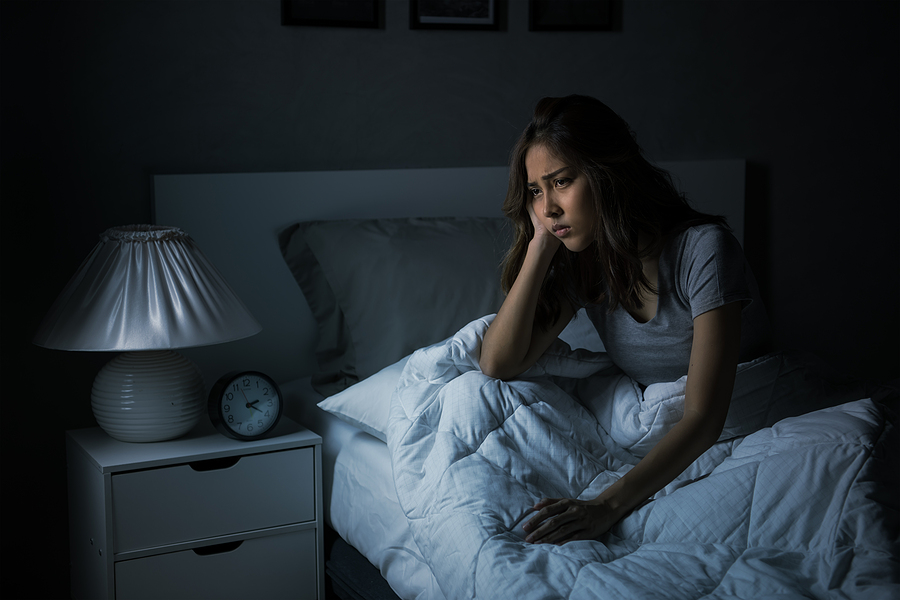
Es posible que duerma bien durante el primer trimestre. Es probable que también necesite dormir más de lo usual. Su cuerpo está trabajando arduamente para formar a un bebé. Así que se cansará fácilmente. Pero más adelante en su embarazo, le puede costar trabajo dormir bien.
Su bebé está creciendo, lo cual puede hacer que sea difícil encontrar una posición cómoda para dormir. Si usted siempre ha dormido boca abajo o boca arriba, es posible que tenga problemas para acostumbrarse a dormir de lado (como los proveedores de atención médica lo recomiendan). Además, cambiar de posición en la cama se hace más difícil a medida que usted se vuelve más grande.
Otras situaciones que pueden impedirle dormir incluyen:
 También se puede presentar estreñimiento.
También se puede presentar estreñimiento.Trate de dormir de lado. Acostarse de lado con las rodillas dobladas probablemente será la posición más cómoda. Esto hace que para su corazón sea más fácil bombear, ya que impide que el bebé ejerza presión sobre la vena grande que lleva sangre de nuevo al corazón desde sus piernas.
Muchos proveedores les recomiendan a las mujeres embarazadas dormir sobre el lado izquierdo. Dormir sobre el lado izquierdo también mejora el flujo de sangre entre el corazón, el feto, el útero y los riñones. Además, quita la presión sobre el hígado. Si su cadera izquierda siente mucha molestia, ESTÁ BIÉN cambiarse un rato al lado derecho. Es mejor no dormir boca arriba.
Si su cadera izquierda siente mucha molestia, ESTÁ BIÉN cambiarse un rato al lado derecho. Es mejor no dormir boca arriba.
Pruebe con el uso de almohadas por debajo del vientre o entre las piernas. Igualmente, el uso de una almohada recogida o una manta enrollada en la parte baja de la espalda puede aliviar algo de la presión. También puede probar con un colchón tipo cartón de huevos en su lado de la cama para brindar un poco de alivio a las caderas adoloridas. El hecho de tener almohadas adicionales disponibles para apoyar su cuerpo también ayuda.
Estos consejos con seguridad mejorarán sus probabilidades de lograr una buena noche de sueño:

Si el estrés o la ansiedad respecto al hecho de convertirse en madre le está impidiendo dormir bien, pruebe:

No tome ninguna ayuda para dormir. Esto incluye medicamentos de venta libre y productos a base de hierbas. No se recomiendan para mujeres embarazadas. No tome ningún medicamento por cualquier razón sin consultar al proveedor.
Cuidado prenatal – dormir; Cuidado durante el embarazo – dormir
Antony KM, Racusin DA, Aagaard K, Dildy GA. Maternal physiology. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe’s Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 3.
Balserak BI, Lee KA. Sleep and sleep disorders associated with pregnancy. In: Kryger M, Roth T, Dement WC, eds. Principles and Practice of Sleep Medicine. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 156.
Versión en inglés revisada por: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A. D.A.M. Editorial team.
D.A.M. Editorial team.
Traducción y localización realizada por: DrTango, Inc.
Hojee la enciclopedia
Ginecología ·Embarazo
Actualizado a
Mª del Rosario Román Gálvez
Enfermera
Los problemas de insomnio durante el embarazo son muy frecuentes y la razón no es simplemente la dificultad por encontrar una posición ideal. Y, además, el tiempo que la mujer tarda en dormirse y el número de veces que se despierta a lo largo de la noche (fragmentación del sueño) aumentan a medida que va avanzando la gestación.
Un reciente estudio de la Universidad de Granada ha comprobado la incidencia del insomnio entre mujeres embarazadas. Y alerta de que no se da la suficiente importancia a este problema, que debería ser abordado adecuadamente por los médicos de forma no farmacológica.
Y es que si el insomnio tiene una repercusión en la salud y calidad de vida de cualquier persona, en la mujer embarazada comporta una serie de riesgos añadidos. Saber Vivir ha hablado con las autoras de esta investigación.
En el estudio liderado por la Universidad de Granada, y que ha publicado la revista “European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology”, han participado 486 mujeres embarazadas sanas a las que se les realizó el seguimiento a lo largo de todo el embarazo.
2 de cada 3 embarazadas sufren insomnio en el tercer trimestre
Y los datos recogidos reflejan que los problemas de insomnio van aumentando durante la gestación, llegando a afectar a 2 de cada 3 mujeres en la última etapa del embarazo:

Esta última cifra es 10 veces superior al número de mujeres que sufren insomnio antes de quedarse embarazadas, que se calcula que ronda el 6%.
“Los resultados de nuestro estudio muestran que en el primer trimestre del embarazo hay una afectación importante de la fragmentación del sueño, es decir, las veces que la mujer se despierta durante la noche y el tiempo que permanece despierta en estos despertares, así como de la somnolencia diurna”, nos explica María Rosario Román Gálvez, autora principal de la investigación.
Los despertares aumentan, pero también el tiempo que la mujer tarda en dormirse
En las siguientes etapas de la gestación, aumenta tanto la frecuencia como la intensidad de esta fragmentación del sueño, “pero además también se ve afectada la inducción, o sea, el tiempo que tarda en dormirse cuando se acuesta, y el tiempo total de sueño“, aclara la investigadora.
Esta falta de horas de sueño y de un descanso reparador puede entrañar una serie de riesgos para la salud. “En la población general, el insomnio se asocia con deficiencias sustanciales en la calidad de vida, con patologías respiratorias, digestivas, metabólicas, neurodegenerativas y psiquiátricas, e incluso con un aumento de la mortalidad”, recuerda Román Gálvez.
El insomnio puede provocar hipertensión o riesgo de parto prematuro
Y nos explica que, en las mujeres embarazadas, el déficit de sueño está vinculado además a un mayor riesgo de sufrir estos otros problemas de salud:

Aunque el trabajo, resultado de una tesis doctoral dirigida por las profesoras de la Universidad de Granada Carmen Amezcua y Aurora Bueno, no se ha centrado en estudiar las causas del insomnio durante el embarazo, las investigadoras apuntan algunos factores.
“Hemos visto que tienen un mayor riesgo de padecer insomnio en cada momento de la gestación aquellas mujeres que ya lo padecían con anterioridad, cosa que parece evidente pero que es muy necesario tener en cuenta para prevenirlo”, advierte Román Gálvez.
Los cambios físicos y hormonales favorecen el insomnio gestacional
Pero hay otros factores. “En el tercer trimestre, la obesidad y el hecho de tener otros hijos aumentan el riesgo de insomnio. También sabemos por otros estudios que los cambios anatómicos y hormonales influyen en el insomnio gestacional”, añade.
“En el tercer trimestre, la obesidad y el hecho de tener otros hijos aumentan el riesgo de insomnio. También sabemos por otros estudios que los cambios anatómicos y hormonales influyen en el insomnio gestacional”, añade.
Las investigadoras alertan de que, aunque se sabe que durante el embarazo se agravan los problemas de sueño previos y con mucha frecuencia surgen otros nuevos, en el sistema sanitario no se les presta la atención que se debería durante el seguimiento del embarazo.
Las autoras del estudio advierten de que no se le da la importancia que se debería
Es más, ni siquiera la Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS) se ocupa del sueño en su guía de atención a mujeres gestantes.
“Existe una tendencia a asumir la dificultad para conciliar y mantener un sueño reparador como un fenómeno propio del embarazo que hay que sufrir con él“, afirma Carmen Amezcua.
Por esta razón, las autoras del estudio consideran muy importante que el sistema sanitario aborde el insomnio durante el embarazo de forma sistémica y que se realice una detección precoz. “Al realizarla no solo se determina si existe o no insomnio, sino también la intensidad del mismo. O incluso la proximidad a la existencia del insomnio cuando este aún no existe”, cuenta María Rosario Román Gálvez.
“Al realizarla no solo se determina si existe o no insomnio, sino también la intensidad del mismo. O incluso la proximidad a la existencia del insomnio cuando este aún no existe”, cuenta María Rosario Román Gálvez.
Dado que la obesidad es uno de los factores de riesgo, “prevenirla en el embarazo o luchar contra ella es también una manera de prevenir el insomnio”, añade la investigadora.
Recomendar la práctica de ejercicio entre las embarazadas podría contribuir a reducir tanto la obesidad como el déficit de sueño. “Las gestantes que realizan actividad física tienen menor riesgo de insomnio. Siempre que por motivos de salud, incluido el riesgo para el embarazo, no esté contraindicado, se recomienda un mínimo de 30 minutos de actividad física moderada durante 5 días a la semana“, aconseja Román Gálvez.
Recomiendan al menos 30 minutos diarios de actividad física y terapias como relajación y yoga
Realizar terapia conductual básica y otras técnicas alternativas, como relajación o yoga perinatal, son algunas de las actividades que pueden ayudar a prevenir y combatir el insomnio durante el embarazo según la investigadora.
Newsletter
Recibe cada semana toda la actualidad y los mejores consejos de salud para cuidarte día a día. Ver ejemplo
Suscribiéndote a nuestra newsletter, estás
aceptando la Política de Privacidad
Deseo recibir comunicaciones comerciales sobre productos y/o servicios ofrecidos por la Comunidad RBA. Ver la Política de Privacidad
Deseo recibir comunicaciones comerciales de terceras empresas colaboradoras de la Comunidad RBA. Ver la Política de Privacidad
Web acreditada por:
Entidades sanitarias colaboradoras:
Saber Vivir es una web especializada en salud y bienestar. Nuestros artículos se redactan con fines informativos y, en ningún caso, pueden sustituir el diagnóstico de un profesional. Ante cualquier problema de salud, consulte con su médico.
¿Deseas dejar de recibir las noticias más destacadas de Saber Vivir?
Therapist, pulmonologist, somnologist
Novikov
Maxim Sergeevich
Experience 16 years
Doctor of the highest category. Member of the European Respiratory Society and the Russian Respiratory Society
Make an appointment
Insomnia is the most common type of sleep disorder, scientifically called insomnia. A healthy sleep of a person should take 7-8 hours a day, and its normal course occurs at night and is replaced by wakefulness during the daytime. Hours of cheerfulness should fall on the time of business activity, this is required by the arrangement of life around a person. In the case when a person did not get enough sleep at night, during the day he begins to work worse. This is most pronounced among intellectual workers. Concentration is also impaired, which increases the risk of injuries and accidents. Chronic insomnia is the most dangerous type of disease. Because it has a negative effect on the human body and its reactions. Irritability, nervousness, malaise, weak immunity and memory impairment are just a small list of the possible effects of insomnia.
Chronic insomnia is the most dangerous type of disease. Because it has a negative effect on the human body and its reactions. Irritability, nervousness, malaise, weak immunity and memory impairment are just a small list of the possible effects of insomnia.
Such a violation in the standard manifestation is expressed in the absence of sleep at night. In this case, the patient has the intention to fall asleep, but he does not succeed. Medicine interprets sleep disturbance in the form of insomnia much more broadly, paying attention not only to the duration of sleep, but also to its quality. Often a person who wakes up does not get enough sleep and suffers from insomnia in the morning. This also includes difficulties in the process of falling asleep. It is considered normal to fall asleep for a maximum of 15 minutes, while sleep disturbance stretches this period for several hours.
Sleep disturbance in adults in the form of very early awakening is one type of insomnia. This also includes post-traumatic failures – fatigue after a whole night of sleep, weakness and lethargy.
This also includes post-traumatic failures – fatigue after a whole night of sleep, weakness and lethargy.
The main feature of the disease is the absence of a restorative stage of sleep.
Symptoms of sleep disorders are varied:
The causes of insomnia are symptomatic or mental and somatic.
The most common risk factors for the development of pathology are:

Depression is an independent cause of insomnia. Since this condition causes defects in the functioning of the adrenal glands, pituitary gland and hypothalamus, too much cortisol is released into the bloodstream, which disrupts the quality of sleep.
Other causes of sleep disturbance include:
Why is insomnia caused by restless legs? The presence of discomfort causes a desire to shift the legs from place to place in search of a comfortable position, resulting in uncontrolled excitement in the body during sleep. The same principle applies to pain or injury.
Insomnia occurs for the following reasons:

Circadian rhythms can be disrupted by shift work. The risk group for developing pathology includes people of all ages of any gender.
The most common risk groups:
Complications of insomnia:
What to do about insomnia? This question is asked very often by people. Going to the doctor is the easiest and surest answer. Consultation can be obtained from a general practitioner, a neurologist or a special somnologist. They will study the cause of your problem, if necessary, prescribe tests and, based on the data obtained, will solve it using effective and safe methods. In our clinic you can get advice from any of these specialists.
In our clinic you can get advice from any of these specialists.
Insomnia is diagnosed on a special scale based on 8 different parameters one way or another related to sleep. The collection of anamnesis data and physical examination allow us to exclude other conditions for the development of pathology.
Diagnosis involves compiling a sleep history, including sleep habits and medications or other substances taken. To this end, the patient should keep a sleep diary to help develop sleep patterns. The diary should include data on the time of falling asleep and waking up, the duration of sleep, the number of awakenings, medications and their effect, as well as other feelings of the patient at night and in the morning. An alternative to the diary is an outpatient actigraphy procedure – a weekly control using non-invasive devices that measure movements. In the event that insomnia is symptomatic, then the diagnosis is aimed at identifying the underlying disease. After all, the treatment of insomnia will depend on the success of the provocateur factor.
After all, the treatment of insomnia will depend on the success of the provocateur factor.
The first step in the treatment of sleep disorders is lifestyle modification and sleep hygiene. This is where cognitive behavioral therapy fits in perfectly. What to do with symptomatic insomnia? Find the causes and treat them first. Mostly, special sleeping pills are prescribed as a remedy for insomnia as a short-term measure. Insomnia pills give you the ability to control sleep.
Music is perceived as a remedy for insomnia. Special trainings can become a cure for insomnia. Self-help is based on the use of psychological training. How to deal with insomnia? One method is forced wakefulness. This means that instead of trying to fall asleep, a person should do everything not to fall asleep. Thus, there is a reprogramming of brain activity.
Measures to prevent insomnia:

You can make an appointment with the specialists of Medicina JSC (Academician Roitberg Clinic) in the center of Moscow (Mayakovskaya metro station) by phone +7 (495) 775-73-60 (24/7) by filling out the application form on the website or with the clinic administrators at : Moscow 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskoy pereulok 10.
{{if type === ‘partner-stocks’}}
{{/if}}
{{/if}}
{{each list}}
${this}
{{if isGorzdrav}}
Delete
{{/if}}
{{/each}}
{{/if}}
Search by drug, disease, substance:
DERMAKOSMETIKA, SOLGAR, NaturAge, Voltaren, Kagocel
Home
Articles
Prevention and treatment of insomnia
Sleep is as much a human need as food and water. If you completely abandon it or reduce the duration to several hours, then after 4-5 days serious health problems will appear. Even the replacement of night sleep with daytime sleep is harmful for those who have to work for days. Lack of proper sleep leads to endocrine disorders, diseases of the cardiovascular and digestive systems, nervous and mental diseases. Therefore, insomnia, or insomnia, is a disease in which the process of falling asleep or sleep itself is disturbed.
If you completely abandon it or reduce the duration to several hours, then after 4-5 days serious health problems will appear. Even the replacement of night sleep with daytime sleep is harmful for those who have to work for days. Lack of proper sleep leads to endocrine disorders, diseases of the cardiovascular and digestive systems, nervous and mental diseases. Therefore, insomnia, or insomnia, is a disease in which the process of falling asleep or sleep itself is disturbed.
Insomnia is more common in women than in men. And in pregnant women, it is observed in 75% of cases. Women are prone to the disease during menopause, when hormonal changes cause a surge in thyroid activity in the evening and at night. This is accompanied by tachycardia, sweating and inability to sleep.
Insomnia has a large number of causes, some of them are related to a person’s lifestyle:

Night sleep disorders can be caused by somatic diseases. Insomnia leads to problems with digestion, heart disease and blood vessels, increased activity of the thyroid gland. Pain and aches in the joints with arthritis or SARS will also not allow you to fall asleep.
At an older age, insomnia is associated with age-related changes in the brain, the development of Parkinson’s disease, dementia and other neurological causes. But regardless of the factors due to which a person cannot sleep, the problem requires treatment.
Scientists believe that healthy sleep is a reflex mechanism. If a person went to bed and did not fall asleep after 15-20 minutes, do not lie further in it. Otherwise, this will lead to the formation of a new reflex: bed-insomnia.
It is possible to deal with acute insomnia on your own, which occurred for the first time. First you need to get rid of the factors that prevent you from falling asleep. To do this, you need to turn off the TV or computer monitor, hang windows if the light of lanterns or the moon breaks through the window.
To do this, you need to turn off the TV or computer monitor, hang windows if the light of lanterns or the moon breaks through the window.
Difficulty falling asleep in a stuffy and hot room. Therefore, if the question arose of how to fall asleep with insomnia, you need to open a window for ventilation, reduce the heat supply in heating batteries. At this time, you can go for a leisurely walk in the fresh air. After returning home, drink a glass of warm milk, herbal tea. This is an old method that has proven effective for mild disorders.
Milk contains substances that help produce melatonin. It is a hormone of the pineal gland that regulates circadian rhythms, changes in the state of sleep and wakefulness, and controls the functioning of the immune and endocrine systems. Therefore, insomnia increases the risk of infectious diseases and metabolic disorders, problems in the male genital area.
Reading helps you fall asleep quickly. But for this you need to choose not an exciting detective story, but literature of a calm orientation, which usually causes drowsiness. If these methods did not help to fall asleep, the violations persist and disturb regularly, examination and consultation with a doctor is necessary.
If these methods did not help to fall asleep, the violations persist and disturb regularly, examination and consultation with a doctor is necessary.
In order not to have to look for ways to treat insomnia, it is necessary to take preventive measures:
Daytime sleep will not interfere with falling asleep in the evening, if you allocate 1-2 hours for it. But if they replace night rest, this will provoke the development of insomnia.
Morning rise is also included in the prevention of insomnia. You need to try to get up at the same time, to increase the tone – do exercises. In order not to disturb the sleep reflex, there is a recommendation not to use the bed for other purposes. You should lie down in it only when drowsiness appears and do not stay for a long time to eat, read or watch a movie.
In order not to disturb the sleep reflex, there is a recommendation not to use the bed for other purposes. You should lie down in it only when drowsiness appears and do not stay for a long time to eat, read or watch a movie.
You can fight bad sleep on your own. For mild forms of insomnia, alternative methods of treatment can be used. At home, they make foot baths with dill, after which they take a glass of warm milk with honey and quickly go to bed. In case of increased nervous excitability, prefabricated infusions of medicinal herbs help, for which they use:
If the cause of the disturbance is stress, it is necessary to use methods of struggle that calm the nervous system. At home, you can apply various methods of relaxation, learn meditation. Complement their action with aromatherapy. Quickly relieve nervous tension essential oil of mint, lemon balm, chamomile.
Sleep rituals help you fall asleep effectively. If you choose the same time for this, perform a certain list of actions (dinner, airing the room, hygiene before bedtime and other options), then with each such preparation, the body will tune in to a quick fall asleep.
For people who are engaged in mental work during the day, hard physical work helps to cure insomnia. This is called the “peasant life effect”. After a heavy load, a person increases the production of the hormone adenosine. This substance causes a feeling of fatigue, inhibits brain activity, which leads to early falling asleep.
It is difficult to deal with insomnia during pregnancy. In the later stages, the deterioration of falling asleep is associated with a deterioration in lung ventilation and excitability of the nervous system. Most drugs are prohibited for use in pregnant women. Therefore, they choose simple ways to improve sleep: a comfortable position on the side of the bed with a raised edge, the use of a special pillow for pregnant women, airing the room and valerian tablets.
If home remedies do not cure insomnia, see a doctor. To restore a normal sleep pattern, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the disturbance. Therefore, the first drugs will be used against the underlying disease.
Drug therapy is initiated with safe agents. Your doctor may prescribe melatonin tablets, which is an analogue of your own hormone. They treat sleep disorders and do not have many side effects. The development of habituation practically does not happen. But if used improperly, nightmares and headaches may appear. Therefore, the drug should be used after consulting a doctor.
The doctor can prescribe tablets for severe sleep disorders. But they do not cure the disease if it is associated with stress, sleep hygiene disorders. Therefore, any treatment should be accompanied by preventive measures. Drugs based on doxylamine, for example, Valocordin-doxylamine, cure sleep disorders. They are available in the form of tablets, drops for oral administration.