vegetables
Wash the eggplants, cut off the ends and cut the fruit in half lengthwise. Remove the middle, salt the remaining parts and set aside. Stew the eggplant core with chopped tomatoes and zucchini, salt to taste. Stuff the halves with the resulting mixture of vegetables. Sprinkle with cheese and bake in the oven until done.
Zucchini roll
For the filling, stew the aubergines and tomatoes cut into small cubes, season with salt. Grate the cheese on a coarse grater. Peel and grate the zucchini on a coarse grater, add a couple of beaten eggs, baking powder, salt and flour to make a thick dough. Put it on a baking sheet on a foil greased with vegetable oil and bake until crusty. Turn the finished layer over on the table, remove the foil and put the filling over the entire surface of the cake. Also sprinkle with cheese. Roll the layer with the filling into a roll and refrigerate.