Autor: Dr. Pedro Pinheiro
Sin comentarios
Actualizado:
Tiempo estimado de lectura: 3 minutos.
Los bebés comienzan a moverse dentro del útero alrededor de la octava semana de embarazo, pero sus movimientos son discretos y aún es demasiado pequeño para que la mujer embarazada lo sienta. Solamente por ecografía se puede detectar la actividad fetal tan temprano.
Por lo tanto, en la mayoría de los embarazos, los primeros movimientos fetales pueden ser percibidos efectivamente por la madre solamente a partir de la 18ª semana de gestación, momento en el cual el bebé ya es lo suficientemente grande.
Si la madre es delgada y ha tenido otros embarazos, puede comenzar a sentir que el bebé se mueve un poco antes, alrededor de la 16ª semana.
Por otro lado, si la madre tiene mucha grasa abdominal, si es el primer embarazo o si la placenta se coloca en la porción anterior del útero, las primeras “patadas” del bebé pueden aparecer solamente después de la 22ª semana.
Sobre los síntomas del embarazo, lee también: 21 primeros síntomas del embarazo.
Inicialmente, los movimientos son discretos, y si es el primer embarazo, puede confundir fácilmente los movimientos del bebé con los movimientos de las asas intestinales.
El sentimiento es realmente de gases. Algunas madres los describen como ampollas que estallan dentro del vientre o el estómago y sienten un gruñido. Otras descripciones comunes incluyen: “mariposas en el vientre”, “palpitaciones en el útero”, “temblores internos”, “algo rodando dentro del vientre”, “contracciones nerviosas”, “frío en el vientre” o “peces nadando”.
A medida que su bebé se hace más grande, más fuerte y activo, ya no tendrá dudas cuando se esté moviendo y comenzará a sentir las patadas, que son movimientos repentinos que extienden la pared del útero.
A partir de la 25ª semana, otras personas también pueden sentir los movimientos. Basta solamente poner tus manos sobre tu vientre y esperar.
En el tercer trimestre (28ª semana en adelante), no solo sentirás, sino que incluso podrás ver a través del abdomen al bebé moviéndose y estirándose. En esta etapa, como la pared abdominal se estira por completo por el útero agrandado, cualquier movimiento repentino del bebé se puede notar fácilmente.
En el primer embarazo, solamente se puede notar los primeros movimientos en la 24ª semana. Esto es especialmente común si la mujer embarazada tiene sobrepeso u obesidad.
También es importante tener en cuenta que a menudo la mujer embarazada ya siente que el bebé se mueve, pero confunde los movimientos con gases intestinales.
Hasta la 24ª semana del embarazo si todo es normal en los exámenes del prenatal, incluyendo la ecografía fetal, no tienes que preocuparte si no sientes que el bebé se mueve.
El bebé no se mueve todo el tiempo, pero es normal sentirlo moverse varias veces durante el día. No hay un número específico de movimientos considerados normales para que sigas contando. Cada bebé tiene sus características.
No hay un número específico de movimientos considerados normales para que sigas contando. Cada bebé tiene sus características.
Por lo tanto, durante el embarazo, debes reconocer el patrón de movimiento individual de tu bebé. Una reducción brusca o un cambio prolongado en el patrón pueden ser un signo de un problema.
El número de movimientos tiende a aumentar hasta las 32 semanas de gestación y luego se mantiene más o menos estable hasta cerca del parto.
Los movimientos generalmente se detienen cuando el bebé duerme, un hecho que generalmente dura de 20 a 40 minutos. Raramente la siesta del bebé toma más de 90 minutos.
El bebé suele estar más activo por la noche, especialmente entre las 9 p.m. y las 2 a.m.
Cuando el bebé está despierto, se mueve unas 30 veces por hora, pero no todos los movimientos son notables.
En el segundo y tercer trimestres, los estudios de ecografía mostraron que los bebés tienen un amplio rango de movimiento, que incluye flexiones del tronco, hipos, rotaciones corporales, estiramientos, movimientos de las extremidades, movimientos de succión, protrusión de la lengua, movimientos de la cabeza, apertura y cierre de manos, etc.
De los movimientos detectados por ultrasonido, aproximadamente el 50% de los movimientos aislados de las extremidades y el 80% de los movimientos que involucran el tronco y una de las extremidades fueron percibidos por la madre.
Si estás ocupada o trabajando durante todo el día, los movimientos pueden pasar desapercibidos. En caso de duda, para confirmar que tu bebé se está moviendo normalmente, debe relajarte y descansar durante al menos 30 minutos con tu vientre hacia arriba y alerta.
Hay otros factores que pueden hacer que los movimientos de tu bebé sean menos notorios sin indicar necesariamente un problema.
Por ejemplo, si tu placenta está en la parte anterior de tu útero (en la parte delantera de tu útero), ella puede actuar como un cojín para sofocar los movimientos del bebé. Una situación similar puede ocurrir cuando la espalda de tu bebé está contra el frente de tu útero, ya que sus brazos y piernas están lejos de tu vientre.
A partir de la 28ª semana de embarazo, la gestante ya puede tener una idea del patrón normal de movimiento de tu bebé.
Si nota un cambio en el patrón normal, acuéstate boca arriba, comienza a cronometrar y cuente tus movimientos. Si no sientes al menos 10 movimientos en 2 horas, consulta a tu obstetra.
En general, cuando todo está bien, la mujer embarazada puede contar 10 movimientos en solamente 30 minutos. Pero algunos bebés, naturalmente, pueden ser más «perezosos».
Existen aplicaciones para teléfonos inteligentes que ayudan a las mujeres embarazadas a contar los movimientos fetales. Si sabes cuál es el patrón normal de su bebé, es más fácil y rápido identificar cuándo surge un problema.
Hasta el 40% de las madres informa una reducción del movimiento fetal en algún momento de su embarazo. En la mayoría de los casos, la imagen no es una reducción real del movimiento, sino algo simplemente transitorio.
Una reducción real en el movimiento fetal es un signo de problemas de embarazo y un mayor riesgo de muerte para el bebé.
Aproximadamente 1 de cada 4 embarazos que progresan con un movimiento fetal reducido tienen uno de los siguientes problemas:
Si sospechas de una reducción en el movimiento fetal, cuenta y contacta a tu obstetra de inmediato. No esperes al día siguiente para ver si mejorarás.
Médico licenciado por la Universidad Federal de Río de Janeiro (UFRJ), con títulos de especialista en Medicina Interna por la Universidad Federal de Río de Janeiro (UFRJ) y de Nefrología por la Universidad Estadual de Río de Janeiro (UERJ) y por la Sociedad Brasileña de Nefrología (SBN). Actualmente vive en Lisboa, Portugal, tiene títulos reconocidos por la Universidad de Oporto y por el Colegio de Nefrología de Portugal.
Categorías Síntomas del embarazo, Embarazo
COMENTARIOS (por favor, lea las reglas del sitio antes de enviar su pregunta).
El distrés fetal es una complicación obstétrica, durante el trabajo de parto y el parto que implica un monitoreo cardiaco fetal anormal que ocurre cuando el feto experimenta privación de oxígeno (asfixia de nacimiento). Se detecta por cambios en la frecuencia cardíaca, disminución del movimiento fetal y sustancias anormales en el líquido amniótico. Debido a que el sufrimiento fetal agudo es una complicación de emergencia, los profesionales médicos deben tratar y manejar inmediatamente para evitar la EHI (encefalopatía hipóxico-isquémica) y una lesión permanente. Las madres embarazadas no siempre están con su médico cuando aparecen signos de sufrimiento fetal agudo. Dentro o fuera de la oficina del médico, es importante conocer los signos que indican que el bebé está en problemas. La acción inmediata es casi siempre necesaria cuando un bebé muestra signos de sufrimiento. A menudo, la única manera de detener el sufrimiento fetal agudo es dar a luz al bebé, apartándolo de condiciones de sufrimiento. Esto se logra frecuentemente mediante la administración de la cesárea.
Se detecta por cambios en la frecuencia cardíaca, disminución del movimiento fetal y sustancias anormales en el líquido amniótico. Debido a que el sufrimiento fetal agudo es una complicación de emergencia, los profesionales médicos deben tratar y manejar inmediatamente para evitar la EHI (encefalopatía hipóxico-isquémica) y una lesión permanente. Las madres embarazadas no siempre están con su médico cuando aparecen signos de sufrimiento fetal agudo. Dentro o fuera de la oficina del médico, es importante conocer los signos que indican que el bebé está en problemas. La acción inmediata es casi siempre necesaria cuando un bebé muestra signos de sufrimiento. A menudo, la única manera de detener el sufrimiento fetal agudo es dar a luz al bebé, apartándolo de condiciones de sufrimiento. Esto se logra frecuentemente mediante la administración de la cesárea.
Señales de Distrés Fetal
1. Signos de distrés fetal: Disminución del Movimiento Fetal en el Vientre
El movimiento fetal dentro del vientre de la madre es una de las partes más emocionantes del embarazo. Más allá de traer alegría a la familia, el movimiento dentro del útero es un indicador importante de la salud de su bebé. La falta de movimiento fetal es algo que requiere monitoreo por parte del médico. Los bebés duermen en el vientre, por lo que eso puede explicar una falta de movimiento. Sin embargo, si los movimientos de su bebé son diferentes de lo normal, debe visitar a su médico para asegurarse de que su bebé no está en peligro.
Más allá de traer alegría a la familia, el movimiento dentro del útero es un indicador importante de la salud de su bebé. La falta de movimiento fetal es algo que requiere monitoreo por parte del médico. Los bebés duermen en el vientre, por lo que eso puede explicar una falta de movimiento. Sin embargo, si los movimientos de su bebé son diferentes de lo normal, debe visitar a su médico para asegurarse de que su bebé no está en peligro.
Los movimientos de un bebé suelen estar bien establecidos alrededor de las 28 semanas de gestación. Si una madre nota que los movimientos de su bebé han cesado o disminuido, debe notificar a su médico para que éste pueda examinarla y asegurarse de que el bebé esté sano y no en peligro. El médico debe realizar una prueba de no estrés (PNE), que consiste en colocar un cinturón en el abdomen de la madre para medir la frecuencia cardíaca del bebé y otro cinturón para medir las contracciones. También se puede realizar un perfil biofísico (PBF). Un PBF incluye múltiples exámenes, como un PNE con monitoreo fetal electrónico del corazón y un ultrasonido fetal. Para obtener más información sobre las pruebas prenatales usadas para monitorear el sufrimiento fetal, visite esta página.
Para obtener más información sobre las pruebas prenatales usadas para monitorear el sufrimiento fetal, visite esta página.
Un ultrasonido puede obtener una medida llamada índice del líquido amniótico, o ILA. El ILA se calcula midiendo la profundidad del líquido amniótico en cuatro secciones del útero y añadiéndolas. A corto plazo, un ILA entre 9-18 centímetros se considera normal, 5-8 se considera límite, y 5 o inferior se considera anormal. Una disminución repentina en el líquido amniótico o una disminución significativa en un período corto de tiempo se considera anormal, incluso si el ILA está por encima de 5. Con un PNE, los médicos buscan ver qué tan bien la frecuencia cardíaca del bebé responde al movimiento. El ritmo cardíaco del bebé debe aumentar cuando se está moviendo o pateando. Un PNE normal se llama “reactivo”, lo que significa que el ritmo cardíaco del bebé aumentó normalmente. “No reactivo” significa que la frecuencia cardíaca del bebé no aumentó lo suficiente. Cuando esto ocurre, se deben realizar más pruebas, y a veces la madre tiene que ser admitida en el hospital y puede tener que dar a luz a su bebé temprano.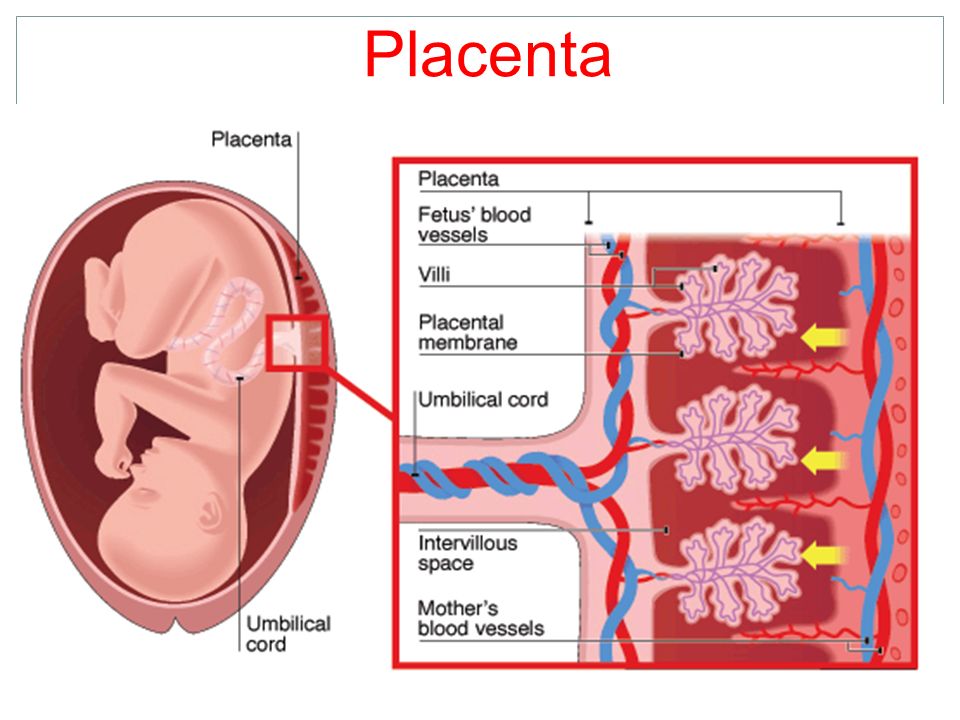
El sufrimiento fetal agudo típicamente indica que el bebé no está recibiendo suficiente oxígeno. Esto puede ocurrir por una serie de razones, incluyendo problemas con la placenta y / o cordón umbilical (la placenta trae sangre rica en oxígeno de la madre al bebé a través del cordón umbilical).
Las lesiones de nacimiento son difíciles para su familia. Podemos ayudar. (248) 593-5100
2. Signos de Distrés Fetal: Sangrado Vaginal
Pequeñas cantidades de sangrado son algo común durante el embarazo. Sin embargo, el sangrado vaginal puede ser una indicación de que algo está mal con el embarazo, como la presencia de desprendimiento placentario, placenta previa y vasa previa. El desprendimiento placentario ocurre cuando la placenta se desprende del útero. Dependiendo de la ubicación y el tamaño del desprendimiento, puede no causar inicialmente sufrimiento fetal agudo en el bebé. Sin embargo, un pequeño desgarro puede aumentar en tamaño y causar sufrimiento, y también puede convertirse en un desgarro grande y grave muy rápidamente.
Por supuesto, un desprendimiento de la placenta también puede estar presente sin sangrado vaginal (el sangrado puede estar oculto), pero si una madre experimenta sangrado vaginal, el médico debe ser notificado para realizar una evaluación adecuada y asegurar que el bebé está recibiendo suficiente oxígeno. El médico debe realizar un ultrasonido para chequear el desprendimiento, y se debe revisar la frecuencia cardíaca del bebé para asegurar que no haya sufrimiento fetal agudo.
Un desprendimiento de placenta y otros problemas de la placenta que causan sangrado requieren un seguimiento muy estrecho de la madre y el bebé, y en muchos casos, la madre y el bebé deben ser admitidos en el hospital.
3. Señales de Distrés Fetal: Cólicos
Algunos cólicos son relativamente normales durante el embarazo. Esto es porque a medida que el bebé crece, el útero necesita expandirse. Sin embargo, los cólicos deben ser discutidos con el médico tan pronto como se producen – especialmente si los calambres se intensifican – para asegurarse de que no hay nada malo. Los cólicos pueden indicar muchas cosas, incluyendo desprendimiento de la placenta. Y los calambres son especialmente preocupantes si el dolor de espalda también está presente. Es crucial que los médicos aprecien los cólicos y realicen pruebas adecuadas para asegurar la salud de la madre y el bebé, y para asegurarse de que no se presenten problemas como el desprendimiento de la placenta.
Los cólicos pueden indicar muchas cosas, incluyendo desprendimiento de la placenta. Y los calambres son especialmente preocupantes si el dolor de espalda también está presente. Es crucial que los médicos aprecien los cólicos y realicen pruebas adecuadas para asegurar la salud de la madre y el bebé, y para asegurarse de que no se presenten problemas como el desprendimiento de la placenta.
4. Signos de Distrés Fetal: Presión Arterial Materna
La presión arterial alta durante el embarazo siempre es una preocupación. Algunas madres pueden haber tenido presión arterial normal antes del embarazo, pero luego tener la presión arterial alta una vez que quedan embarazadas, que es una condición de salud materna llamada preeclampsia. La presión arterial alta puede hacer que el bebé sea privado de oxígeno debido a problemas de placenta. En primer lugar, los problemas de la placenta en realidad pueden causar presión arterial alta en la madre debido a ciertos factores liberados por su cuerpo. Además, la presión arterial alta se asocia con los vasos sanguíneos estrechados, y esto en sí mismo causa una disminución en el flujo sanguíneo al bebé. Los problemas de los vasos sanguíneos pueden causar problemas en la placenta, y los problemas de la placenta pueden comprometer los vasos sanguíneos. Sea cual sea el mecanismo, existe una asociación entre la presión arterial alta y la disminución del flujo de oxígeno al bebé. Además, las mujeres que tienen preeclampsia están en alto riesgo de experimentar un desprendimiento placentario. Por lo tanto, es imprescindible que los médicos trabajen con la madre para hacer todo lo posible por mantener la presión arterial normal. Los profesionales médicos deben evaluar continuamente a las mujeres embarazadas con preeclampsia y vigilar a sus bebés.
Además, la presión arterial alta se asocia con los vasos sanguíneos estrechados, y esto en sí mismo causa una disminución en el flujo sanguíneo al bebé. Los problemas de los vasos sanguíneos pueden causar problemas en la placenta, y los problemas de la placenta pueden comprometer los vasos sanguíneos. Sea cual sea el mecanismo, existe una asociación entre la presión arterial alta y la disminución del flujo de oxígeno al bebé. Además, las mujeres que tienen preeclampsia están en alto riesgo de experimentar un desprendimiento placentario. Por lo tanto, es imprescindible que los médicos trabajen con la madre para hacer todo lo posible por mantener la presión arterial normal. Los profesionales médicos deben evaluar continuamente a las mujeres embarazadas con preeclampsia y vigilar a sus bebés.
5. Signos de Distrés Fetal: Ganancia de Peso
Los expertos creen que un aumento de peso de entre 20 y 40 libras es normal durante el embarazo. Si una madre gana mucho menos o mucho más que eso, podría señalar un problema. Una madre debe tener visitas prenatales regulares, y si se percata de ganar demasiado peso o perder peso, debe decirle a su médico para que se puedan realizar las pruebas prenatales apropiadas.
Una madre debe tener visitas prenatales regulares, y si se percata de ganar demasiado peso o perder peso, debe decirle a su médico para que se puedan realizar las pruebas prenatales apropiadas.
El exceso de aumento de peso materno también se asocia con dar a luz a un bebé que es anormalmente grande, que es una condición conocida como macrosomía. La macrosomía puede ser muy peligrosa para un bebé. La macrocosmía puede crear una situación de riesgo de nacimiento, como la desproporción cefalopélvica (CPD), en la que la pelvis de la madre es demasiado pequeña para el tamaño del bebé y la distocia del hombro, que es cuando el hombro del bebé queda atascado en el hueso pélvico de la madre durante el parto. La macrosomía es especialmente peligrosa si el médico no está al tanto de la condición. Un médico en esta situación puede tratar de hacer nacer al bebé por vía vaginal, y cuando el parto no progresa de la manera que debería, el médico puede utilizar dispositivos peligrosos, como fórceps y aspiradoras de vacío, o medicamentos de inducción de trabajo, tales como Cytotec y Pitocina.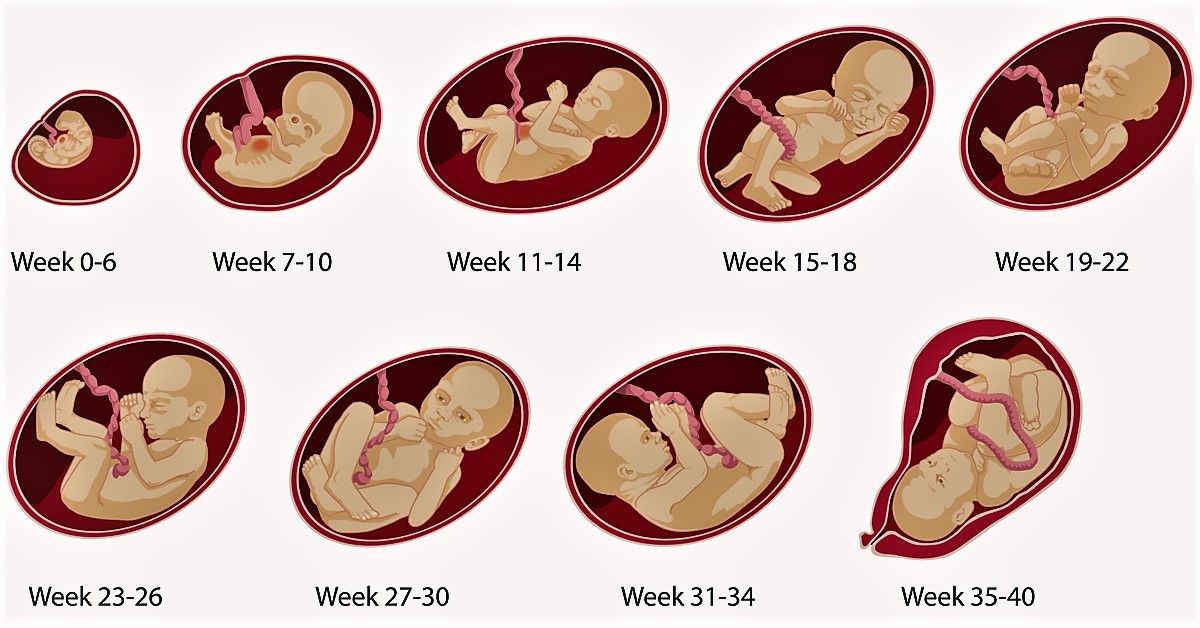 Los fórceps y aspiradoras de vacío pueden causar traumatismo craneal y hemorragias cerebrales, y los fármacos de inducción del parto pueden hacer que las contracciones sean tan fuertes, largas y frecuentes que el bebé se vea privado de oxígeno. La privación de oxígeno y las hemorragias cerebrales pueden causar daño cerebral permanente en un bebé y parálisis cerebral resultante, encefalopatía hipóxico-isquémica (EHI), leucomalacia periventricular y discapacidades intelectuales y de desarrollo. Por lo general, la mejor manera de hacer nacer a un bebé macrocósmico es mediante la cesárea.
Los fórceps y aspiradoras de vacío pueden causar traumatismo craneal y hemorragias cerebrales, y los fármacos de inducción del parto pueden hacer que las contracciones sean tan fuertes, largas y frecuentes que el bebé se vea privado de oxígeno. La privación de oxígeno y las hemorragias cerebrales pueden causar daño cerebral permanente en un bebé y parálisis cerebral resultante, encefalopatía hipóxico-isquémica (EHI), leucomalacia periventricular y discapacidades intelectuales y de desarrollo. Por lo general, la mejor manera de hacer nacer a un bebé macrocósmico es mediante la cesárea.
Mal manejo del Distrés Fetal, Lesiones de Nacimiento y Mala Praxis Médica
Con el fin de prevenir lesiones permanentes y discapacidad en un bebé recién nacido, es fundamental que los profesionales médicos rápidamente reconozcan y aborden los signos de sufrimiento fetal agudo. Debido a que las señales de sufrimiento fetal casi siempre indican que un feto está experimentando privación de oxígeno, el parto por cesárea de emergencia es típicamente la mejor manera de apartar rápidamente al bebé de condiciones peligrosas que lo privan de oxígeno.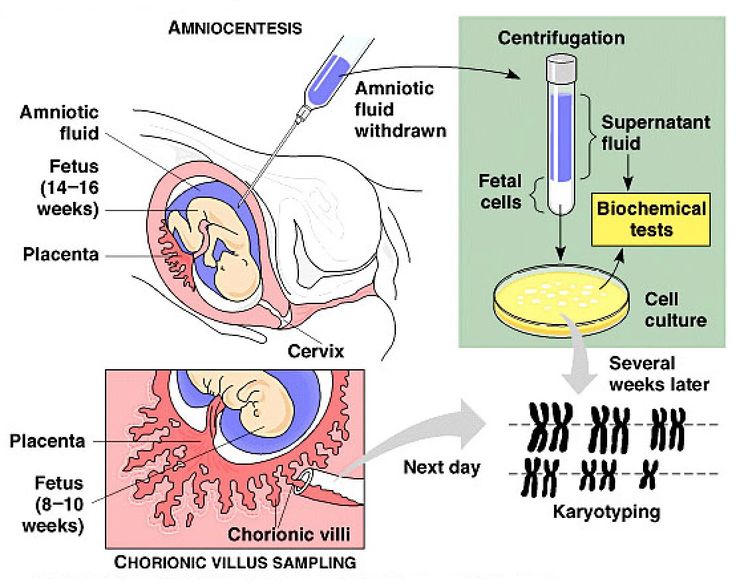 El personal médico debe monitorear de cerca a las mujeres con embarazos de alto riesgo y evaluar continuamente la salud de sus bebés. El incumplimiento de las normas de atención cuando una madre tiene un embarazo de alto riesgo es negligencia médica. También es negligencia si los médicos descartan signos o indicios de sufrimiento fetal. El sufrimiento fetal siempre debe ser apreciado, y si una madre tiene una condición que pone a su bebé en riesgo de estar en peligro, como la preeclampsia, el médico debe manejar adecuadamente la situación de alto riesgo para minimizar el riesgo para el bebé. De no hacerlo es mala praxis médica.
El personal médico debe monitorear de cerca a las mujeres con embarazos de alto riesgo y evaluar continuamente la salud de sus bebés. El incumplimiento de las normas de atención cuando una madre tiene un embarazo de alto riesgo es negligencia médica. También es negligencia si los médicos descartan signos o indicios de sufrimiento fetal. El sufrimiento fetal siempre debe ser apreciado, y si una madre tiene una condición que pone a su bebé en riesgo de estar en peligro, como la preeclampsia, el médico debe manejar adecuadamente la situación de alto riesgo para minimizar el riesgo para el bebé. De no hacerlo es mala praxis médica.
Reiter y Walsh, P. C. | Abogados de Michigan Ayudando a los Niños con Lesiones de Nacimiento desde 1997
Las lesiones de nacimiento son un área difícil de la ley debido a la compleja naturaleza de los registros médicos. Los galardonados abogados de Reiter & Walsh tienen décadas de experiencia conjunta en lesiones de nacimiento, encefalopatía hipóxico-isquémica (EHI) y casos de parálisis cerebral. Para saber si tiene un caso, comuníquese con nuestro bufete para hablar con uno de nuestros abogados en traumas de nacimiento. Tenemos numerosos veredictos y acuerdos multimillonarios que dan fe de nuestro éxito, y nunca se pagan cargos a nuestro bufete hasta que ganemos su caso. Prestamos atención personalizada a cada niño y familia que ayudamos y nuestros galardonados abogados están disponibles las 24 horas del día para hablar con usted.
Para saber si tiene un caso, comuníquese con nuestro bufete para hablar con uno de nuestros abogados en traumas de nacimiento. Tenemos numerosos veredictos y acuerdos multimillonarios que dan fe de nuestro éxito, y nunca se pagan cargos a nuestro bufete hasta que ganemos su caso. Prestamos atención personalizada a cada niño y familia que ayudamos y nuestros galardonados abogados están disponibles las 24 horas del día para hablar con usted.
Revisión de caso libre | Disponible 24/7 | Sin cuota hasta que ganemos
Teléfono (gratis): 888-419-2229
Presiona el botón de chat en vivo en tu navegador
Complete nuestro formulario de contacto en línea
“Dear patients, we are glad to welcome you to the website of the Fetal Medicine Center – a medical center of expert level in the field of modern prenatal medicine.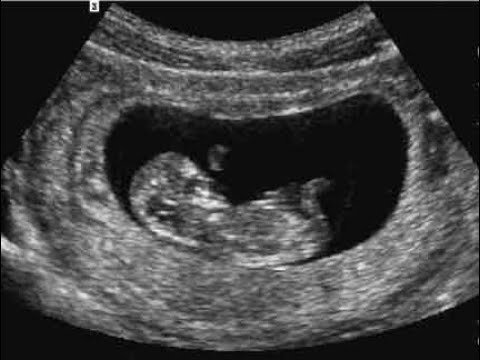 nine0018
nine0018
We see our mission in making the expectation of a child and its birth a happy, calm and most comfortable period for every woman. By providing professional medical support, we help couples plan pregnancy, control its harmonious course, conduct expert-level prenatal diagnostics, providing comprehensive care for the health of the expectant mother and baby.”
Roza Saidovna Bataeva
Head of the Fetal Medicine Center in Moscow
From the very beginning of pregnancy, every expectant mother begins to listen carefully to the sensations inside her growing belly. Can’t wait to feel your baby move. When does the fetus begin to move? At what time can a pregnant woman begin to listen carefully to herself, waiting for the first movements of her child? Should I be worried if they are not felt or the baby suddenly calmed down? And can movements carry any other information, besides communicating with mom? nine0018
The first movements of the future baby begin early – already at 7-8 weeks of pregnancy . It was at this time that the first muscles and the rudiments of the nervous system of the fetus are formed. Naturally, at this time, the movements of the embryo are still very primitive – these are muscle contractions in response to nerve impulses.
It was at this time that the first muscles and the rudiments of the nervous system of the fetus are formed. Naturally, at this time, the movements of the embryo are still very primitive – these are muscle contractions in response to nerve impulses.
Approximately from 10 weeks of pregnancy the fetus begins to move more actively in the uterus, and, encountering an obstacle on its way (walls of the uterus), change the trajectory of movements. However, the baby is still very small and the impacts on the uterine wall are very weak, the expectant mother cannot yet feel them. At 11-12 weeks of intrauterine life, a little man already knows how to clench his fists, grimace, frown, by 16 weeks of pregnancy he begins to react to loud, sharp sounds with increased motor activity, at 17 weeks the first facial expressions appear, and at 18 weeks he covers his face with his hands and plays with the umbilical cord, compresses and unclenches the fingers of the hands. nine0003
Gradually, with increasing gestational age, movements become more coordinated and more like conscious. When the baby grows up, the pregnant woman begins to feel his movements.
When the baby grows up, the pregnant woman begins to feel his movements.
It is generally accepted that during the first pregnancy, the expectant mother feels the first fetal movements at 20 weeks of pregnancy, with repeated pregnancies – at 18 weeks. This is not entirely true. A mother who is expecting her first child, indeed, most often begins to feel the movements of the fetus a little later than a multiparous woman. This is due to the fact that “experienced” mothers know how the movements of the crumbs are felt at first and what they should feel. Some primigravidas perceive the first movements of the fetus as an increase in intestinal peristalsis, “gaziki”. Many women describe the first movements of the fetus as a feeling of fluid transfusion in the abdomen, “fluttering butterflies” or “swimming fish.” nine0003
The first movements are usually rare and irregular. The time of the first sensations of fetal movements naturally depends on the individual sensitivity of the woman. Some future mothers feel the first movements as early as 15-16 weeks, and someone only after 20. Slender women, as a rule, begin to feel movements earlier than full ones. Women who lead an active lifestyle, work hard, usually feel the movements of the fetus later.
Some future mothers feel the first movements as early as 15-16 weeks, and someone only after 20. Slender women, as a rule, begin to feel movements earlier than full ones. Women who lead an active lifestyle, work hard, usually feel the movements of the fetus later.
By 20 weeks, due to the formation of the spinal cord and brain, as well as the accumulation of a certain amount of muscle mass in the fetus, movements become more regular and noticeable .
From 24 weeks of pregnancy, the movements of the fetus are already reminiscent of the movements of a newborn – the expectant mother feels how the fetus changes position, moves its arms and legs. The motor activity of the fetus increases gradually and its peak falls on the period from the 24th to the 32nd week of pregnancy. At this time, the activity of the baby’s movements becomes one of the indicators of its normal development. After 24 weeks, the child begins to “communicate” with the mother with the help of movements, respond to the sounds of voice, music, and the emotional state of the mother. With an increase in the gestational age of more than 32 weeks, the motor activity of the fetus gradually decreases due to the fact that the baby is growing up and he simply does not have enough space for active movements. This becomes especially noticeable at the time of childbirth. By the end of the third trimester of pregnancy, the number of fetal movements may decrease somewhat, but their intensity and strength remain the same or increase. nine0003
With an increase in the gestational age of more than 32 weeks, the motor activity of the fetus gradually decreases due to the fact that the baby is growing up and he simply does not have enough space for active movements. This becomes especially noticeable at the time of childbirth. By the end of the third trimester of pregnancy, the number of fetal movements may decrease somewhat, but their intensity and strength remain the same or increase. nine0003
The baby in the mother’s belly moves almost constantly. At the 20th week of pregnancy, the fetus makes about 200 movements per day, and between the 28th and 32nd weeks, the number of movements reaches 600 per day. Naturally, a pregnant woman does not feel all the movements of the fetus, but only a small part of them. So, after 28 weeks, the frequency of fetal movement, according to the sensations of a woman, is usually 4 to 8 times per hour, with the exception of periods of fetal sleep (3-4 hours in a row). nine0003
nine0003
In the third trimester, a pregnant woman may notice that her baby has regular sleep and wake cycles. Children are usually most active from 19:00 to 4:00 in the morning, and the period of “rest” occurs more often from 4 to 9:00 in the morning. Of course, the movements of the fetus depend on the mood of the mother, if the mother is worried or happy, the baby can move more actively, or vice versa, calm down. The fact is that when a mother rejoices, her body significantly increases the amount of hormones of joy – endorphins, which regulate the work of the heart and blood vessels, including the vessels of the placenta. During stress or pronounced negative emotions, biologically active substances are also produced – stress hormones, they also affect the work of the heart and blood vessels. It is thanks to this biological interaction between the organisms of mother and baby that the fetus feels the state of the mother. When the expectant mother is resting, the baby usually becomes more active, if the pregnant woman is active, busy with some kind of work, the child most often calms down. The movements also change depending on the satiety of the expectant mother. Usually the baby begins to move actively after the mother eats, especially something sweet. At the same time, the level of glucose in the blood increases sharply, which causes the fetus to be more active. nine0003
The movements also change depending on the satiety of the expectant mother. Usually the baby begins to move actively after the mother eats, especially something sweet. At the same time, the level of glucose in the blood increases sharply, which causes the fetus to be more active. nine0003
Fetal movements are the language in which the unborn child speaks to the mother. Naturally, a pregnant woman should listen to the movements, because in some cases, changes in the movements of the fetus may indicate a violation of its intrauterine state and a not entirely successful pregnancy.
If, after 20 weeks of pregnancy, the expectant mother does not feel the movement of the fetus, it may be worthwhile to see a doctor and make sure that everything is in order with the baby.
The easiest way to assess fetal movements is to count the number of movements of the pregnant woman herself. Self-assessment methods are very easy to use, do not require additional equipment, the presence of a doctor and are easily reproducible by any woman. Their disadvantages are that each woman has different thresholds of susceptibility.
Self-assessment methods are very easy to use, do not require additional equipment, the presence of a doctor and are easily reproducible by any woman. Their disadvantages are that each woman has different thresholds of susceptibility.
The most common method for assessing fetal movements is called count to ten . It can be carried out after 28 weeks of pregnancy, when the fetus is mature enough for active movements. Its essence lies in the fact that the expectant mother counts the movements of the fetus for a 12-hour time interval, for example, from 9 am to 9 pm. The time when a pregnant woman catches the tenth movement is recorded on a tablet. If the fetus makes less than 10 movements in 12 hours, this is a reason to consult a doctor for an additional examination.
In the evening after dinneruntil 11 p.m.), the woman lies on her left side and counts the movements of the fetus. At the same time, everything is considered, even the smallest movements. If 10 or more movements are noted within an hour, this indicates that the baby is moving quite actively and feels good. If the fetus moved less than 10 times in an hour, then the movements are counted for the next hour. Evening time for this assessment method was not chosen by chance. It is in the evening hours, especially after dinner and the associated increase in glucose, that the greatest activity of the fetus is noted. If the number of fetal movements during this test is less than 10 per two hours, this should be considered as a sign of a violation of his condition and additional studies should be carried out. nine0003
If 10 or more movements are noted within an hour, this indicates that the baby is moving quite actively and feels good. If the fetus moved less than 10 times in an hour, then the movements are counted for the next hour. Evening time for this assessment method was not chosen by chance. It is in the evening hours, especially after dinner and the associated increase in glucose, that the greatest activity of the fetus is noted. If the number of fetal movements during this test is less than 10 per two hours, this should be considered as a sign of a violation of his condition and additional studies should be carried out. nine0003
For an obstetrician-gynecologist, fetal movements are also an important diagnostic criterion for some deviations in the course of pregnancy from the norm. Too active, violent, painful fetal movement or weak, rare movements may indicate its unfavorable condition.
Changes in fetal activity may be associated with external influences. For example, if a pregnant woman lies on her back for a long time, then the enlarged uterus compresses a large vessel – the inferior vena cava, the blood flow to the fetus is disrupted, which immediately causes its violent reaction – active movements. The same changes in the activity of the baby can occur in any other uncomfortable position of the mother – if she leans forward, squeezing her stomach, sits with her legs crossed, the child forces her mother to change her position with her activity. A similar situation occurs if the baby himself squeezes or presses the loops of the umbilical cord, limiting the flow of blood through it. He begins to move more actively, changes his position and relieves pressure on the umbilical cord. However, in some cases, an increase or vice versa, a subsidence of fetal movements can be a sign of a serious pathology. nine0003
For example, if a pregnant woman lies on her back for a long time, then the enlarged uterus compresses a large vessel – the inferior vena cava, the blood flow to the fetus is disrupted, which immediately causes its violent reaction – active movements. The same changes in the activity of the baby can occur in any other uncomfortable position of the mother – if she leans forward, squeezing her stomach, sits with her legs crossed, the child forces her mother to change her position with her activity. A similar situation occurs if the baby himself squeezes or presses the loops of the umbilical cord, limiting the flow of blood through it. He begins to move more actively, changes his position and relieves pressure on the umbilical cord. However, in some cases, an increase or vice versa, a subsidence of fetal movements can be a sign of a serious pathology. nine0003
After 28 weeks of pregnancy, if your baby does not let you know for 3-4 hours, he may just be sleeping. In this case, the expectant mother needs to eat something sweet and lie down on her left side for half an hour. If these simple manipulations do not lead to a result, it is worth repeating them again after 2-3 hours. If this time the baby does not make itself felt, this is an occasion to consult a doctor. Rare and weak movements can also indicate a fetal problem, most often a lack of oxygen for the baby, that is, fetal hypoxia. nine0003
If these simple manipulations do not lead to a result, it is worth repeating them again after 2-3 hours. If this time the baby does not make itself felt, this is an occasion to consult a doctor. Rare and weak movements can also indicate a fetal problem, most often a lack of oxygen for the baby, that is, fetal hypoxia. nine0003
To determine the condition of the fetus, the doctor conducts a series of examinations:
The simplest is auscultation (listening) using a special wooden tube (obstetric stethoscope) or a special device that captures the fetal heartbeat, doctor listens to the baby’s heartbeat. Normally, it is about 120-160 beats per minute. A decrease in heart rate less than 120 or an increase of more than 160 indicates intrauterine suffering of the child. nine0003
During ultrasound, the doctor visually assesses the size of the fetus, the correspondence of the development of the fetus to the gestational age, because with oxygen starvation, the growth rate of the fetus slows down and its size lags behind the norm for each period of pregnancy. Also important is the structure of the placenta, the presence of signs of aging in it, as a result of which the function of transferring blood, oxygen and nutrients to the fetus usually worsens. During ultrasound, the amount and type of amniotic fluid is assessed, which can also change with intrauterine fetal suffering. Dopplerometry of the vessels of the placenta and umbilical cord is a method for studying blood flow velocities in these vessels. With a decrease in the speed of blood flow in any vessel, one can speak of fetal malnutrition of varying severity. nine0003
Also important is the structure of the placenta, the presence of signs of aging in it, as a result of which the function of transferring blood, oxygen and nutrients to the fetus usually worsens. During ultrasound, the amount and type of amniotic fluid is assessed, which can also change with intrauterine fetal suffering. Dopplerometry of the vessels of the placenta and umbilical cord is a method for studying blood flow velocities in these vessels. With a decrease in the speed of blood flow in any vessel, one can speak of fetal malnutrition of varying severity. nine0003
Learn more about the services:
This is an important method for assessing the condition of the fetus. CTG is performed at a gestational age of 33 weeks or more, since only in this period of intrauterine development of the baby is a full-fledged regulation of the activity of the cardiovascular system of the fetus by the centers of the spinal cord and brain. Recording of fetal heartbeats is carried out for at least 40 minutes, and if necessary, the study can be extended up to one and a half hours. The device registers and records the baby’s heart rate. For example, with a decrease in the concentration of oxygen in the blood of the fetus, the supply of oxygen to the cells of the nervous system decreases, which in turn affects the heart rate, especially during the period of wakefulness of the child. The obstetrician-gynecologist evaluates the heartbeat recording curve, episodes of slowing down and a sharp increase in the fetal heart rate, and based on these data, makes a conclusion about how comfortable the baby feels in the mother’s stomach. nine0003
Recording of fetal heartbeats is carried out for at least 40 minutes, and if necessary, the study can be extended up to one and a half hours. The device registers and records the baby’s heart rate. For example, with a decrease in the concentration of oxygen in the blood of the fetus, the supply of oxygen to the cells of the nervous system decreases, which in turn affects the heart rate, especially during the period of wakefulness of the child. The obstetrician-gynecologist evaluates the heartbeat recording curve, episodes of slowing down and a sharp increase in the fetal heart rate, and based on these data, makes a conclusion about how comfortable the baby feels in the mother’s stomach. nine0003
If during additional methods for assessing the condition of the fetus, initial disturbances in the supply of oxygen to the baby are detected, drug treatment is carried out aimed at increasing the access of blood and oxygen through the placenta and mandatory control examinations against the background of ongoing therapy. If the changes are deep and the baby experiences a pronounced deficiency of oxygen and nutrients, his condition suffers, an emergency delivery of such a patient is performed.
If the changes are deep and the baby experiences a pronounced deficiency of oxygen and nutrients, his condition suffers, an emergency delivery of such a patient is performed.
Fetal movements are not only an indicator of his condition, it is a way of communication between the baby and parents. The movements of the crumbs in the mother’s tummy are unforgettable sensations that a woman can experience only in this short, but such a happy period of her life. nine0003
The main activities of our center are the early detection of congenital malformations in the fetus, prenatal screening for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, as well as pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia, fetal growth retardation and threatened abortion.
Our center is organized in such a way that the whole range of services is concentrated in one place, where a woman receives the results of various types of examinations, including ultrasound, biochemical, and specialist consultation within 1-1.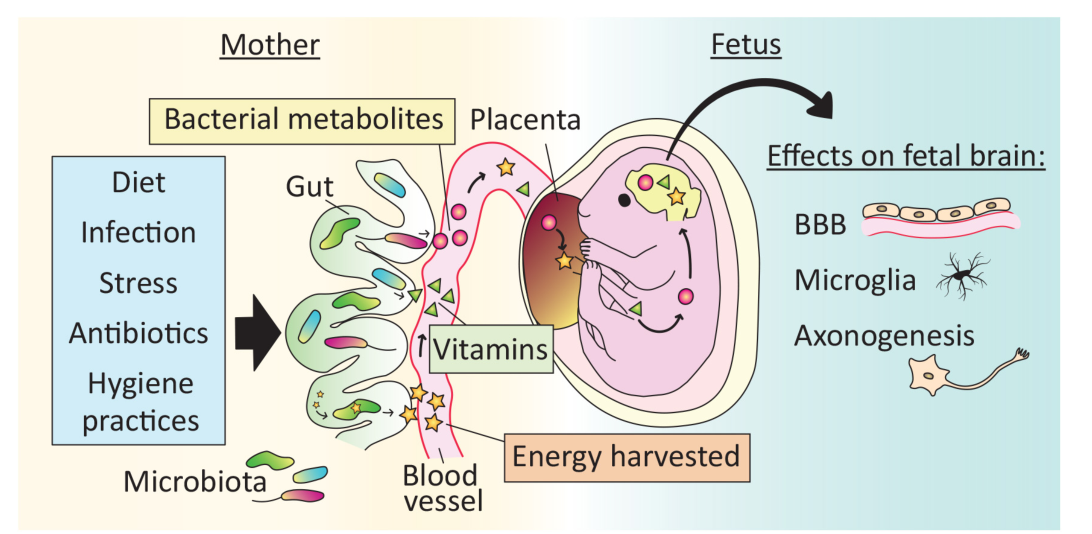 5 hours. In the presence of a high risk for chromosomal diseases in the fetus, invasive diagnostics and genetics consultation are carried out here in the center. nine0003
5 hours. In the presence of a high risk for chromosomal diseases in the fetus, invasive diagnostics and genetics consultation are carried out here in the center. nine0003
Fetal echocardiography is given special attention in our center, since congenital heart defects in the fetus are increasingly common today, but, unfortunately, are often missed during ultrasound during pregnancy.
In view of the ever-increasing number of multiple pregnancies, which requires more time and a special approach, the observation of women with multiple pregnancies has been allocated to us in a separate clinic for multiple pregnancies.
All examinations in the center are carried out according to the international standards FMF (Fetal Medicine Foundation) and ISUOG (International Society for Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology). In complex clinical cases, we can consult with specialists from King’s College Hospital, King’s College Hospital (London, UK). nine0003
The team is a special pride of the center. Our doctors are not only one of the leading specialists, professors, doctors and candidates of medical sciences, doctors of the highest categories, they are also a team of like-minded people and real enthusiasts in their field. All ultrasound diagnostic doctors in our center have international FMF certificates. Having extensive experience in prenatal diagnostics, we share our knowledge with our colleagues by conducting training courses.
Our doctors are not only one of the leading specialists, professors, doctors and candidates of medical sciences, doctors of the highest categories, they are also a team of like-minded people and real enthusiasts in their field. All ultrasound diagnostic doctors in our center have international FMF certificates. Having extensive experience in prenatal diagnostics, we share our knowledge with our colleagues by conducting training courses.
The Center is equipped with the most modern diagnostic equipment: these are the latest generation ultrasound machines, GE Voluson E8 Expert, with a complete set of modern technologies, including three-dimensional ones, this is a biochemical analyzer, Delfia Xpress, these are workplaces with professional computer programs. nine0003
Gynecological Clinic – “Women’s Health Resort Clinic”
Pregnancy
Assessment of fetal movement activity
The cost of visiting a gynecologist
Authors of the article: candidate of medical sciences – O. Yu.Ermolaev, obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound doctor, specialist in nutrition during pregnancy – E.K.Ermolaeva
Yu.Ermolaev, obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound doctor, specialist in nutrition during pregnancy – E.K.Ermolaeva
Getting used to active movements
baby and when he calms down,
you are afraid that something is wrong with him …
From a conversation with a Patient
A PRIMARY pregnant woman begins to FEEL FETAL MOVEMENT (the first movement of the fetus), usually from 20 weeks of pregnancy.
The first movements of the fetus during the first pregnancy (the first movements of the fetus) are felt in the form of timid jolts, which can hardly be called jolts. Rather, unexpected and incomparable STROKE FEELINGS inside, like the fluttering of butterfly wings. nine0003
|
3D photo of a 15 week fetus. “Pulls”. Pay attention to the excellent quality of the photo. You can see the photos of the fetus taken by our doctors on many Russian and foreign websites. |
In rare cases, particularly expectant pregnant women with their first pregnancy, the first movements of the fetus are noted as unusual sensations, starting from 18-19 weeks of pregnancy. nine0003
nine0003
REPEATED pregnant women who remember the sensations of a previous pregnancy are able to feel the first fetal movement (first fetal movement) from 18 weeks of gestation.
In the majority of multiparous pregnant women, the memory retains the sharpness of impressions/sensations for 4-5 years.
Thus, if more than 5 years have passed since the last birth, a woman experiences sensations of fetal movement and other sensations during pregnancy and childbirth “like for the first time”. nine0003
A clear relationship between the ACTIVITY of the fetus and its HEALTH has been revealed.
Your baby’s daily activity assessment (fetal movement assessment) will help your OB/GYN doctor identify potential problems with your baby’s development.
Starting at 28 weeks gestation:
 nine0006
nine0006
NORM OF FETUS MOVEMENTS: within 60 minutes the fetus must make at least 5 and no more than 10 movements-perturbations.
The activity (frequency) of fetal movements depends on the psycho-emotional state and lifestyle of the pregnant woman.
Increased anxiety, indignation, elation and other emotional outbursts are accompanied by the release of stress hormones into the general bloodstream and are manifested by similar sensations and reactions of the fetal motor activity (the child is pushing). nine0003
With a physically active lifestyle, the fetus is also in relative motion: the organ of balance (the cerebellum) is being trained, metabolic products are supplied to the fetus with the blood flow from the mother, the level of glucose in the blood decreases . ..
..
During ultrasound, we often observe and WE SHOW OUR PATIENTS on a remote monitor how the baby develops violent motor activity when the umbilical cord is squeezed by his own fingers, shoulder, or when the umbilical cord is in an uncomfortable position around the neck, thigh. Having taken a comfortable position, freeing the umbilical cord, the baby calms down. nine0170 Excessive activity of the fetus disappears when it is comfortable.
Another reason for active fetal movement (the baby pushes) can be HYPOXIA (lack of oxygen) that occurs in a stuffy room, vehicle, with a woman lying down, sitting, standing for a long time.
CARDIOTOCOGRAPHY — an examination on a modern fetal monitor “Toitu”, Japan, is performed for all patients of the Women’s Health Resort Clinic after 34 weeks of pregnancy and allows you to determine the presence of hypoxia and motor activity (number of movements) of the fetus, uterine tone. Research cost. nine0003
Leading specialists in the management of complex pregnancy in the Southern Federal District
Ermolaeva Elvira Kadirovna
A well-known and recognized specialist in the North Caucasus in the field of diagnosis and treatment of miscarriage, pregnancy fading, recurrent miscarriage, management of pregnant women with thrombophilia, antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), uterine fibroids, management of pregnancy in young and older pregnant women (after 38 years), management of capricious pregnant women, management of overweight pregnant women. nine0003
nine0003
A good obstetrician-gynecologist, a specialist in rational nutrition during pregnancy, a physiotherapist-resortologist, an experienced ultrasound doctor.
Those who want to keep their figure and successfully endure a woman’s pregnancy turn to her.
Ermolaev Oleg Yurievich
Candidate of Medical Sciences, gynecologist-endocrinologist with 30 years of experience and successful experience in managing pregnancy in women with uterine prolapse, bicornuate uterus, saddle uterus and other malformations of the genital organs, managing pregnant women with livedo, thrombophilia and antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), polycystic ovaries . nine0003
Management of multiple pregnancies requiring special attention and experience from physicians.
Pregnancy management after IVF, ICSI, after artificial insemination.
Management of pregnant women with placental insufficiency.
Management of pregnancy on the background of the IUD.
INTERNATIONAL RECOGNITION of the reputation and achievements of the Women’s Health Resort Clinic in the development and implementation of effective and safe treatment methods and the quality of the medical services provided IS THE AWARDING of the Women’s Health Resort Clinic in Pyatigorsk with the SIQS International QUALITY CERTIFICATE in the field of medicine and healthcare. International Socratic Committee, Oxford, UK and Swiss Institute for Quality Standards, Zurich, SWITZERLAND. More…
nine0003
A good obstetrician-gynecologist, who specializes in proper nutrition during pregnancy, sees you at the Women’s Health Spa Clinic.
A NUTRITION SPECIALIST during pregnancy WILL CHOOSE for you the necessary vitamins, HEALTHY FOOD during pregnancy, which will not allow you and your baby to gain excess weight, and will help organize tasty and NOT HUNGRY FOOD during the trimesters of pregnancy.
In addition, our experienced pregnancy nutrition specialist WILL CALCULATE for you the possibility of figure-safe SWEET CONSUMPTION during pregnancy and tell you in detail WHAT NOT TO EAT during pregnancy and how to balance foods that are prohibited by public opinion during pregnancy. But who so want! nine0003
On the basis of foreign and Russian experience, we DEVELOPED and successfully time-tested a NUTRITION SYSTEM that allows you to select products during pregnancy depending on the INDIVIDUAL characteristics of a pregnant woman: her complexion, taste preferences, body weight and height, fetal sex and external features …
We work without weekends and holidays:
Monday – Friday from 8.00 to 20.00,
Saturday – Sunday from 8.00 to 17.00.
nine0003
Reception of an obstetrician-gynecologist specialist in proper breathing during childbirth and ultrasound of the fetus by appointment by multi-channel phone 8 (800) 500-52-74 (free call in Russia), or +7 (928) 022-05-32 (for foreign calls).