La pérdida de un bebé debido a que nació sin vida (muerte fetal) continúa siendo una triste realidad para muchas familias y afecta seriamente su salud y bienestar. A continuación, obtenga más información sobre la muerte fetal.
La muerte fetal es la muerte o pérdida de un bebé antes o durante el parto. Tanto el aborto espontáneo como la muerte fetal describen la pérdida de un embarazo, pero se diferencian según cuándo ocurre esta pérdida. En los Estados Unidos, el aborto espontáneo generalmente se define como la pérdida de un bebé antes de la 20.a semana de embarazo, y la muerte fetal es la pérdida de un bebé a las 20 semanas de embarazo o después.
La muerte fetal, a su vez, se clasifica como temprana, tardía o a término.
La muerte fetal afecta aproximadamente a 1 de cada 175 nacimientos y cada año alrededor de 21 000 bebés nacen muertos en los Estados Unidos.1 Eso es aproximadamente lo mismo que el número de bebés que mueren durante el primer año de vida. Gracias a los avances en la tecnología médica durante los últimos 30 años, el cuidado prenatal (la atención médica durante el embarazo) ha mejorado, lo cual ha reducido notablemente la cantidad de casos de muertes fetales tardías y a término. Sin embargo, la tasa de mortalidad fetal temprana se ha mantenido prácticamente igual a lo largo del tiempo.
A la muerte fetal sin una razón conocida se la llama “muerte fetal sin causa aparente”. Cuanto más avanzada esté una mujer en su embarazo, más probable es que la muerte fetal sea sin causa aparente. Para tratar de comprender por qué el bebé murió antes de nacer, es importante que se le realice una autopsia y otras pruebas de laboratorio. Su proveedor de atención médica puede darle más información sobre este tema.
Para tratar de comprender por qué el bebé murió antes de nacer, es importante que se le realice una autopsia y otras pruebas de laboratorio. Su proveedor de atención médica puede darle más información sobre este tema.
Los casos de muerte fetal ocurren en familias de todas las razas, grupos étnicos y niveles de ingreso, y en mujeres de todas las edades. Sin embargo, ocurren con mayor frecuencia entre ciertos grupos de personas, que incluyen a mujeres que:
Esto no significa que cada persona de raza negra o de mayor edad tenga un mayor riesgo de sufrir la pérdida de un bebé por muerte fetal. Significa simplemente que, como grupo en general y en comparación, entre todas las madres de raza negra o de mayor edad ocurren más casos de muerte fetal que entre las madres de raza blanca y las madres menores de 35 años. Algunos factores que podrían contribuir a estas disparidades en muertes fetales incluyen diferencias en la salud materna antes de la concepción, la situación socioeconómica, el acceso a atención médica de calidad y el estrés.2 Se necesita más investigación para determinar cuál es la razón subyacente por la cual algunos de estos factores están asociados con la muerte fetal.
Algunos factores que podrían contribuir a estas disparidades en muertes fetales incluyen diferencias en la salud materna antes de la concepción, la situación socioeconómica, el acceso a atención médica de calidad y el estrés.2 Se necesita más investigación para determinar cuál es la razón subyacente por la cual algunos de estos factores están asociados con la muerte fetal.
Muchos de estos factores también están asociados a otros desenlaces adversos del embarazo, como el nacimiento prematuro.
Los CDC trabajan para aprender más sobre quiénes podrían sufrir la pérdida de un bebé por muerte fetal y por qué. El modo en que lo hacen es a través del seguimiento de la frecuencia en que estos casos ocurren, e investigando qué los causan y cómo prevenirlos. Los conocimientos sobre las causas potenciales de la muerte fetal se pueden usar para elaborar recomendaciones, políticas y servicios para ayudar a prevenirlas. Si bien seguimos aprendiendo más sobre la muerte fetal, queda mucho trabajo por hacer.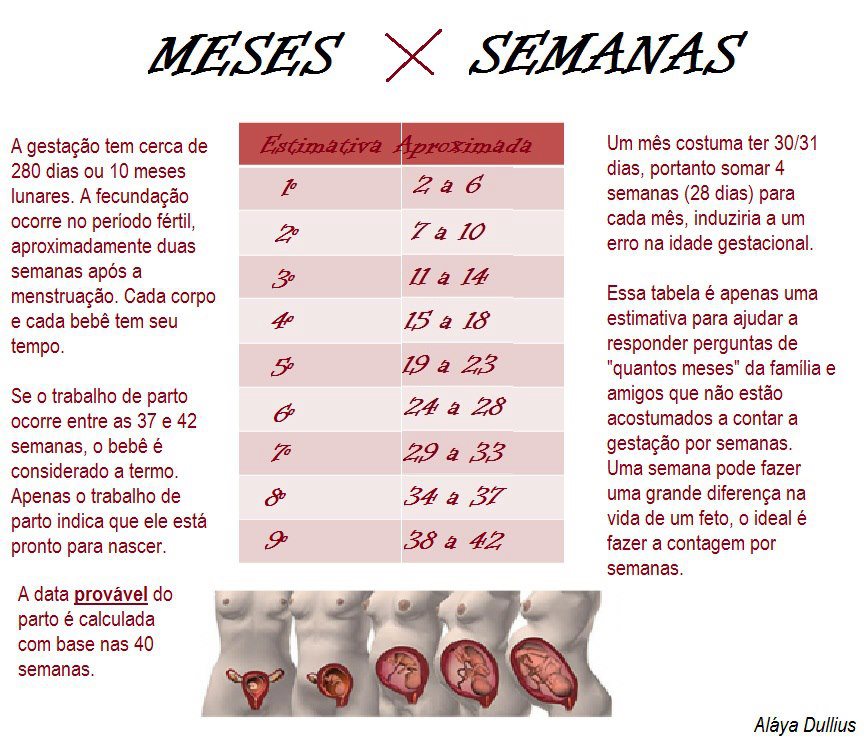 Visite la página de actividades de los CDC relativas a la muerte fetal para obtener más información sobre lo que se está haciendo.
Visite la página de actividades de los CDC relativas a la muerte fetal para obtener más información sobre lo que se está haciendo.
El embarazo es el periodo de gestación de un ser humano en el útero materno; toma un tiempo de 37 a 42 semanas (9 meses). La temporalidad durante la gestación es vital para la formación adecuada de los órganos, tejidos y sistemas del bebé.
El embarazo se mide por semanas a partir del inicio del ciclo menstrual. Por lo tanto, las primeras dos semanas la mujer no está embarazada, sino que su organismo se prepara para un embarazo. En este tiempo el endometrio se ensancha para almacenar al óvulo fecundado; de lo contrario, se produce la menstruación.
En la tercera semana del periodo es cuando el esperma fecunda al óvulo en la trompa de falopio y se convierte en cigoto. Esta nueva célula contiene toda la información genética y el sexo del feto. Finalmente, seguirá avanzando hasta implantarse en el endometrio; en este punto ya no es cigoto, sino mórula, que es un conjunto de muchas células.
La implantación de la mórula termina durante la cuarta semana de embarazo para posteriormente convertirse en embrión.
La madre aumentará sus niveles de hormonas durante la quinta semana de embarazo; producirá gonadotropina coriónica humana que ayuda a que los ovarios no liberen óvulos y desarrollen mayor cantidad de estrógenos y progesterona. Esta producción hormonal genera los síntomas propios del primer trimestre del embarazo, como las nauseas matutinas, vómito, fatiga, etcétera.
Esta producción hormonal genera los síntomas propios del primer trimestre del embarazo, como las nauseas matutinas, vómito, fatiga, etcétera.
Por consiguiente, en la sexta semana de la gestación el crecimiento del embrión es más rápido. En esta etapa se cierra el tubo neural, que más adelante dará paso a la formación de la médula espinal y el encéfalo. También el corazón comienza a latir.
A partir de la séptima semana, el cerebro y rostro del embrión comienzan a formarse. También brotan las extremidades, que más adelante serán los brazos y piernas. Para la octava semana, el feto alcanza una medida de 11 a 14 milímetros aproximadamente; los ojos, boca, nariz y extremidades están casi definidas.
A partir de la novena semana la cabeza del embrión es grande y las facciones del rostro son cada vez más detalladas. Además, los brazos son suficientemente largos y se forman los codos. En la décima semana ya podrá flexionar los codos, además el cordón umbilical comienza a ser visible.
En la décima semana ya podrá flexionar los codos, además el cordón umbilical comienza a ser visible.
Entrando a la semana once, se le puede considerar un feto debido a la formación del cuerpo que comenzará a crecer (esta denominación se le puede otorgar a partir de la semana ocho). Durante esta etapa, aparecen brotes dentarios, el hígado del feto comienza a formar glóbulos rojos y son visibles los genitales externos.
En la decimosegunda semana, el feto ya tiene el rostro definido, sus órganos digestivos se encuentran formados, así como sus extremidades y manos, incluso tiene uñas. Puede llegar a medir casi 7 cm y pesar aproximadamente 14 gramos.
Tercer mes de embarazo
A partir de este momento, comienza el segundo trimestre. En la semana trece el feto ya tiene micciones que libera en el líquido amniótico. También su piel y huesos se van engrosando y definiendo; el cráneo también se define y endurece poco a poco.
El sexo del bebé comienza a ser evidente a partir de la semana catorce, además su cabeza se va separando más del cuerpo, definiendo el cuello. Durante la semana quince, el cuero cabelludo del feto comienza a desarrollarse y sus huesos ya son casi visibles mediante el ultrasonido.
Es probable que la madre aún no sienta los movimientos del feto durante la semana dieciséis, sin embargo, sus movimientos son definidos. Además, sus ojos y orejas están situadas casi en su lugar. En esta etapa, el feto mide casi 12 cm.
Cuarto mes de embarazo
Para la semana diecisiete el feto se mueve con más libertad y su corazón late con rapidez. A partir de la semana dieciocho el sistema digestivo del feto comienza a funcionar y comienza a percibir sonidos.
Si el feto es femenino, en la semana diecinueve se desarrolla el útero. Además, independientemente del sexo, se genera una capa de grasa para proteger la piel del feto, a este recubrimiento se le denomina unto sebáceo. En la vigésima semana la madre comenzará a sentir el movimiento del bebé; este tendrá lapsos de sueño y podrá despertarse por los sonidos del exterior.
En la vigésima semana la madre comenzará a sentir el movimiento del bebé; este tendrá lapsos de sueño y podrá despertarse por los sonidos del exterior.
Quinto mes de embarazo
A partir de la semana veintiuno el feto comienza a desarrollar el reflejo de succión y puede chupar su dedo pulgar. Además, se desarrolla el lanugo, que es un vello fino que recubre la piel del bebé y cae poco a poco una vez que nace.
Si el feto es masculino, comenzarán a descender los testículos en la semana veintidós. Además, independientemente del sexo, el cabello y cejas del feto comenzarán a notarse. Durante la semana veintitrés, podrán sentirse más movimientos debido a que puede tener hipo. También en esta etapa comienza a desarrollar sus huellas dactilares de manos y pies.
La piel del bebé es rosácea durante la a semana veinticuatro, eso se debe a que nota la sangre de los capilares. En este momento, puede pesar 650 g y medir un poco más de 20 cm.
En este momento, puede pesar 650 g y medir un poco más de 20 cm.
Sexto mes de embarazo
A partir de la semana veinticinco el feto tiene movimientos oculares rápidos aún con los párpados cerrados. Además, el bebé ya responde a los sonidos exteriores como las voces que conoce, sobre todo la de la madre.
La semana veintiséis es muy importante, debido a que es cuando se comienza a producir surfactante que es una sustancia que ayudará a que los pulmones puedan inflarse y desinflarse sin colapsar al momento de recibir aire.
El tercer trimestre termina a partir de la semana veintisiete, durante este periodo el bebé seguirá creciendo, ganando peso y desarrollando sus órganos y tejidos.
TERCER TRIMESTRE
Iniciando el tercer trimestre, el bebé puede medir 25 cm y pesar aproximadamente 1 kg, esto es a partir de la semana veintiocho. Durante este periodo su sistema nervioso central ya puede dirigir los signos vitales del bebé como respiración y temperatura.
Durante este periodo su sistema nervioso central ya puede dirigir los signos vitales del bebé como respiración y temperatura.
En la semana veintinueve los movimientos del bebé son muy fuertes, patea y se estira dentro del útero y puede sujetar su cordón. Además, en la semana treinta la médula ósea del feto comienza a desarrollar glóbulos rojos; físicamente, ya abre sus ojos y ya tiene bastante cabello.
A partir de este tiempo el feto gana peso y talla muy rápido. Para la semana treinta y uno, puede alcanzar los 27 cm y el kilo 300 gramos. El lanugo comenzará a caerse a partir de la semana treinta y dos.
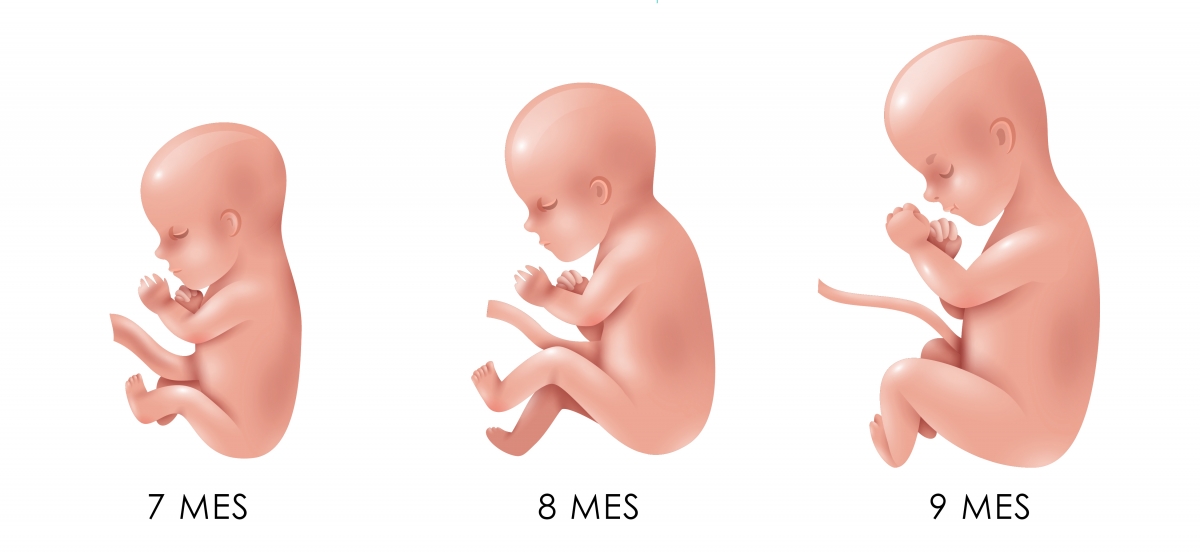
Octavo mes de embarazo
En la semana treinta y tres las pupilas del bebé reaccionan a la luz y a partir de la semana treinta y cuatro sus huesos siguen creciendo y endureciéndose, a excepción del cráneo, que madura meses después del nacimiento.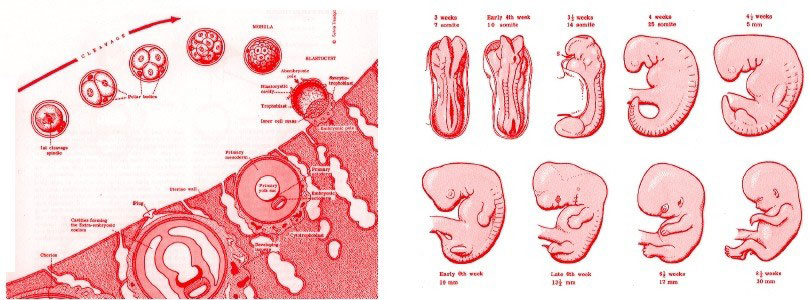
La piel del bebé se irá fortaleciendo y alisándose a partir de la semana treinta y cinco, además, comenzará a generar grasa, teniendo una percepción robusta. Durante la semana treinta y seis el bebé tendrá un espacio más estrecho, por lo tanto, sus movimiento podrán sentirse más bruscos dentro del vientre.
En la semana treinta y siete el feto se posicionará boca abajo, acomodando su cabeza en la pelvis de la madre, permaneciendo en esta posición hasta el día del nacimiento.
Noveno mes de embarazo
Para la semana treinta y ocho el bebé alcanzará un peso de casi 3kg, además, sus uñas serán lo suficientemente largas como para sobresalir de sus dedos. Ya habrá perdido casi todo el lanugo que lo recubría.
El cuerpo del bebé también se prepara para el nacimiento, en la semana treinta y nueve generará una capa de grasa para regular la temperatura del exterior.
Finalmente, llega el parto en la semana cuarenta, el bebé habrá ganado la talla que necesita para su nacimiento, que es en promedio entre 40 y 50 cm y un peso de 3. 5 kg. Sin embargo, hay bebés que nacen sanos con más o menos peso y talla.
5 kg. Sin embargo, hay bebés que nacen sanos con más o menos peso y talla.
Con información de Mayo Clinic
Puede consultar una lista de médicos obstetras en nuestro directorio. También puede solicitar información sobre nuestros servicios de ultrasonidos de embarazo vía WhatsApp.
Consulte a su médico. Los artículos del blog «Salud de Hierro» no constituyen orientación médica ni deben ser utilizados con fines diagnósticos.
Common spruce (Picea abies) is the oldest evergreen species of the pine family, a slender and beautiful long-lived woody plant with a pyramidal wide crown. In nature, it reaches 50 m in height. Its straight trunk can reach 1 – 2 m in diameter. The top of the spruce is always sharp, the branches grow horizontally or arcuately raised upwards. The bark is red or grey. The needles are short, 15-20 mm long, bright green or dark green in color, with a characteristic aroma. Although we are talking about conifers as evergreens, in fact, needles have their own lifespan: in spruce, they stay on a tree for a maximum of 6 to 12 years. nine0005
Although we are talking about conifers as evergreens, in fact, needles have their own lifespan: in spruce, they stay on a tree for a maximum of 6 to 12 years. nine0005
Norway spruce is the most common coniferous plant in Russia, the main forest-forming species. In nature, you can find trees over 250 – 300 years old.
The cones of the common spruce are oblong, cylindrical. During their life, they change color from red to green, and as they mature, they become brown. The seeds are easily dispersed by the wind thanks to their wings. The crop ripens every 3-4 years, but old cones can hang on a tree for more than one year.
In different cultures, spruce is considered a symbol of eternal life, courage and fidelity. But in Rus’, she was never planted next to the house – this was considered a bad omen. All because it is good … burns. And if suddenly there was a fire in some house, the tree flared up like a match, fell and spread the fire to other houses. But now it is willingly planted in many areas: dwarf varieties and non-hot building materials have appeared.
But in Rus’, she was never planted next to the house – this was considered a bad omen. All because it is good … burns. And if suddenly there was a fire in some house, the tree flared up like a match, fell and spread the fire to other houses. But now it is willingly planted in many areas: dwarf varieties and non-hot building materials have appeared.
But now spruce is very popular in landscape design due to frost resistance, shade tolerance, and most importantly – a variety of varieties. nine0005
Nidiformis. Refers to the dwarf subspecies of the common spruce. This compact beautiful plant has long won its place in small gardens. A shrub with an original flat-rounded (in young trees it is nest-shaped), a very dense crown of thin twigs with light green needles in height reaches only 1 – 1.2 m and 2.5 m in width. But it takes a long time to grow to these sizes – in 10 years the spruce will hardly be 40 cm. It is undemanding to soils, although it develops better on fresh, moist soils. Grows well in both full light and partial shade. nine0005
Grows well in both full light and partial shade. nine0005
The variety was introduced into cultivation at the beginning of the 20th century. Used by landscapers in rocky gardens and low borders (1). There is a positive experience of growing Nidiformis in containers.
Acrocona. One of the most picturesque varieties, known since the end of the 19th century. Its irregular wide columnar shape of the crown, asymmetrically and arched hanging branches give the garden lightness. An adult Acrocona reaches a height of 3 m with a crown width of up to 3 m. The dark green needles are short, kept on branches for up to 12 years. Numerous beautiful large cones, originally growing at the ends of the shoots, become a real decoration of the tree. At first they are bright red, then turn brown. nine0005 Acrocona spruce (Acrocona). Photo: Jagel, globallookpress.com
The variety grows slowly, withstands frosts down to -40°C, is photophilous, prefers fertile and moist soils with slightly alkaline reaction.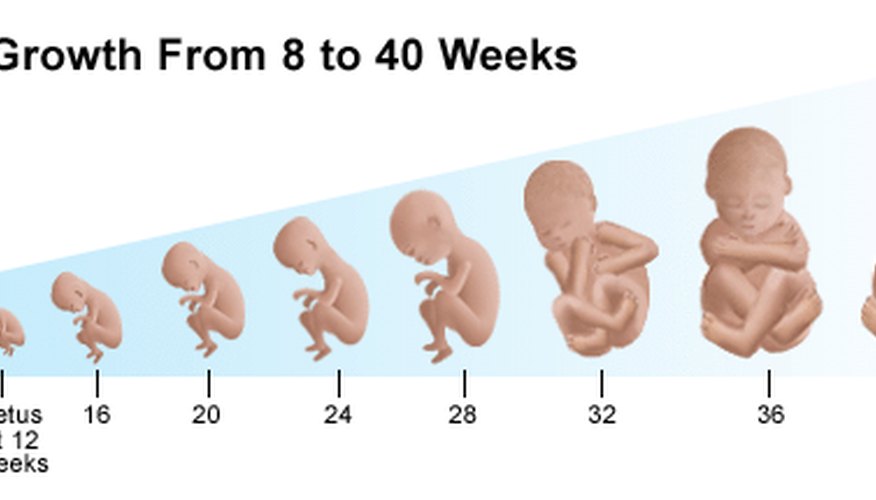
In landscape design, it is valued as a tapeworm (single plant). It is often used to create rocky and Japanese gardens.
Inversa. One of the most interesting variations on the “weeping spruce” theme. Found in England in 1884. A tree with a narrow crown, falling branches forming a plume on the ground. Grow it as a slow-growing shrub on a support, or plant it on a tall trunk. Hanging branches fit snugly to the trunk, so even in an adult tree, the crown diameter does not exceed 2.5 m.
Inversa spruce. Photo: pixabay.com
Variety Inversa (2) is very winter-hardy (withstands down to -40 °C), can grow even in harsh mountainous conditions. Likes bright places, but is able to grow in partial shade. Soils prefer moist, nutritious, tolerant to both acidic and alkaline.
In landscape design it plays the role of a spectacular tapeworm.
Will’s Zwerg . Began to be actively sold since 1956. Undersized, slow-growing, by the age of 30 it gains 2 m in height, but barely reaches 1 m in width. The crown is beautiful, dense, pin-shaped or conical. It looks very elegant and spectacular at the beginning of the growth of shoots, which, against the background of dark green paws, stand out with yellow-orange growth. And in summer, young shoots differ in color – they are light green. nine0005
The crown is beautiful, dense, pin-shaped or conical. It looks very elegant and spectacular at the beginning of the growth of shoots, which, against the background of dark green paws, stand out with yellow-orange growth. And in summer, young shoots differ in color – they are light green. nine0005
The variety is very winter-hardy (up to -40 °C), photophilous, although it can also grow in shady places. It needs well-drained, moderately fertile soils.
Used in small garden landscape design as a specimen and in groups as a supporting plant.
Little Gem . One of the smallest and slowest growing spruce mutations. Discovered in the 50s of the last century in Holland. The crown is cushion-shaped, dense, the branches are short, slightly raised. The needles are delicate, thin, dark green. In the spring, against this background, a young growth with bright green needles looks very impressive. By the age of 10, the Christmas tree grows to a height of only 20 cm.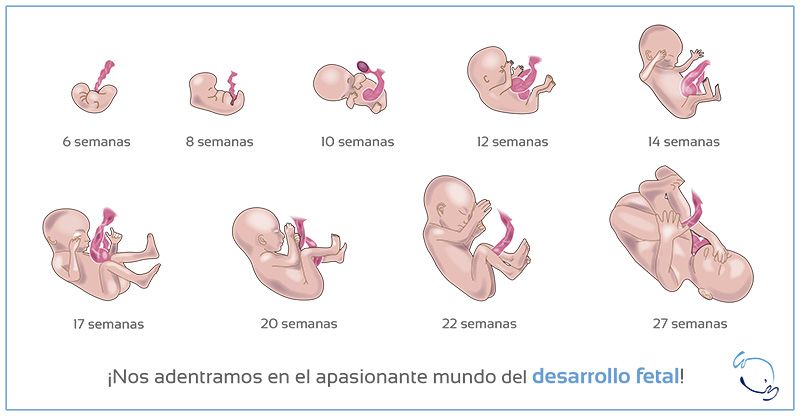 And after 50 cm, its growth stops. A characteristic feature of this dwarf is that it never blooms. nine0005
And after 50 cm, its growth stops. A characteristic feature of this dwarf is that it never blooms. nine0005
Frost-resistant spruce (down to -35 °C), photophilous, prefers moderately moist and nutritious soils.
In landscape design it is used in miniature and small gardens, rockeries and screes, effective in containers.
An important rule: before buying a seedling, you must clearly determine the planting site, realizing what size the plant will be in 10 – 20 years. Spruces are not the kind of plants that easily tolerate transplantation. For plants with a closed root system (ZKS), the best planting time is from mid-April to October, for seedlings with an open root system – until mid-April and the second half of September – early November. nine0005
The best option is seedlings in a container or with a packed earthen clod. The landing pit must be prepared in advance.
It should be remembered that young plants in the first two winters can suffer from sunburn, so protection from withering winds and bright sun at the end of winter is needed.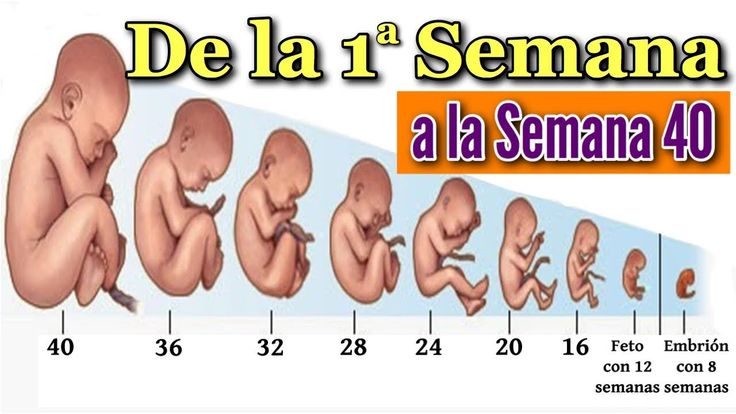
Varieties and forms of Norway spruce are diverse, very winter-hardy (with rare exceptions), some have peculiarities in care, but most often basic knowledge is enough for plants to develop and grow beautiful, healthy and durable. nine0005
Norway spruce develops best on moderately moist, well-drained, fairly fertile soils. Ideally – slightly acidic rich loam. Some varieties need a slightly alkaline soil reaction, but in general spruces grow well on slightly acidic and neutral soils. On poor sandy soils, when planting in pits, clay and humus are added in a ratio of 1: 1.
Most cultivars tolerate direct sunlight well, but dwarf forms need some shade for the first two winters. Many cultivars are shade tolerant, however, a beautiful crown shape develops only with sufficient sunlight. nine0005
In nature, Norway spruce grows on moderately moist soils, although many spruce forests are found in mountainous areas where there is not much moisture. However, when planting, all varieties of spruce need high-quality watering, especially in the first year.
However, when planting, all varieties of spruce need high-quality watering, especially in the first year.
After planting, watering is needed once a week at the rate of 10 – 12 liters of water per seedling no more than 1.5 m high. In hot weather, in the evening or morning, a shower has a beneficial effect. To preserve moisture, trunk circles can be mulched with a thick layer of bark or sawdust of conifers. nine0005
After a year or two, most varieties of Norway spruce no longer need watering, although they respond well to a water shower on hot days.
The most important condition for a good wintering of young plants is moisture-charging watering. No matter how wet autumn is, in October, under each coniferous tree, at least 20-30 liters of water should be poured onto small plants and 50 liters per meter of crown height.
When planting, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers and old sawdust of coniferous species are used. No manure or fresh compost, however, as well as any nitrogen fertilizer, as well as ash.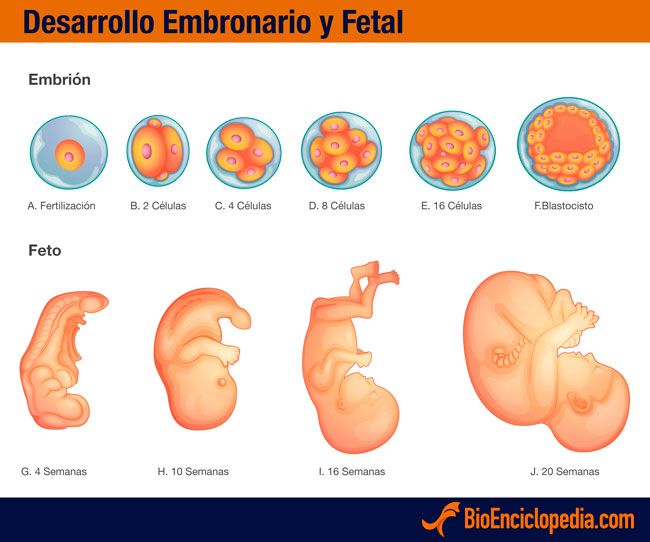 Under dwarf varieties, it is permissible to put half a bucket of well-ripened compost in the planting hole. nine0005
Under dwarf varieties, it is permissible to put half a bucket of well-ripened compost in the planting hole. nine0005
On fertile soils in the first 2-3 years after planting spruce do not need top dressing. In the future, special fertilizers are applied to the trunk circles. When the needles turn yellow and fall off, as well as in the first year, it is useful to spray the crown with solutions of Epin and Ferrovit.
Spruces can be propagated in three ways.
Seeds. With this method, varietal characteristics are not preserved. However, this method is popular with those who need a lot of planting material, and they are in no hurry. With this method of growing, it is important that the seeds are fresh and stratified. nine0005
Vaccination. This is an option for varietal plants – it allows you to keep all the characteristics of the mother plant.
Cuttings.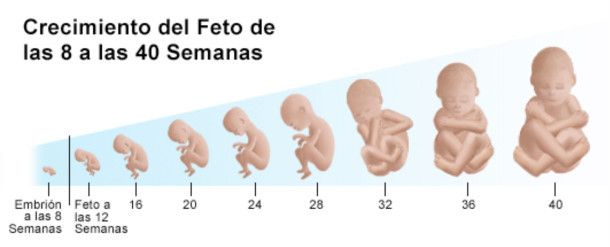 Also used for propagating varietal spruces. But it requires patience, time and compliance with a large number of rules.
Also used for propagating varietal spruces. But it requires patience, time and compliance with a large number of rules.
Photo: commons.wikimedia.org
Rooting cuttings are taken from mother plants on a cloudy day in late March – early April, tearing off from a branch with a heel – a piece of trunk bark. A good cutting should be 7-10 cm long. Immediately after harvesting, the ends of the cuttings are placed for a day in a solution of a root formation stimulator (for example, Heteroauxin). Then the cuttings are planted in pots with light fertile soil at an angle of 30 °, deepening by 2-3 cm. The pots are placed in a greenhouse or covered with a plastic bag. It is important to air the plantings once a day. nine0005
Be patient – the rooting process can take up to one year. And during this period, it is important to regularly water and ventilate the plants. Once every 2 weeks, you can add a weak solution of Heteroauxin to the water.
In the spring, rooted cuttings are planted in a school, which is arranged under the canopy of trees. Only after a year or two grown plants can be planted in a permanent place.
Only after a year or two grown plants can be planted in a permanent place.
Rust (spruce spinner). This is a fungal disease. The disease manifests itself on the cortex in the form of small, 0.5 cm in diameter swellings of orange color. Then the needles begin to turn yellow and fall off. Cones can also be affected by rust. nine0005
It is important to collect diseased needles and cones already at the initial stage, cut and burn the branches affected by the fungus, and treat the plants with Hom (copper oxychloride) (3) or Rakurs. For prevention, spring spraying with Bordeaux liquid is practiced.
Schütte. Although pines are more likely to suffer from this disease, Schütte (snow mold) often affects Norway spruce. The culprit is a fungus pathogen. It populates plants in autumn. Rapidly develops in winter, especially under snow. In spring, brown needles with a white coating appear on the plants. Sick needles can stay on spruce for another year. This leads to a stop in the development of the plant, and in some cases to death. nine0005
This leads to a stop in the development of the plant, and in some cases to death. nine0005
The treatment consists in removing the affected branches and treating the plants three times with Hom or Rakurs (3).
Spruce spider mite. The most common pest that breeds most actively during the hot dry months. Ticks pierce needles, drinking juices, leaving small yellow spots on them. With a strong infection, the needles turn brown and crumble. A web appears on the branches.
Prevention – regular dousing of crowns with water. Treatment – spraying infected plants with Actellik, Antiklesch, Fitoverm. It is important to carry out at least 3 treatments from June to September. nine0005
Spruce sawfly. A small insect colonizes spruce with larvae that feed on needles. It is not so easy to notice the sawfly invasion at first – the larvae literally merge with the needles. But when the young needles turn reddish-brown in color, urgent measures must be taken to protect the plants.
The drug Pinocid is effective against the sawfly. The tree is sprayed with a solution at least twice, it is also important to spill the near-stem circles with the solution – the larvae dig into the ground. In the initial stage of infection, spraying with Actellik or Fury is effective. nine0005
Spruce needle leaf roller. Moth moth infects spruce with larvae that bite into the needles, making mines. After some time, the needles are covered with cobwebs and crumble.
Calypso and Confidor are effective against leafworm. With a slight lesion, two or three treatments of the affected branches with Green soap are enough.
Spruce false shield. Often affects young plants. Small insects settle on the bark and needles, which is noticeable by the sticky coating. Plants are oppressed, needles turn brown and fall off, branches bend and dry out. nine0005
Aktara and Confidor are most effective against this pest.
We asked agronomist Oleg Ispolatov about Norway spruce – he answered the most popular questions of summer residents.
How to use Norway spruce in landscape design?
Norway spruce is represented on our market by a large number of varieties. Therefore, you can choose plants for both a large plot and a small garden. Dwarf varieties are great in rocky gardens and containers. nine0005
Fir trees with an unusual crown become the highlight of the garden, emphasizing the luxury of the lawn or acting as a dominant among small ornamental shrubs, lying junipers or ground covers.
Is it possible to trim and cut Norway spruce?
Of course, you can, but it is important to meet the deadlines. Sanitary haircut is needed for all varieties of spruce – it is carried out in the fall. Decorative haircut is designed to restrain growth, maintain the shape of the crown – it is carried out in the spring. In young plants, it is better not to cut the branches, but to pinch the growth. nine0005
It is not recommended to cut more than 1/3 of the shoot.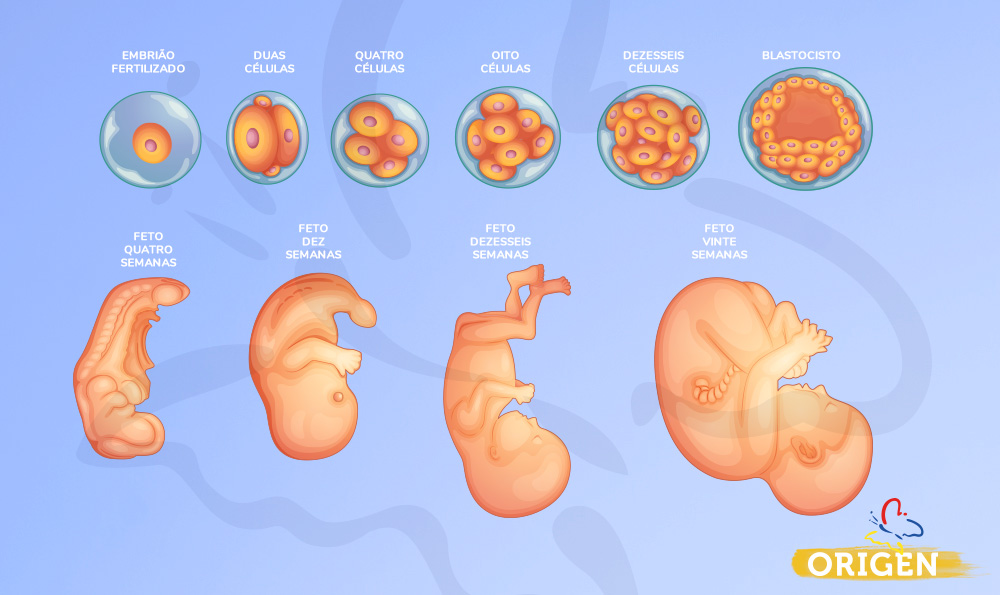
Before starting decorative pruning, water the plant and pour water over the crown.
Is it possible to make a hedge out of Norway spruce?
Norway spruce hedge is beautiful, green and impenetrable at any time of the year. Protective hedges are created from species plants along large gardens. In a small garden, this is not so rational, because it will take a lot of time to form a compact hedge, because the annual growth is from 40 to 60 cm.
Sources
 gov.ru/ministry/departments/departament-rastenievodstva-mekhanizatsii-khimizatsii-i-zashchity-rasteniy/industry-information/info-gosudarstvennaya-usluga-po-gosudarstvennoy-registratsii-pestitsidov-i- agrokhimikatov/
gov.ru/ministry/departments/departament-rastenievodstva-mekhanizatsii-khimizatsii-i-zashchity-rasteniy/industry-information/info-gosudarstvennaya-usluga-po-gosudarstvennoy-registratsii-pestitsidov-i- agrokhimikatov/
Holy Week is the most solemn and bright, but the entire period of Great Lent is full of religious events and processions. It seems to the uninitiated tourist that the Andalusians are happy and having fun, but in fact, all these events are very serious for the locals. This can be seen even in the clothes of their participants: the spectators come in solid costumes, and the participants in the processions – in the uniform of their brotherhoods.
nine0005
Seville starts preparing for Easter in advance. Immediately after Christmas, figures and figures that look like members of the Ku Klux Klan appear all over the city. Small ones are sold in souvenir shops, chocolate or caramel ones are sold in pastry shops, and in some places you can also find full-fledged costumes for an adult.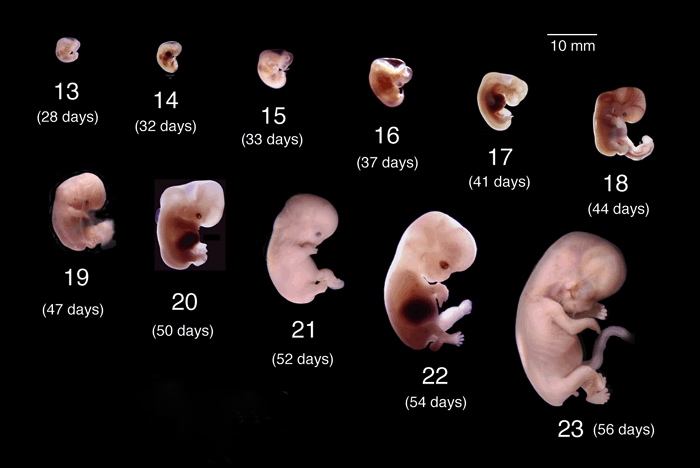 I even saw such candlesticks.
I even saw such candlesticks.
Me and a Nazarenos mannequin
These are “ nazarenos ” (nazarenes), or “penitent sinners”: this is the name of the participants in the Easter processions that pass through the city and publicly repent of sins. Participation in such a procession grants forgiveness to the sinner, caps covering the face capirote are needed for anonymity, and their pointed shape should lift the prayer as high as possible into the sky.
Nazarenos outfits are sold throughout the city, but most of the shops are concentrated on Alcaiceria de la Loza. The cap is customized in size right at the buyer.
Tourists associate these costumes with the clan, but they have nothing to do with it. And the reaction of tourists causes irritation among the locals – who likes to explain several times a day that “this is not the Ku Klux Klan, but a Spanish tradition”?
nine0005 Nazarenos figurines in a souvenir shop in Cadiz
It is believed that the tradition of processions originated with the first Christian preachers on this earth. To tell the pagans the story of Christ and his suffering, they carried figures and images with them. New converts joined these processions: they accompanied the preachers and repented of their sins. Later, these parades were streamlined and limited until the period of Lent.
Holy Week is the culmination of Lent. During this week, several dozen processions take place in Seville. For a tourist, they seem the same, but each is unique and is conducted by a separate brotherhood: 36 people, hiding under a veil, carry on their shoulders carts with images of the Virgin Mary or Jesus in human growth. No wagon is alike: they depict different situations, with different meanings, and the brotherhood keeps it all year round and decorates it for the holiday.
nine0005
 It is worth taking places along the route in the morning, and the best view is from balconies and terraces along the procession. The most interesting and spectacular moment of the procession is the removal of figures from the church.
It is worth taking places along the route in the morning, and the best view is from balconies and terraces along the procession. The most interesting and spectacular moment of the procession is the removal of figures from the church. Information about processions and events – on the Semana Santa website
Semana Santa lasts from Palm Sunday (analogue of Palm Sunday) until Great Saturday. There are no religious processions on Easter Sunday itself.
nine0005
Semana Santa dates in Spain:
| 2020: | April 5 — April 11 |
| 2021: | March 29 — April 3 |
| 2022: | April 10 — April 16 |
| 2023: |
April 2 — April 8 nine0243 |
| 2024: | March 24 — March 30 |
Since Holy Week falls at the end of Lent, traditional dishes do not contain meat. But they contain fish and seafood. Therefore, at this time, there are especially a lot of seasonal marine offers in establishments.
In the period before Easter, you can try some local sweets: torrija (torrija) – egg-dipped toast, soaked in wine or milk, fried, sweetened with sugar and sprinkled with cinnamon; and pestiño (pestiño) – fried pastries glazed with honey. At other times, these desserts are almost impossible to find.
Almost immediately after the New Year, edible “nazarenos” appear in all confectioneries: caramel, chocolate, gingerbread – ranging in size from a small candy to a 30-centimeter figure.
Torrijas – Andalusian Easter PastryPestinhos Easter Cookies
From Maundy Thursday to Easter Sunday, traffic in the city center stops, and solemn processions take place in the afternoon. If you are going to shop – do it before lunch, and if you want to watch the processions – the question of “where to live” becomes more important than ever in Seville.
nine0005
Processions take place in all districts of the city, but the brightest are in the center, near the cathedral. Considering that ground transport will be blocked, it is worth stopping either in the very historical center and within walking distance from it, or not far from any station of the only metro line in Seville.
I recommend two inexpensive hotels 10 minutes walk from the Cathedral and the Alcazar, where I stayed myself.
A small hotel on 3 floors with a roof terrace and a good view – in the evening we drank tea here with a view of the Giralda and several more city bell towers.
nine0005
Rooms for two at Boutike Hostel are decently sized, freshly refurbished and with private bathrooms starting at €70. The price includes a good breakfast with freshly baked waffles and 24/7 access to tea and coffee. During the day, the kitchen always has something for tea: muffins, waffles, cookies, muffins. You can use the refrigerator. And upon arrival, they are treated to welcame beer – which is especially nice when the famous Seville heat is already on the street.
From the hotel – 5 minutes walk to the “Seville mushrooms”, 10-15 minutes – to the cathedral and 20 minutes to the central railway station.
nine0005 Cozy lobby of a boutique hotel The common kitchen is well equipped: there is even a smoothie blender
Santiago 15 Casa Palacio is a small boutique hotel set in a historic building with a spacious Andalusian courtyard.